Home » Age
Category Archives: Age
25 years of Criminology

When the world was bracing for a technological winter thanks to the “millennium bug” the University of Northampton was setting up a degree in Criminology. Twenty-five years later and we are reflecting on a quarter of a century. Since then, there have been changes in the discipline, socio-economic changes and wider changes in education and academia.
The world at the beginning of the 21st century in the Western hemisphere was a hopeful one. There were financial targets that indicated a raising level of income at the time and a general feeling of a new golden age. This, of course, was just before a new international chapter with the “war on terror”. Whilst the US and its allies declared the “war on terror” decreeing the “axis of evil”, in Criminology we offered the module “Transnational Crime” talking about the challenges of international justice and victor’s law.
Early in the 21st century it became apparent that individual rights would take centre stage. The political establishment in the UK was leaving behind discussions on class and class struggles and instead focusing on the way people self-identify. This ideological process meant that more Western hemisphere countries started to introduce legal and social mechanisms of equality. In 2004 the UK voted for civil partnerships and in Criminology we were discussing group rights and the criminalisation of otherness in “Outsiders”.
During that time there was a burgeoning of academic and disciplinary reflection on the way people relate to different identities. This started out as a wider debate on uniqueness and social identities. Criminology’s first cousin Sociology has long focused on matters of race and gender in social discourse and of course, Criminology has long explored these social constructions in relation to crime, victimisation and social precipitation. As a way of exploring race and gender and age we offered modules such as “Crime: Perspectives of Race and Gender” and “Youth, Crime and the Media”. Since then we have embraced Kimberlé Crenshaw’s concept of intersectionality and embarked on a long journey for Criminology to adopt the term and explore crime trends through an increasingly intersectional lens. Increasingly our modules have included an intersectional perspective, allowing students to consider identities more widely.
The world’s confidence fell apart when in 2008 in the US and the UK financial institutions like banks and other financial companies started collapsing. The boom years were replaced by the bust of the international markets, bringing upheaval, instability and a lot of uncertainty. Austerity became an issue that concerned the world of Criminology. In previous times of financial uncertainty crime spiked and there was an expectation that this will be the same once again. Colleagues like Stephen Box in the past explored the correlation of unemployment to crime. A view that has been contested since. Despite the statistical information about declining crime trends, colleagues like Justin Kotzé question the validity of such decline. Such debates demonstrate the importance of research methods, data and critical analysis as keys to formulating and contextualising a discipline like Criminology. The development of “Applied Criminological Research” and “Doing Research in Criminology” became modular vehicles for those studying Criminology to make the most of it.
During the recession, the reduction of social services and social support, including financial aid to economically vulnerable groups began “to bite”! Criminological discourse started conceptualising the lack of social support as a mechanism for understanding institutional and structural violence. In Criminology modules we started exploring this and other forms of violence. Increasingly we turned our focus to understanding institutional violence and our students began to explore very different forms of criminality which previously they may not have considered. Violence as a mechanism of oppression became part of our curriculum adding to the way Criminology explores social conditions as a driver for criminality and victimisation.
While the world was watching the unfolding of the “Arab Spring” in 2011, people started questioning the way we see and read and interpret news stories. Round about that time in Criminology we wanted to break the “myths on crime” and explore the way we tell crime stories. This is when we introduced “True Crimes and Other Fictions”, as a way of allowing students and staff to explore current affairs through a criminological lens.
Obviously, the way that the uprising in the Arab world took charge made the entire planet participants, whether active or passive, with everyone experiencing a global “bystander effect”. From the comfort of our homes, we observed regimes coming to an end, communities being torn apart and waves of refugees fleeing. These issues made our team to reflect further on the need to address these social conditions. Increasingly, modules became aware of the social commentary which provides up-to-date examples as mechanism for exploring Criminology.
In 2019 announcements began to filter, originally from China, about a new virus that forced people to stay home. A few months later and the entire planet went into lockdown. As the world went into isolation the Criminology team was making plans of virtual delivery and trying to find ways to allow students to conduct research online. The pandemic rendered visible the substantial inequalities present in our everyday lives, in a way that had not been seen before. It also made staff and students reflect upon their own vulnerabilities and the need to create online communities. The dissertation and placement modules also forced us to think about research outside the classroom and more importantly outside the box!
More recently, wars in Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Asia have brought to the forefront many long posed questions about peace and the state of international community. The divides between different geopolitical camps brought back memories of conflicts from the 20th century. Noting that the language used is so old, but continues to evoke familiar divisions of the past, bringing them into the future. In Criminology we continue to explore the skills required to re-imagine the world and to consider how the discipline is going to shape our understanding about crime.
It is interesting to reflect that 25 years ago the world was terrified about technology. A quarter of a century later, the world, whilst embracing the internet, is worriedly debating the emergence of AI, the ethics of using information and the difference between knowledge and communication exchanges. Social media have shifted the focus on traditional news outlets, and increasingly “fake news” is becoming a concern. Criminology as a discipline, has also changed and matured. More focus on intersectional criminological perspectives, race, gender, sexuality mean that cultural differences and social transitions are still significant perspectives in the discipline. Criminology is also exploring new challenges and social concerns that are currently emerging around people’s movements, the future of institutions and the nature of society in a global world.
Whatever the direction taken, Criminology still shines a light on complex social issues and helps to promote very important discussions that are really needed. I can be simply celebratory and raise a glass in celebration of the 25 years and in anticipation of the next 25, but I am going to be more creative and say…
To our students, you are part of a discipline that has a lot to say about the world; to our alumni you are an integral part of the history of this journey. To those who will be joining us in the future, be prepared to explore some interesting content and go on an academic journey that will challenge your perceptions and perspectives. Radical Criminology as a concept emerged post-civil rights movements at the second part of the 20th century. People in the Western hemisphere were embracing social movements trying to challenge the established views and change the world. This is when Criminology went through its adolescence and entered adulthood, setting a tone that is both clear and distinct in the Social Sciences. The embrace of being a critical friend to these institutions sitting on crime and justice, law and order has increasingly become fractious with established institutions of oppression (think of appeals to defund the police and prison abolition, both staples within criminological discourse. The rigour of the discipline has not ceased since, and these radical thoughts have led the way to new forms of critical Criminology which still permeate the disciplinary appeal. In recent discourse we have been talking about radicalisation (which despite what the media may have you believe, can often be a positive impetus for change), so here’s to 25 more years of radical criminological thinking! As a discipline, Criminology is becoming incredibly important in setting the ethical and professional boundaries of the future. And don’t forget in Criminology everyone is welcome!

Are my interests childish or are you missing the bigger picture?

In semester 2, the level 4 BA Criminology students have been navigating different forms of socialisation for children, and thinking critically about where standards, assumptions and pressures on our children come from. Its been an interesting few weeks full of discussions building on personal experiences, documentaries and the wider academic literature. Now, whilst I could write a detailed reflection on the classroom discussions, what instead I want to, shockingly, moan about in the blog this week are the labels applied to young adults and adults implying being ‘childish’ is something to be ashamed of.
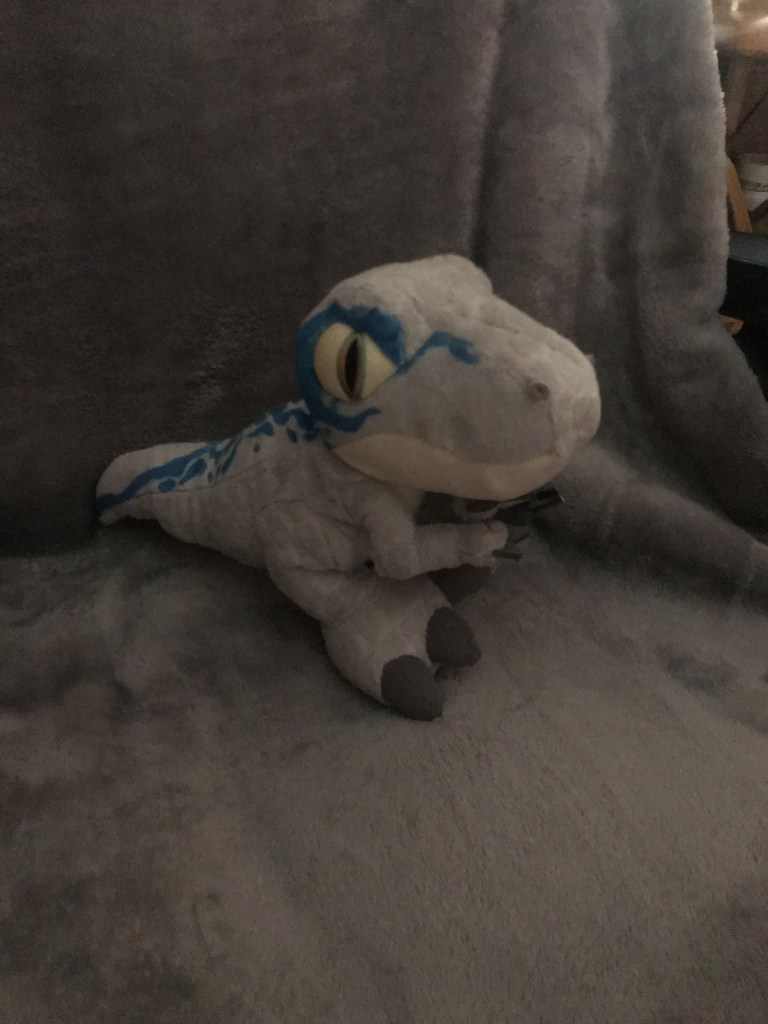

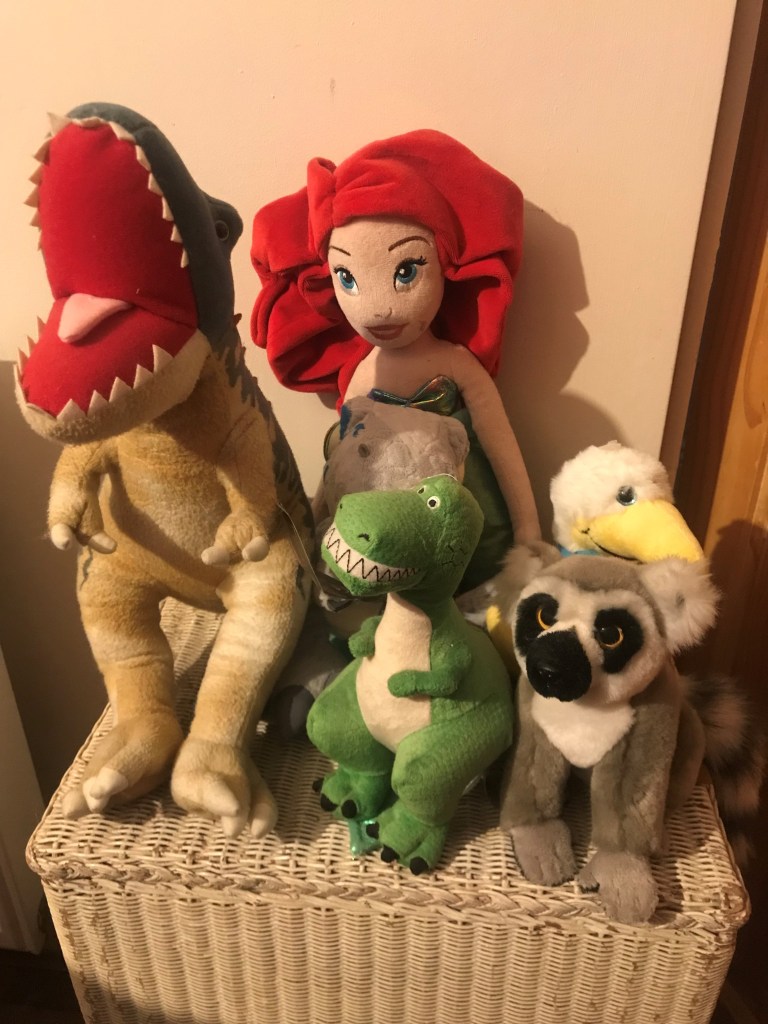
Many who know me will be aware I am a huge Disney fan, particularly Disney and Disney Pixar animations, which includes watching, gaming, clothing and accessories which all match my love for these films. I am also a big, big, big fan of dinosaurs, although if I’m being honest, its more so the Jurassic Park/World franchise. Again, books, films, toys, stuffed dinosaurs (shout out to my Beta stuffed toy – pictured above) from the Natural History Museum) and also a tattoo. These things bring me joy and also peace. Many a times when I’m overwhelmed, the go to is a Disney animation or Jurassic Park (much to my partner’s pain) for familiarity, comfort and relaxation. Yet despite the comfort and joy it brings me, often I am met with commentary about my ‘childish’ interests and questions around ‘when will I grow up’.
Now for clarity, most of these comments (but not all) are from friends and loved-ones who are saying so (I presume) in jest. There is no malice behind the comments, but still it has given me food for thought. Lots of people of all ages share the same joys as myself (social media fan pages are many), but is there any harm in pressing people to justify and commenting on their pastimes? Possibly. I am in a fortunate position to be able to afford various Disney-themed items of clothing (huge shout out to Primark and their Stitch section), Jurassic Park official merchandise, POP! Figures, clothes, posters etc whereas when I was younger, this was not something we could afford. Being in a privileged position and having a disposable income means I get to explore interests from my childhood, and have them develop into passions. Something which wasn’t available to me as a child, or even as a young adult at University. Being older and engaging with interests from childhood also uncovers new ways of appreciating the messages, artwork, and stories.
The presumption that my interests are ‘childish’ is not clearly explained by those who comment. What is meant by ‘childish’ and why is it presumed to be negative is not clear. But there appears to be some stigma around it. There is a push, as we are slowly uncovering in classroom discussions, for everyone to ‘grow-up’, but is this what is best for the individual? Or does this serve some greater purpose for society? I’m not sure what the point of the above ramblings are for, other than it might be best to keep opinions to yourself if you do not share the same interest. In a word that is full of harm and disadvantage, especially for children, let people enjoy their interests and passions, commentary free, if they aren’t harming you!
Christmas Toys

In CRI3002 we reflected on the toxic masculine practices which are enacted in everyday life. Hegemonic masculinity promotes the ideology that the most respectable way of being ‘a man’ is to engage in masculine practices that maintain the White elite’s domination of marginalised people and nations. What is interesting is that in a world that continues to be incredibly violent, the toxicity of state-inflicted hegemonic masculinity is rarely mentioned.
The militaristic use of State violence in the form of the brutal destruction of people in the name of apparent ‘just’ conflicts is incredibly masculine. To illustrate, when it is perceived and constructed that a privileged position and nation is under threat, hegemonic masculinity would ensure that violent measures are used to combat this threat.
For some, life is so precious yet for others, life is so easily taken away. Whilst some have engaged in Christmas traditions of spending time with the family, opening presents and eating luxurious foods, some are experiencing horrors that should only ever be read in a dystopian novel.
Through privileged Christmas play-time with new toys like soldiers and weapons, masculine violence continues to be normalised. Whilst for some children, soldiers and weapons have caused them to be victims of wars with the most catastrophic consequences.
Even through children’s play-time the privileged have managed to promote everyday militarism for their own interests of power, money and domination. Those in the Global North are lead to believe that we should be proud of the army and how it protects ‘us’ by dominating ‘them’ (i.e., ‘others/lesser humans and nations’).
Still in 2023 children play with symbolically violent toys whilst not being socialised to question this. The militaristic toys are marketed to be fun and exciting – perhaps promoting apathy rather than empathy. If promoting apathy, how will the world ever change? Surely the privileged should be raising their children to be ashamed of the use of violence rather than be proud of it?
Regulation and the Internet
*Trigger warning: article contains mentions of suicide, mental illness and self harm in regard to a recent news article*
It seems that internet usage, regulation and monitoring can be a divisive topic for some. The internet can be a fantastic tool for learning, communicating and employment, among other things. However, as with everything, there is a dark side to it. I once watched a video about the internet and regulation, the narrator likened internet usage to when people drove cars with no seatbelts. The world now has this wonderful tool, with little to no effective safety mechanisms, and with many young people, and vulnerable people being able to view harmful content without regulation, we are seeing extreme and negative repercussions.
I think one of the main appeals of the internet is the inherent freedom that it gives the user, the key word here is freedom. It seems that some people believe that unregulated usage of the internet is now an inherent part of their freedoms. This is perhaps why attempting to further regulate usage could result in disagreement and objection. The topic of internet regulation is a very nuanced topic; it toes the line of freedom and restriction and profit and protection. Algorithms are one way that social media companies can prolong the amount of time a person is scrolling through their newsfeed, for example: If you ‘liked’ a picture of a cat, it is more likely that related content would then be shown to you. For social media companies, more engagement equals more money. The algorithmic style of newsfeeds seems great in theory but they can become harmful. If we replace viewing cat content on Instagram with viewing suicide related content, we can see how this can become very problematic very quickly.
Questions concerning the ‘wild west’ type environment that is the internet are becoming more common. With the recent inquest concerning the suicide of Molly Russel, these questions are even more relevant. Molly Russel saved thousands of images related to self harm and suicide months before her death, posts also included some promoting depressive content and encouragement to not seek the help from a mental health professional. Tech giant Meta’s response in the inquest was that the majority of these posts did not breach their social media posting guidelines (they conceded a few did breach the rules). Their response totally contradicts the reactions of those present at the court, with Molly Russel’s father stating that these images were graphic, dark and harmful. With mental health resources already being stretched beyond capacity, this unregulated environment that is legally accessible to children will surely exacerbate these problems. Molly Russel’s experience will not be the only one, thousands of vulnerable and impressionable people, young and old experience similar things and view similar medias. Whether it be accessing pro-anorexia content, content which promotes weapons and violence or content which advocates for avoiding professional mental health support.
The repercussions of an ineffectively regulated internet are unmeasured and the continuation of this deregulation is for the pursuit of profit fuelled by misguided ideas about what freedom of action and freedom of expression mean.
The dance of the vampires

We value youth. There is greater currency in youth, far greater than wisdom, despite most people when they are looking back wishing they had more wisdom in life. Modernity brought us the era of the picture and since then we have become captivated with images. Pictures, first black and white, then replaced by moving images, and further replaced by colour became an antidote to a verbose society that now didn’t need to talk about it…it simply became a case of look and don’t talk!
The image became even more important when people turned the cameras on themselves. The selfie, originally a self-portrait of reclusive artists evolved into a statement, a visual signature for millions of people using it every day on social media. Enter youth! The engagement with social media is regarded the gift of computer scientists to the youth of today. I wonder how many people know that one of the first images sent as a jpeg was that of a Swedish Playboy playmate the ‘lady with the feathers’. This “captivating” image was the start of the virtual exchange of pictures that led to billions of downloads every day and social media storing an ever-expanding array of images.
The selfie, brought with it a series of challenges. How many times can you take a picture, even of the most beautiful person, before you become accustomed to it. Before you say, well yes that is nice, but I have seen it before. To resolve the continuous exposure the introduction of filters, backgrounds and themes seems to add a sense of variety. The selfie stick (banned from many museums the world over) became the equipment, along with the tripod, the lamp and the must have camera, with the better lens in the pursue of the better selfie. Vanity never had so many accessories!
The stick is an interesting tool. It tells the individual nature of the selfie. The voyage that youthful representation takes across social media is not easy, it is quite a solitary one. In the representation of the image, youth seem to prefer. The top “influencers” are young, who mostly like to pose and sometimes even offer some advice to their followers. Their followers, their contemporaries or even older individuals consume their images like their ‘daily (visual) bread’. This seems to be a continuous routine, where the influencer produces images, and the followers watch them and comment. What, if anything, is peculiar about that? Nothing! We live in a society build on consumption and the industry of youth is growing. So, this is a perfect marriage of supply and demand. Period!
Or is it? In the last 30 years in the UK alone the law on protecting children and their naivety from exploitation has been centre stage of several successive governments. Even when discussing civil partnerships for same sex couples, Baroness Young, argued against the proposed act, citing the protection of children. Youth became a precious age that needed protection and nurturing. The law created a layer of support for children, particularly those regarded vulnerable. and social services were drafted in to keep them safe and away from harm. In instances when the system failed, there has been public outrage only to reinforce the original notion that children and young people are to be protected in our society.
That is exactly the issue here! In the Criminology of the selfie! Governments introducing policies to generate a social insulation of moral righteousness that is predicated on individual – mostly parental – responsibility. The years of protective services and we do not seem to move passed them. In fact, their need is greater than ever. Are we creating bad parents through bad parenting or are people confronted with social forces that they cannot cope with? The reality is that youth is more exposed than ever before. The images produced, unlike the black and white photos of the past, will never fade away. Those who regret the image they posted, can delete it from their account, but the image is not gone. It shall hover over them for the eternity of the internet. There is little to console and even less to help. During the lockdown, I read the story of the social carer who left their job and opened an OnlyFans account. These are private images provided to those who are willing to pay. The reason this experience became a story, was the claim that the carer earned in one month of OnlyFans, more than their previous annual income. I saw the story being shared by many young people, tagging each other as if saying, look at this. The image that captures their youth that can become a trap to contain them in a circle of youth. Because in life, before the certainty of death there is another one, that of aging and in a society that values youth so much, can anyone be ready to age?
As for the declared care for the young, would a society that cares have been closing the doors to HE, to quality apprenticeships, a living wage and a place to live? The same society that stirs emotions about protection, wants young people to stay young so that they cannot ask for their share in their future. The social outrage about paedophiles is countered with high exposure to a particular genre in the movies and literature that promotes it. The vampire that has been fashioned as young adult literature is the proverbial story of an (considerably) older man who deflowers a young innocent girl until she becomes infatuated with him. The movies can be visually stunning because it involves the images of young beautiful people but there is hardly any mention of consent or care!
It is one of the greatest ironies to revive the vampire image in youth culture. A cultural representation of a male prototype that is manipulative, intruding into the lives of seemingly innocent young people who become his prey. There is something incredibly unsettling to explore the semiology of an immortal that is made through a blood ritual. A reverse Peter Pan who consumes the youth of his victims. The popularity of this Victorian literary character, originally conceived in the era of industrial advancement,at a time when modernity challenged tradition, resurfaces with other monsters at times of great uncertainty. The era of the picture has not made everyday life easier, and modernity did not improve quality of life to the degree it proclaimed. Instead, whilst people are becoming captivated by ephemera they are focused on the appearance and missing substance. An old experience man, dark, mysterious with white skin may be an appealing character in literature but in real life a someone who feeds on young people’s blood is hardly an exciting proposition.
The blood sacrifice demanded by a vampire is a metaphor of what our society requires for those who wish to retain youth and save their image into the ether of the cyberworld as a permanent Portrait of Dorian Gray. In this context, the vampire is not only a man in power, using his privilege to dominate, but a social representation of what a consumer society places as the highest value. It is life’s greatest irony that the devouring power of a vampire is becoming a representation of how little value we place on both youth and life! A society focused on appearance, ignoring the substance. Youth looking but not youth caring!
Things I used to could do without a phone. #BlackenAsiaWithLove
A Spoken Word poem for young people everywhere, esp Youth in Asia, who may never know WE LIVED before smartphones…and live to tell about it.
Walk.

Walk down the street.
Find my way.
Go someplace.
Go someplace I had previously been.
Go someplace I had previously not been.
Meet.
Meet friends.
Meet friends at a specific time and place.
Meet new people.
Meet new people without suspicion.
Strike up a conversation with a stranger.
Make myself known to a previously unknown person.
Now, everything and everyone unknown is literally described as ‘weird’.

Eat.
Eat in a restaurant by myself.
Pay attention to the waiter.
Wait for my order to arrive.
Sit.
Sit alone.
Sit with others.
Listen.
Listen to the sound of silence.
Listen to music.
Listen to a whole album.
Listen to the cityscape.
Overhear others’ conversations in public.
Watch kids play.

Shop.
Share.
Share pictures.
Take pictures.
Develop pictures.
Frame pictures.
See the same picture in the same spot.
Read.
Read a book.
Read a long article.
Read liner notes.
Pee.
I used to be able to stand at a urinal and focus on what I was doing,
Not feeling bored,
Not feeling the need to respond to anything that urgently.
Nothing could be so urgent that I could not, as the Brits say, ‘take a wee’.
Wait.
Wait at a traffic light.
Wait for a friend at a pre-determined place and time.

Wait for my turn.
Wait for a meal I ordered to arrive.
Wait in an office for my appointment.
Wait in line.
Wait for anything!
I used to appreciate the downtime of waiting.
Now waiting fuels FOMO.
I used to enjoy people watching…
Now I just watch people on their phones.
It’s genuine anxiety.
Walk.
Walk from point A to B.
I used to could walk between two known points without having to mark the moment with a post.
Now I can’t walk down the hall,
Or through the house or even to the toilet without checking my phone.
I avoid eye contact with strangers.
Anyone I don’t already know is strange.
I used to could muscle through this awkwardness.
Talk.
Have a conversation.
A friend and I recently lamented about how you used to could have a conversation and
Even figure out a specific thing that you couldn’t immediately recall…
Just by talking.
I also appreciate the examples we discussed.
Say you wanted to mention a world leader but couldn’t immediately remember their name. What would you do before?
Rattle off the few facts you could recall and in so doing you’d jog your memory.
Who was the 43rd US president?
If you didn’t immediately recall his name,
You might have recalled that the current one is often called “45” since
Many folks avoid calling his name.
You know Obama was before him, therefore he must’ve been number “44.”
You know Obama inherited a crap economy and several unjust wars,

Including the cultural war against Islam. And
That this was even one of the coded racial slurs used against him: “A Muslim.”
Putting these facts together,
You’d quickly arrive at Dubya! And
His whole warmongering cabinet. And
Condi Rice. And
General Powell’s botched PowerPoint presentation at the UN. And
Big dick Cheney, Halliburton and that fool shooting his friend while hunting.
That whole process might have taken a full minute,
But so would pulling up 43’s name on the Google.
This way, however, you haven’t lost the flow of conversation nor the productive energy produced between two people when they talk.
(It’s called ‘limbic resonance’, BTW).
Yeah, I used to be able to recall things…
Many more things about the world without my mobile phone.

Wonder.
Allow my mind to wander.
Entertain myself with my own thoughts.
Think.
Think new things.
Think differently just by thinking through a topic.
I used to know things.
Know answers that weren’t presented to me as search results.
I used to trust my own knowledge.
I used to be able to be present, enjoying my own company,
Appreciating the wisdom that comes with the mental downtime.
Never the fear of missing out,
Allowing myself time to reflect.
It is in reflection that wisdom is born.
Now, most of us just spend our time simply doing:
Surfing, scrolling, liking, dissing, posting, sharing and the like.
Even on a wondrous occasion, many of us would rather be on our phones.
Not just sharing the wonderful occasion –
Watching an insanely beautiful landscape through our tiny screens,
Phubbing the people we’re actually with,
Reducing a wondrous experience to a well-crafted selfie –

But just making sure we’re not missing out on something rather mundane happening back home.
I used to could be in the world.
Now, I’m just in cyberspace.
I used to be wiser.
A crime, but who cares?

“IMG_8755 – Copy” by stivoberlin is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Amongst all the furore over Brexit, the European elections and the disintegration of the main political parties in the United Kingdom, a small but not insignificant news story crept into the news melee.
‘The number of physically disabled people affected by homelessness in England increased by three quarters during an almost 10- year period’ (BBC, 2019a, Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government, 2019). It is not merely coincidental that the ‘almost 10-year period’ aligns with the austerity measures introduced by the coalition government in 2010. Measures, continuously pursued by the Conservative Government until October 2018 when Theresa May, the soon to be former prime minister, declared at a Tory party conference that austerity was over adding, ‘the end is in sight’ and there are ‘better days ahead’ (Independent, 2018a). Give her her dues, with the demise of the Tory party, the latter part was an insightful prediction. Let’s not let the Liberal Democrats off the hook though, reluctant bedfellows they may have been in the coalition government, but bedfellows they were, and they had the power to vote down many of the Tory party dictats. They may have curried favour with the electorate during the European elections, but we should not forget their part in the austerity measures.
Alongside the issues of homelessness, we see the use of foodbanks has increased phenomenally (Independent, 2018b), fuel poverty affects over 10% of English households (Independent, 2018c) and social care is collapsing (BBC, 2019b; Guardian, 2018). To put it as simply as possible, the common denominator is the austerity measures introduced by government that directly impact on the most vulnerable in our so-called civilised society. This and previous governments can point to the budget deficit, the ineptitude of the previous government and the economic downturn caused by the banking crisis (The Economist, 2013), but how do they justify the impact of their policies on the disadvantaged and those who can least afford any cuts? Bizarrely, the least vulnerable have seen little or no impact on their standard of living other than perhaps for the middle classes there is the monotonous moan about access to doctors or dentists in a timely manner (the rich don’t even have to worry about this).
In my visits around schools I discuss what we mean by the term crime. Reiner (2007:21) states that ‘[t]he term ‘crime’ is usually tossed about as if it has a clear and unambiguous meaning’, but nothing of course is further from the truth. One of the key ideas I posit is that of harm caused. This of course has its own problems in terms of definition and scope, but it does allow one to focus on what is important. If harm done is a measure of crime, or crime is defined by the harm done then we begin to see the world, actions by government, institutions and individuals in a different light. With this notion in mind, we can start to ask when and how do we bring the greedy and those that abuse their power either intentionally or recklessly to book? Maybe, just as Boris Johnson might well be prosecuted for misconduct in a public office over the alleged lies, he made relating to Brexit (BBC, 2019c), we might see ministers held to account for decisions they make that have catastrophic consequences for thousands of the most vulnerable in society.
BBC (2019a) Homeless and disabled: ‘I’m at my wits’ end’, [online] Available at www.bbc.co.uk/news/av/disability-48433225/homeless-and-disabled-i-m-at-my-wits-end [accessed 29 May 2019].
BBC (2019b) English ‘short-changed on care funding’ [online] Available at http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-48438132 [accessed 30 May 2019].
BBC (2019c) Brexit: Boris Johnson ordered to appear in court over £350m claim, [online] Available at http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-politics-48445430 [accessed 29 May 2019].
Independent (2018a) Theresa May declares ‘austerity is over’ after eight years of cuts and tax increases, (3 Oct. 2018), [online] Available at www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/politics/theresa-may-austerity-end-over-speech-conservative-conference-tory-labour-a8566526.html [accessed 30 May 2019].
Independent (2018b) Food bank use in UK reaches highest rate on record as benefits fail to cover basic costs (24 April 2018) [online] Available at www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/food-bank-uk-benefits-trussell-trust-cost-of-living-highest-rate-a8317001.html [accessed 30 May 2019].
Independent (2018) More than one in 10 households living in fuel poverty, figures show (26 June 2018) [online] Available at www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/fuel-poverty-uk-figures-poor-bills-cost-households-a8417426.html, [accessed 30 May 2019].
Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government (2019) Live tables on homelessness [online] Available at http://www.gov.uk/government/statistical-data-sets/live-tables-on-homelessness , [accessed 30 May 2019].
Reiner, R. (2007) Law and Order: An Honest Citizen’s Guide to Crime and Crime Control, Cambridge: Polity.
The Economist (2013) The origins of the financial crisis: Crash course [online] Available at www.economist.com/schools-brief/2013/09/07/crash-course [accessed 30 May 2019].
The Guardian (2018) The social care system is collapsing. So why the government inaction? (3 Oct. 2019) [online] Available at www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2018/oct/03/social-care-collapsing-government-inaction [accessed 30 May 2019].
“Political Drillin”

A recent track that has come to light which incorporates Drill Music is that called ‘Political Drillin’. On the track the artist manages to incorporate quotes from politicians; which proves he is highly deserving of his title ‘DrillMinister’.
What was particularly shocking to me was how easy it was for the governmental quotes to actually fit in with what he was initially rapping about, considering how frowned upon the genre is by these same figures.
It becomes very obvious that the slurs deemed as “violent” are ones that much of us are accustomed to hearing on a daily basis. In my interpretation, the artist seems to be bringing this to light. When young people use similar racial, derogatory terms towards one another it is seen to be violent and makes headlines, but politicians seem to throw these around in parliament without being reprimanded for their actions. Why is this continuously tolerated?
The fact that these comments are known to all and no action is taken against them demonstrates that there is a certain calibre of people that can be deemed as criminal and those who will not. Once again shedding light on the class, age and racial division that is hanging over society.
So once again I put the question out…is drill music a cause of violent crime, or are we simply a criminal society? If the DrillMinister can be labelled violent, surely politicians should be too?
*The image contains a quote from Jess Phillips MP utilised as a lyric by DrillMinister:












