Home » Law (Page 3)
Category Archives: Law
More Grotesque Black Death #BlackenAsiaWithLove
Each time I turn on the news I see more black death.
It’s grotesque. In my country, ‘Merika, there are peaceful protestors all around the country combatting police violence. Initially, when George Floyd was murdered, these peaceful protests spread across the world, as folks rose in solidarity for peace against white supremacy in America. Many more Black bodies have died in dubious police circumstances since. In the popular rhetoric, sadly, the peaceful protestors are held to account for the violence sweeping our streets. One of Dr. King’s major battles was to convince a people who’d been born into a nation of violence, how to be peaceful; we are a nation born of violence. Dr. King believed and taught that “non-violent resistance… [is] a courageous confrontation of evil by the power of love” (King, Stride, 80). That was just to boycott the local busses in the 1950’s. Working people choosing to spend their hard-earned money as they pleased, and still Jim and Jane Crow showed up to verbally and physically harass each one of them. By the 60’s Black university students worked in solidarity with students of all colors to teach, preach and practice non-violent civil disobedience.
It’s in bad faith to focus on the rioters and overlook those attempting to exercise their first amendment rights. I say “attempting,” because even the lone Black woman in Kentucky house of representatives, Attica Scott, can be arrested in our hometown for peacefully protesting #JusticeForBreonnaTaylor, #AtticaScott4Ky. Without the 1st amendment, there’s no second. And let’s not forget all those anti-mask protestors that showed up at city and state halls around the country – in 2020 – armed to the teeth, so-called peacefully protesting any ordinance to protect ‘us’ from the spread of CoVit. How peacefully will the po-po resolve this conflict instigated by their own violence? The white supremacist way, of course. Look at 45, head hood and chief of their klan. “’Cause God’s stopped keeping score,” as George Michael sang.
Back then leading the cause of segregation, we had white supremacists like 4-term Alabama governor George Wallace, and Birmingham public safety commissioner, Bull Connor, (in)famous for sending in fire hoses and attack dogs against children peacefully protesting. Right now, there are all kinds of icons named after ole George. Just a few years ago, I went to my little cousin’s high school basketball game in Tallassee, Alabama, and the public high school gym was named after good ole George’s wife, who’d held onto his governorship for a bit because law forbade him from serving consecutive terms. It’s as if only a few strong survivors believe us when we speak about how white supremacy has its hooves on our necks. It tuns out 8 minutes and 46 seconds changed that.

Read, will you, what good ole George said in a 1986 interview about sending in troops to squash the peaceful protests in Birmingham, after those four little girls got bombed in the 16th Street Baptist Church, on a Sunday in September 1963. As you’d expect, no one was held to account. The good governor says:
“I sent Colonel Lingo there because they were, there was some trouble there, we tried to maintain law and order, we’re not trying to maintain segregation there, it was a matter of law and order, and uh, as I recall that nobody got hurt in any of the things, in the demonstrations, uh, except that whoever those evil mean, minded men were who had something to do with the blowing up of that church.”

Sound familiar? Sounds like 45. Like then, today’s protestors are regularly intimidated and assaulted by the police and troops. This too often seals the cycle of violence instigated by the police, who are further instigated by the commanders and their chief.
It’s grotesque, and understandably, even more grotesque to look at, if you’ve rarely looked at it before, tucked it away, and not thought about it because it did not impact your daily life. “It’s hard to love, there’s so much to hate,” and you sang along. You knew it was happening, but your eyes betrayed you, and because you didn’t see it in your neighborhood, in your schools and streets, you let your faith in humanity go.
You let yourself believe that we, Black people, did something to deserve to be the nightly feature on the news: Weather, sports, celebrities, national headlines, and the local Black criminal; that’s literally fed into our homes each night on the news. And if you’ve been spending your time with Fox and ilk, then certainly you’ve been trained in a language that pits them against us, and posits losers and sinners against the righteous folks like you who are just trying to make it in this world. How could the Blacks live such a radically different existence? You lie to yourself and say that they can’t, that all the opportunities they lose are theirs alone. It’s all down to individual decisions, just like you. We each chose our own fates, right? There’s no system, and certainly no systemic oppression. F #MeToo, too, you say… at home with only the family and kids to hear. The kids repeat it at school, grow up and vote like that. They cycle repeats, whiteness is rendered, effectively, invisible. Only the Blacks are not acting right.

Ignorance is bliss: the problem with education

I woke up this morning with a feeling of the weight of the world on my shoulders. My problems are insignificant compared to many others, but I did think, wouldn’t it be nice to get off this merry-go-round. Wouldn’t it be nice if I could stop thinking about the injustices in the world and the part I play in them, how the problems might be solved, how best I can do my job online and give all of my students what they need, how best I can deal with tricky relationships at work and do my best for all concerned How I might ensure that my family are looked after and take on significant responsibilities in looking after the interests of an elderly relative whilst ensuring fairness all round. How can I do the right thing and not send myself into bouts of depression?
And as I thought of all of these things I came to an interesting question. Is it better to be ignorant, inept and irresponsible?
If I was ignorant, if I didn’t bother to watch the news, to critique, to engage in discussion, to think about the social world and my place in it. If I was to carry on in blissful ignorance of what is going on around me would I not be happier? If I am not aware of social injustices, then it would be easy to take a stance that what matters is simple, law and order for instance. I could become a Sun reader, more interested in the pictures than the content. The headlines would capture my imagine for a nano second and I could simply agree about how terrible this or that issue is before blissfully moving on to something else. I don’t know what everyone else is complaining about, I’m alright Jack, or should that be Jill, I must stop thinking.
If I was inept, I make a bit of an assumption here that I’m not, I guess others will judge, then that ineptitude would ensure that I wasn’t given any responsibilities, well none that really mattered. Cock things up a few times and suddenly you find that nobody wants to give you the work and nobody really wants to do any work to deal with your ineptitude, and nobody thanks them if they do. In other words, you are ‘quids in’, minimal work and nobody on your back. Couple this with blissful ignorance and life is so much easier.
If I was irresponsible, or at least seen as that, then I wouldn’t be asked to take on responsibility and all of the ramifications that go with it. No longer asked to do something that is important and has significant ramifications if you cock it up. That takes us back to ineptitude, being inept leads to no responsibility, being irresponsible gives the appearance of being inept. If I am blissfully ignorant of what people might think of me or what I might have cocked up, then no need to worry.
The only fly in the ointment here, is that in being educated, I am able to write this blog. I am able to place myself in society and sadly acknowledge my part in it. I pride myself in doing a good job and I don’t shy away from responsibility although I might get there kicking and screaming at myself for the angst and inner turmoil it sometimes creates. Knowledge is powerful, education gives you knowledge and self-awareness. The greater the knowledge the greater the self-awareness, the greater the self-awareness, the greater the thirst for knowledge. Unfortunately, there is nothing blissful to be found there though.
When the Police takes to Tweeter HashTags to Seek ‘Justice’

https://twitter.com/PoliceNG/status/1159548411244371969?s=20)
I am tempted to end this blog in one sentence with the famous Disney lyrics, “disaster is in the air” but this may do no justice to the entry as it lacks a contextual background. So last week, Nigerian Twitter was agog with numerous tweets, retweets, comments, and reactions following the news that soldiers of the Nigerian Army had allegedly killed one civilian and three police personnel in the line of duty. A brief summary of the case is that the killed police personnel had arrested an alleged notorious and ‘wanted’ kidnaper and were transporting him to a command headquarters when they ran into a military checkpoint. Soldiers at the checkpoint allegedly opened fire at close range, killed the police who were said to have attempted identifying themselves, and freed the handcuffed ‘kidnapper.’
In a swift reaction, a Joint Investigation Panel comprised of the Police and the Army was constituted to investigate the incident. Notwithstanding this, the Police took to their Twitter handle @PoliceNG calling out for justice and expressing dissatisfaction and concerns in what metamorphosed into series of threads and hashtags – #WhereIsEspiritDCorp and #ProvideAnswersNigerianArmy. Ordinarily, this should have aroused and generated wide condemnation and national mourning, but, the comments, tweets and reactions on twitter suggests otherwise. While Nigerians expressed sympathy to the victims of the unfortunate incident, they also took to the social media platform to unravel their anger with many unleashing unsympathetic words and re-stating their distrust in the Police. In fact, it was the strong opinion of many that the incident was just a taste of their medicine as they often infringe on the rights of civilians daily, and are notoriously stubborn and predatory.
Certainly, this issue has some criminological relevance and one is that it brings to light the widely debated conversation on the appropriateness and the potency of deploying the military in society for law enforcement duties which they are generally not trained to do. Hence, this evokes numerous challenges including the tendency for it to make civilians loathe to interact with the military. I have previously argued that the internal use of the Nigerian military in law enforcement duties has exacerbated rather than ameliorated insecurity in several parts of the country. As with this instance, this is due to the penchant of the military to use force, the unprofessional conduct of personnel, and a weak system of civil control of the military to hold personnel accountable for their actions.
Similarly, this issue has also raised concerns on the coordination of the security forces and the need for an active operational command which shares security information with all the agencies involved in internal security. However, the reality is that interagency feud among the numerous Nigerian security agencies remains a worrying concern that not only undermine, but hinders the likelihood for an effective coordination of security activities.
Another angle to the conversation is that the social media provides a potent weapon for citizens to compel response and actions from state authorities – including demanding for justice. However, when the police is crippled and seemingly unable to ensure the prosecution of rights violations and extrajudicial killings, and they resort to twitter threads and hashtags to call out for justice, overhauling the security architecture is extremely necessary.
Majority Verdicts and Reasonable Doubt

Recently I attended an Inside Justice Live Crime event hosted by Anglia Law School at Anglia Ruskin University. The last speaker for the evening was Kevin Lane who is trying to have his wrongful conviction overturned, during his discussion he mentioned that he was found guilty of murder by a 10-2 majority verdict. It came as quite a shock to me to hear that majority verdicts are used for murder charges in England.
In 1994 Robert Magill was shot dead by a hitman while walking his dog in Hertfordshire, two men fled the scene in a BMW car. In 1995 Lane and a co-accused were charged with the murder of Magill. The prosecution alleged that Lane had received payment for this murder and submitted that fingerprints were found in bin liners in the car. Police were unable to link Lane to the scene of the crime, were unable to prove he had received payment, and he has always maintained his innocence.
There were a number of limitations and concerns in this case – the murder weapon was never recovered, two prime suspects who were brought to the police’s attention soon after the murder were not properly investigated and were later found to have an inappropriate relationship with the investigating police officer, and there were on going disclosure problems. Further, in 2002 the investigating officer was sent to prison for four years of conspiracy to steal £160,000 from the Hertfordshire Police and misconduct in a public office. (This is a very brief summary of a complicated case).
A majority verdict is used when the jury cannot reach a unanimous verdict and where the jury consists of usually 12 jurors and at least 10 or 11 agree (depending on the jurisdiction) – under certain conditions the judge is able to accept the jury’s verdict. The provision of a majority verdict is generally used when a prescribed period of time has elapsed, and the judge is satisfied that the jury are unlikely to reach a unanimous verdict after further deliberation. Majority verdicts have been used in England since 1974 and were originally introduced to prevent the intimidation or bribing of jurors.
While I am aware of majority verdicts, as they are used in Queensland, Australia (where I completed my legal education). Majority verdicts cannot be used for murder trials, for an offence which has mandatory life imprisonment as a penalty, and Commonwealth offences. The overall concern with majority verdicts is that if the jury is unable to reach a unanimous decision then they cannot be said to have reached a decision ‘beyond a reasonable doubt’ which is the standard of proof for criminal matters, and as a consequence have demonstrated reasonable doubt.
Unanimous jury verdicts have been part of the common law since the 14thcentury. Prior to 1866, if a jury could not reach an agreement they could be ‘carried around in a wagon with the court without meat or drink, fire or candle until they were starved or frozen into agreement.’ We have obviously come a long way since the days of locking jurors up and separating them from their family and friends until they reached a decision.
Using unanimous verdicts is argued to reduce the risk of convicting an innocent person, that unanimity is a fundamental feature of a jury trial, it leads to better deliberation, and that disagreement in a jury is not unreasonable. When considering the issue from the perspective of the accused, majority verdicts place them at a great disadvantage when one considers that the prosecution has much more resources. There are already a number of contributors to wrongful convictions which the accused needs to contest with, and the fact that appeals are very difficult.
It can be argued there are benefits for majority verdicts – they reduce the instance of a hung jury (where the accused is neither acquitted or convicted) and the potential for a retrial (and the economic cost associated for a criminal justice system which is already overloaded). Majority verdicts are said to overcome problems with ‘rogue’ jurors, bribery and intimidation. The use of majority verdicts allows there to be finality in the case for the victim/s, the accused, the family and friend of the victim/s and accused, and the community.
Personally, I believe that in the interest of justice majority verdicts should not be used in serious criminal cases – such as murder and offences which carry mandatory life imprisonment penalty. These cases are much too serious and if reasonable doubt is present then this should be recognised. In Kevin Lane’s case he would not have been convicted, served 18 years in prison, and still be trying to overturn his conviction.
Further reading
Cowdery, N. (2007). Majority jury verdicts. Reform Issue. 90, 18-19.
Garrett, B.L. & Neufeld, P.J. (2009). Invalid forensic science testimony and wrongful convictions. Virginia Law Review. 95(1), 1-97.
Gray, A. (2009). A guarantee right to trial by jury at state level? Australian Journal of Human Rights. 15(1), 97-125.
Roberts, S. & Weathered, L. (2009). Assisting the factually innocent: The contradictions and compatibility of Innocence Projects and the Criminal Cases Review Commission. Oxford Journal of Legal Studies. 29(1), 43-70.
Sankoff, P. (2006). Majority jury verdicts and the Charter of Rights and Freedoms. UBC Law Review. 39(2), 333-369.
The roots of criminology; the past in the service of the future;
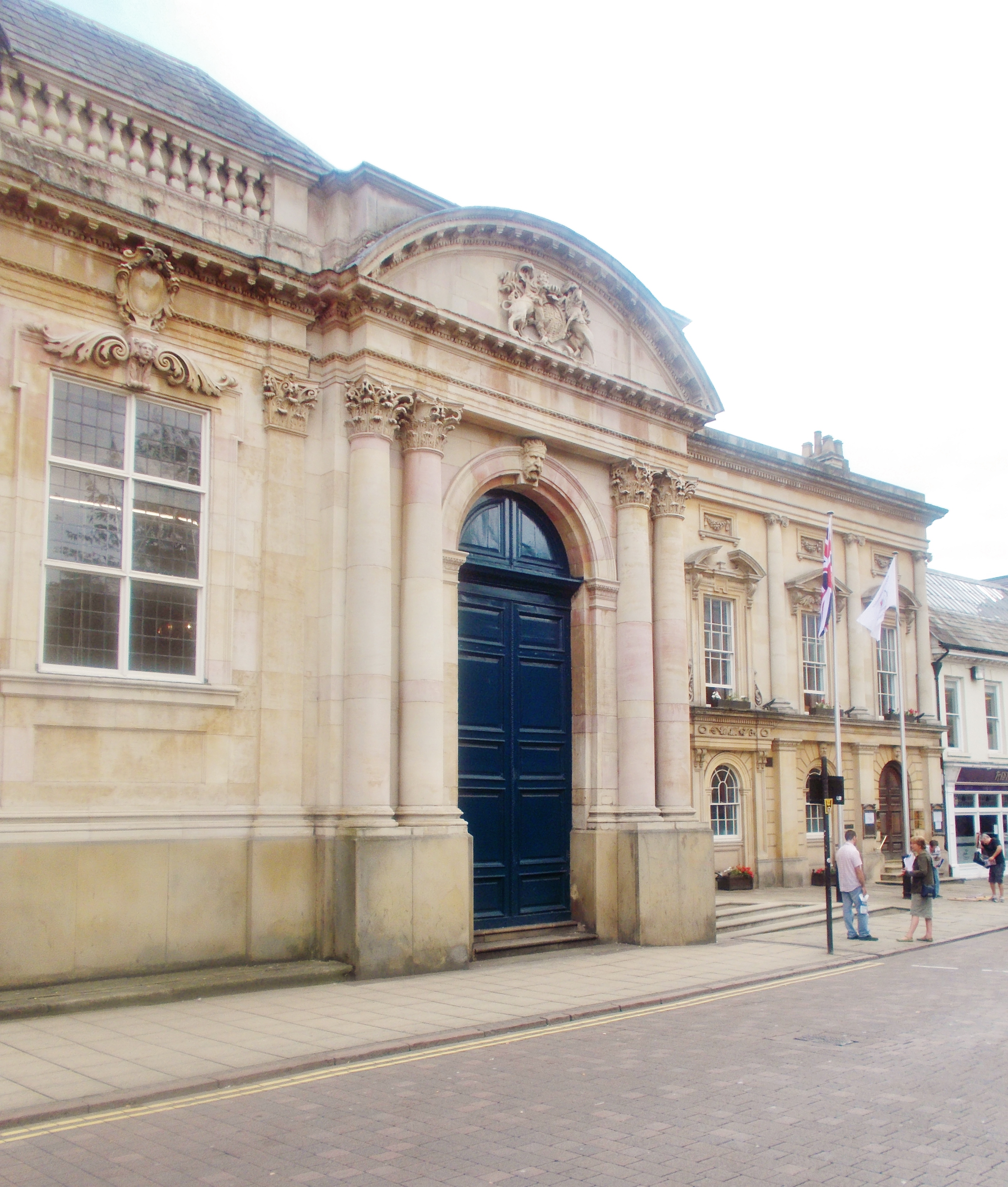

In a number of blog posts colleagues and myself (New Beginnings, Modern University or New University? Waterside: What an exciting time to be a student, Park Life, The ever rolling stream rolls on), we talked about the move to a new campus and the pedagogies it will develop for staff and students. Despite being in one of the newest campuses in the country, we also deliver some of our course content in the Sessions House. This is one of the oldest and most historic buildings in town. Sometimes with students we leave the modern to take a plunge in history in a matter of hours. Traditionally the court has been used in education primarily for mooting in the study of law or for reenactment for humanities. On this occasion, criminology occupies the space for learning enhancement that shall go beyond these roles.
The Sessions House is the old court in the centre of Northampton, built 1676 following the great fire of Northampton in 1675. The building was the seat of justice for the town, where the public heard unspeakable crimes from matricide to witchcraft. Justice in the 17th century appear as a drama to be played in public, where all could hear the details of those wicked people, to be judged. Once condemned, their execution at the gallows at the back of the court completed the spectacle of justice. In criminology discourse, at the time this building was founded, Locke was writing about toleration and the constrains of earthy judges. The building for the town became the embodiment of justice and the representation of fairness. How can criminology not be part of this legacy?
There were some of the reasons why we have made this connection with the past but sometimes these connections may not be so apparent or clear. It was in one of those sessions that I began to think of the importance of what we do. This is not just a space; it is a connection to the past that contains part of the history of what we now recognise as criminology. The witch trials of Northampton, among other lessons they can demonstrate, show a society suspicious of those women who are visible. Something that four centuries after we still struggle with, if we were to observe for example the #metoo movement. Furthermore, from the historic trials on those who murdered their partners we can now gain a new understanding, in a room full of students, instead of judges debating the merits of punishment and the boundaries of sentencing.
These are some of the reasons that will take this historic building forward and project it forward reclaiming it for what it was intended to be. A courthouse is a place of arbitration and debate. In the world of pedagogy knowledge is constant and ever evolving but knowing one’s roots allows the exploration of the subject to be anchored in a way that one can identify how debates and issues evolve in the discipline. Academic work can be solitary work, long hours of reading and assignment preparation, but it can also be demonstrative. In this case we a group (or maybe a gang) of criminologists explore how justice and penal policy changes so sitting at the green leather seats of courtroom, whilst tapping notes on a tablet. We are delighted to reclaim this space so that the criminologists of the future to figure out many ethical dilemmas some of whom once may have occupied the mind of the bench and formed legal precedent. History has a lot to teach us and we can project this into the future as new theoretical conventions are to emerge.
Locke J, (1689), A letter Concerning Toleration, assessed 01/11/18 https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/A_Letter_Concerning_Toleration