Home » Transgender
Category Archives: Transgender
25 years of Criminology

When the world was bracing for a technological winter thanks to the “millennium bug” the University of Northampton was setting up a degree in Criminology. Twenty-five years later and we are reflecting on a quarter of a century. Since then, there have been changes in the discipline, socio-economic changes and wider changes in education and academia.
The world at the beginning of the 21st century in the Western hemisphere was a hopeful one. There were financial targets that indicated a raising level of income at the time and a general feeling of a new golden age. This, of course, was just before a new international chapter with the “war on terror”. Whilst the US and its allies declared the “war on terror” decreeing the “axis of evil”, in Criminology we offered the module “Transnational Crime” talking about the challenges of international justice and victor’s law.
Early in the 21st century it became apparent that individual rights would take centre stage. The political establishment in the UK was leaving behind discussions on class and class struggles and instead focusing on the way people self-identify. This ideological process meant that more Western hemisphere countries started to introduce legal and social mechanisms of equality. In 2004 the UK voted for civil partnerships and in Criminology we were discussing group rights and the criminalisation of otherness in “Outsiders”.
During that time there was a burgeoning of academic and disciplinary reflection on the way people relate to different identities. This started out as a wider debate on uniqueness and social identities. Criminology’s first cousin Sociology has long focused on matters of race and gender in social discourse and of course, Criminology has long explored these social constructions in relation to crime, victimisation and social precipitation. As a way of exploring race and gender and age we offered modules such as “Crime: Perspectives of Race and Gender” and “Youth, Crime and the Media”. Since then we have embraced Kimberlé Crenshaw’s concept of intersectionality and embarked on a long journey for Criminology to adopt the term and explore crime trends through an increasingly intersectional lens. Increasingly our modules have included an intersectional perspective, allowing students to consider identities more widely.
The world’s confidence fell apart when in 2008 in the US and the UK financial institutions like banks and other financial companies started collapsing. The boom years were replaced by the bust of the international markets, bringing upheaval, instability and a lot of uncertainty. Austerity became an issue that concerned the world of Criminology. In previous times of financial uncertainty crime spiked and there was an expectation that this will be the same once again. Colleagues like Stephen Box in the past explored the correlation of unemployment to crime. A view that has been contested since. Despite the statistical information about declining crime trends, colleagues like Justin Kotzé question the validity of such decline. Such debates demonstrate the importance of research methods, data and critical analysis as keys to formulating and contextualising a discipline like Criminology. The development of “Applied Criminological Research” and “Doing Research in Criminology” became modular vehicles for those studying Criminology to make the most of it.
During the recession, the reduction of social services and social support, including financial aid to economically vulnerable groups began “to bite”! Criminological discourse started conceptualising the lack of social support as a mechanism for understanding institutional and structural violence. In Criminology modules we started exploring this and other forms of violence. Increasingly we turned our focus to understanding institutional violence and our students began to explore very different forms of criminality which previously they may not have considered. Violence as a mechanism of oppression became part of our curriculum adding to the way Criminology explores social conditions as a driver for criminality and victimisation.
While the world was watching the unfolding of the “Arab Spring” in 2011, people started questioning the way we see and read and interpret news stories. Round about that time in Criminology we wanted to break the “myths on crime” and explore the way we tell crime stories. This is when we introduced “True Crimes and Other Fictions”, as a way of allowing students and staff to explore current affairs through a criminological lens.
Obviously, the way that the uprising in the Arab world took charge made the entire planet participants, whether active or passive, with everyone experiencing a global “bystander effect”. From the comfort of our homes, we observed regimes coming to an end, communities being torn apart and waves of refugees fleeing. These issues made our team to reflect further on the need to address these social conditions. Increasingly, modules became aware of the social commentary which provides up-to-date examples as mechanism for exploring Criminology.
In 2019 announcements began to filter, originally from China, about a new virus that forced people to stay home. A few months later and the entire planet went into lockdown. As the world went into isolation the Criminology team was making plans of virtual delivery and trying to find ways to allow students to conduct research online. The pandemic rendered visible the substantial inequalities present in our everyday lives, in a way that had not been seen before. It also made staff and students reflect upon their own vulnerabilities and the need to create online communities. The dissertation and placement modules also forced us to think about research outside the classroom and more importantly outside the box!
More recently, wars in Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Asia have brought to the forefront many long posed questions about peace and the state of international community. The divides between different geopolitical camps brought back memories of conflicts from the 20th century. Noting that the language used is so old, but continues to evoke familiar divisions of the past, bringing them into the future. In Criminology we continue to explore the skills required to re-imagine the world and to consider how the discipline is going to shape our understanding about crime.
It is interesting to reflect that 25 years ago the world was terrified about technology. A quarter of a century later, the world, whilst embracing the internet, is worriedly debating the emergence of AI, the ethics of using information and the difference between knowledge and communication exchanges. Social media have shifted the focus on traditional news outlets, and increasingly “fake news” is becoming a concern. Criminology as a discipline, has also changed and matured. More focus on intersectional criminological perspectives, race, gender, sexuality mean that cultural differences and social transitions are still significant perspectives in the discipline. Criminology is also exploring new challenges and social concerns that are currently emerging around people’s movements, the future of institutions and the nature of society in a global world.
Whatever the direction taken, Criminology still shines a light on complex social issues and helps to promote very important discussions that are really needed. I can be simply celebratory and raise a glass in celebration of the 25 years and in anticipation of the next 25, but I am going to be more creative and say…
To our students, you are part of a discipline that has a lot to say about the world; to our alumni you are an integral part of the history of this journey. To those who will be joining us in the future, be prepared to explore some interesting content and go on an academic journey that will challenge your perceptions and perspectives. Radical Criminology as a concept emerged post-civil rights movements at the second part of the 20th century. People in the Western hemisphere were embracing social movements trying to challenge the established views and change the world. This is when Criminology went through its adolescence and entered adulthood, setting a tone that is both clear and distinct in the Social Sciences. The embrace of being a critical friend to these institutions sitting on crime and justice, law and order has increasingly become fractious with established institutions of oppression (think of appeals to defund the police and prison abolition, both staples within criminological discourse. The rigour of the discipline has not ceased since, and these radical thoughts have led the way to new forms of critical Criminology which still permeate the disciplinary appeal. In recent discourse we have been talking about radicalisation (which despite what the media may have you believe, can often be a positive impetus for change), so here’s to 25 more years of radical criminological thinking! As a discipline, Criminology is becoming incredibly important in setting the ethical and professional boundaries of the future. And don’t forget in Criminology everyone is welcome!

Gen Z’s gender divide
How can we help bridge Gen Z’s global gender divide as they negotiate for their futures? Unique to Gen Z, according to a recent study, women and men aged 16 to 29 diverge greatly on how they perceive existing inequality as well as assess their futures. That’s according to a widely-reported King’s College study, ‘Emerging tensions? How younger generations are dividing on masculinity and gender equality’, which also found:
- Men are around twice as likely as women to say doing housework and caring for family members are things that apply to both genders equally, despite evidence showing that in reality women do more of both on average. (See also: the Mental Load)
- A higher proportion of men also think there is no gender difference in likelihood of being a senior manager or earning a high income, yet research suggests these characteristics apply to men more than women in the UK. (See also: the UK government’s Gender Pay Gap index, and the Economist)
Family and parental leave – is just one way home and work lives overlap in policy, practice and legislation, acknowledging the importance of unpaid (domestic) labour. BBC news reports on one study that found, “men who take paternity leave do more childcare later.” How might these ‘emerging tensions’ impact the gender inequality in parental leave laws, policies, and practices?
One trend is for companies to create equal and pro-social family policies far beyond laws, not least of which is hybrid working. Flexible/hybrid work has been a lobbying target long before Covid by the Fawcett Society, which champions the Equal Pay Day campaign, and consults the government on the Gender Pay Gap. In 2023 their data highlighted that: “77% of women agreed that they would be more likely to apply for a job that advertises flexible working options.”
Other parental leave policies are gender-neutral, include IVF, adoptive and LGBTQAI+ parents, incentivise paternity leave, and host gendered employee networks. How else will these ‘emerging tensions’ show up in the workplace? One wonders how are other policies and practices promoting a fairer workplace and a healthier work/life balance?
It’s hard out here for…
Notably, all sorts of business news outlets have been reporting about this issue, and more recently about King’s College study, including Forbes, which found it curious that: “for those aged between 16 and 29…some 68% of women said that it was harder to be a woman, while only 35% of men agreed with that statement.” This article shines light on a gap and leaves it at that.
The Guardian has produced a series of articles and podcasts about the growing number of studies and polls reflecting this same cross-gender cultural rift: Here are a few headlines from just this past February:
1/2/24: Gen Z boys and men more likely than baby boomers to believe feminism harmful, says poll.
2/2/24: Friday briefing: Why the politics of young men and women are drifting further and further apart.
7/2/24: Why is generation Z so divided on gender? [Podcast]
Reporting on the study, The Independent headlines: “Of course Gen Z boys believe feminism is harmful – they’ve learnt it from the internet.” Indeed, the author reminds us that social media is quite apt at seeding and feeding division. “Algorithms often operate on extremes: because people tend to click on and engage with the most sensational, hyperbolic content, this is what the algorithm serves up.” Subsequently, young men and women grew up in two very different virtual worlds.

Feminism, the new F-word
According to the King’s College study: 42% of the public say, “equal rights … have had a positive impact on today’s young men.” This is acknowledged in the 2019 Government Equalities Office report, Changing Gender Norms: Engaging with Men and Boys, regarding the Advertising Standards Authority’s guidance on toxic masculine images, stating: “stereotypes implying that men should be physically strong, unemotional and family breadwinners are limiting and potentially damaging.”
Ironically, my career began in international development, which has long since addressed the role of boys and men in gender equality and masculinities, especially through the lens of sexual and reproductive health. In parallel, the work to decriminalise LGBTQAI+ communities simultaneously made alternative masculinities more visible to the wider society which lead even more to question, well frankly, patriarchy.
Still, in America, the majority, “whether they identify as feminists or not – say it is very important for women to have equal rights with men.” Could this be cognitive dissonance?
As these changes grow in wider society, we see organisations responding externally, e.g. virtue-signalling, diversity training, and rainbow advertising. How will organizations shift internally, e.g. in recruitment, retention, leadership, and reward?
Reproductive Healthcare Ramblings
Reproductive health in England and Wales is a shambles: particularly for women and people who menstruate. The failings start early, where, as with most things, stereotypes and ‘norms’ are enforced upon children from GPs, schools, from parents/guardians who have experienced worse, or who do not know any different, which keep children from speaking up. These standards and stereotypes come from a male dominated health care system especially in relation to gynaecology, and our patriarchal society silences children without the children even realising they are being silenced. As a child, you are expected to go about your daily routine, sit your exams, look after your siblings, represent the school at the tournament of the week, and do all this while, for some, bleeding, cramping, being fatigued but not be expected to talk about it. After all, you are told time and time again: it’s normal.
Moving through life, women and people who menstruate face similar stigma, standards, assumptions during adulthood as they faced during childhood. There is more awareness now of endometriosis, adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Condition (PCOS) to name but a few. But women and people who menstruate report feelings of being gaslighted by [male] gynaecologists, encouraged to have children in order to regulate their hormones (pregnancy and childbirth comes with a whole new set of healthcare problems and conditions), to take the contraceptive pill and deal with the migraines, mood swings, weight gain and depression which many women and girls report. Some of the above chronic illnesses impact fertility, so ‘try for a baby’ is not an easy, or even a wanted path. Diagnosis is also complex: for example a diagnosis for endometriosis takes on average 8 years (Endometriosisuk, 2023), and can only be confirmed with surgery. That relies on women and people who menstruate going to their GP, reporting their symptoms, listening to the ‘have you tried the pill’ or ‘having a baby will help manage your symptoms’: which relies on trust. Not everyone trusts the NHS, not everyone feels comfortable being dismissed by a nurse, or GP or then their gynaecologist. Especially when a number of these illnesses are framed and seen as a white-woman illness. Communities of women and people who menstruate remain hidden, dealing with the stigma and isolation that our reproductive health system carries in England and Wales. And this is not a new issue.
The reproductive healthcare for women and people who menstruate is dire. Just ask anyone who has experienced it. What then is it like for women in prison? The pains of imprisonment are well documented: deprivation of goods, loss of liberty, institutionalisation, no security, depreciation of mental health (Sykes, 1958; Carlen, 1983). The gendered pains, fears and harms less so, but we know women in prison are fearful about the deterioration of relationships (especially with children), lack of facilities to support new mothers, physical and sexual abuse, and poor mental and physical health support including reproductive health. The poor reproductive healthcare available to women and people who menstruate within society, is a grade above what is available in prisons. These women are quite literally isolated, alone and withdrawn from society (through the process of imprisonment), and for some, they will become further isolated and withdrawn via the pains of their chronic illness.
There isn’t really a point to this blog: more like a rambling of frustrations towards all the children who will journey through our subpar reproductive healthcare system, who will navigate the stigma and assumptions littered within society. To all the women and people who menstruate who are currently wading through this sh*t show, educating themselves, their family, their friends and in some cases their GPs, those people unable to speak out, not knowing how or simply not wanting to. And to those in the Secure Estate, grappling with the pains of imprisonment and having their reproductive healthcare needs ignored, overlooked or missed.
I haven’t even mentioned menopause…
References:
Carlen, P. (1983) Women’s Imprisonment, Abingdon: Routledge.
Corston, Baroness J. (2007) The Corston Report: A Review on Women with Particular Vulnerabilities in the Criminal Justice System, London: Home office.
Endometriosis UK (2023) Endometriosis Facts and Figures [online] Available at: https://www.endometriosis-uk.org/endometriosis-facts-and-figures#:~:text=Endometriosis%20affects%201.5%20million%20women,of%20those%20affected%20by%20diabetes.&text=On%20average%20it%20takes%208,symptoms%20to%20get%20a%20diagnosis. [Accessed 24th August 2023]
Sykes, G. (1958/2007) The Society of Captives: A Study of a Maximum Security Prison, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
I am not your “ally” (or am I?)
Today’s blog entry is a stream of consciousness rather than a finished entry with an introduction, middle and conclusion. It’s something that has been puzzling me for sometime, trying to work out why the term “ally” discomforts me and yet, not really coming to a firm conclusion. So I thought I’d explore it through a blog entry and would welcome anyone’s input to help me clarify and refine my own thinking and either embrace or reject the term.
Anyone that knows me, knows I love reading and of course, I love words. I love to play with them, say them, write them, discover new ones and trace the etymology as far as I can. Equally, I do not hide the fact that I try to understand the world through both pacifism and feminism. This makes me rather susceptible to interrogating and challenging the things that I see around me, including the written and spoken word.
The most obvious place to start when exploring words, is a dictionary, and this blog entry does similar. According to the Cambridge English Dictionary the term “ally” has three distinct definitions:
“a country that has agreed officially to give help and support to another one, especially during a war”
“someone who helps and supports someone else”
“someone who helps and supports other people who are part of a group that is treated badly or unfairly, although they are not themselves a member of this group”
Now for obvious reasons, I find the first definition problematic, put simply for me, war is a crime. The act of waging war includes multiple violences, some individual, some institutional, some structural and all incredibly harmful decades, or even centuries later. Definitions which have roots in the military and warfare leave me cold and I hate the way in which they infiltrate civilian discourse. For example “the war on drugs”, “the war on poverty”, “officer to the meeting” and the reshaping of the term “ally” for the twenty-first century” I definitely don’t want to be the “ally” described in that definition.
Definition two is also problematic, albeit for different reasons. This definition seems far too broad, if I hold the door open for you, is that me being an ally? If I help you carry your heavy bags, can I say I’m your ally? This seems a nonsensical way to talk about everyday actions which would be better described as common civility, helping each other along the way.Should I say “thank you kind ally” every time, someone moves out of my way, or offers their seat on the bus? It seems evident that this definition does not help me explore my reservations.
The third definition appears to come closest to modern usage of the term “ally”. This term can be applied to many different groups (as can be seen from the badges below and these are just some of the many examples). “whilst I identify as cisgender, I’m a trans ally”, whilst currently heterosexual, I’m a LGBTQ+ ally”, despite being white, I’m a BLM ally” and so on. On the surface this is very positive, moving society away from the nonsense of people describing themselves as “colour-blind”, “gender-blind” or such trite phrases as “we all bleed the same”, ignoring the lack of equity in society and pretending that everyone has the same lived experience, the same opportunities, the same health, wealth and happiness. Buying into the hackneyed idea that if only you work hard enough, you will succeed, that we live in a classless society and the only thing holding anyone back is their own inertia.
However, maybe my problem isn’t with the word “ally” but the word “I”, and the fact that the two words seem inseparable, After all who decides who is an ally or who is not, is there a organisation somewhere that checks your eligibility to be an ally? I’m pretty sure there’s not which means that that “ally” is a description you apply to yourself. After all you can buy the badge, the t-shirt, the mug etc etc, capitalism is on your side, provided the tills are ringing, there’s every reason to sign up. Maybe a tiny percentage of your purchases goes to financially benefit the people you aim to support, for example the heavily criticised Skittles Pride campaign which donated only 2p to LGBTQ+ charities (and stands accused of white supremacy and racism). Of course, once you have bought the paraphernalia, there is no need to do anything else, beyond carrying/wearing/eating your “ally” goods with pride.
All of the above seems to marketise and weaponise behaviour that should be standard practice, good manners if you like, in a society. Do we need a special word for this kind of behaviour or should we strive to make sure we make space for everyone in our society? If individuals or groups gain civil rights, I don’t lose anything, I gain a growing confidence that the society in which I live is improving, that there is some movement (however small) toward equity for all. Societies should not make life more difficult for the people who live in them, regardless of religious or spiritual belief, we have one opportunity to make a good life for ourselves and others and that’s right now, so why seek to dehumanise and disadvantage other humans who are on the same journey as we are.
Ultimately, my main concern with the use of term of “ally” is that it obscures incredibly challenging social harms, with colour and symbols hiding inaction and apathy. Accept the label of “ally”, wear the badge, if you think it has meaning, but if you do nothing else, this is meaningless. if you see inequality and you do not call it out, take action to remedy the situation, the word “ally” means nothing other than an opportunity to make yourself central to the discussion, taking up, rather than making, room for those focused on making a more just society.
I still remain uncomfortable with the term “ally” and I doubt it will ever appear in my lexicon, but it’s worth remembering that an antonym of ally is enemy and nobody needs those.
DIE in Solidarity with Diversity-Inclusion-Equality
As an associate lecturer on a casual contract, I was glad to stand in solidarity with my friends and colleagues also striking as part of UCU Industrial Action. Concurrently, I was also glad to stand in solidarity with students (as a recent former undergrad and masters student … I get it), students who simply want a better education, including having a curriculum that represents them (not a privileged minority). I wrote this poem for the students and staff taking part in strike action, and it comes inspired from the lip service universities give to doing equality while undermining those that actually do it (meanwhile universities refuse to put in the investment required). This piece also comes inspired by ‘This is Not a Humanising Poem’ by Suhaiymah Manzoor-Khan, a British author-educator from Bradford in Yorkshire.
Some issues force you to protest
the way oppression knocks on your front door
and you can’t block out the noise
“protest peacefully, non-violently”
I have heard people say
show ‘the undecided’, passive respectability
be quiet, leave parts of yourself at home
show them you’re just as capable of being liked
enough for promotion into the canteen,
protest with kindness and humour
make allusions to smiling resisters in literature
they’d rather passive images of Rosa Parks all honestly
but not her politics against racism, patriarchy, and misogyny

but I wanna tell them about British histories of dissent
the good and the bad – 1919 Race Riots
the 1926 general strikes, and the not so quiet
interwar years of Caribbean resistance to military conscription
I wanna talk about how Pride was originally a protest
I wanna talk about the Grunwick Strike and Jayaben Desai
and the Yorkshire miners that came to London in solidarity
with South Asian migrant women in what was 1980s austerity
I want to rant about Thatcherism as the base
for the neoliberal university culture we work in today
I want to talk about the Poll Tax Riots of 1990
and the current whitewashing of the climate emergency
they want protesters to be frugal in activism,
don’t decolonise the curriculum
they say decolonise
they mean monetise, let’s diversify …
but not that sort of diversity
nothing too political, critical, intellectual
transform lives, inspire change?
But no,
they will make problems out of people who complain
it’s your fault, for not being able to concentrate
in workplaces that separate the work you do
from the effects of Black Lives Matter and #MeToo
they make you the problem
they make you want to leave
unwilling to acknowledge that universities
discriminate against staff and students systemically
POCs, working-class, international, disabled, LGBT
but let’s show the eligibility of staff networks
while senior leaders disproportionately hire TERFs

staff and students chequered with severe floggings
body maps of indenture and slavery
like hieroglyphics made of flesh
but good degrees, are not the only thing that hold meaning
workers rights, students’ rights to education
so this will not be a ‘people are human’ poem
we are beyond respectability now
however, you know universities will DIE on that hill
instead,
treat us well when we’re tired
productive, upset, frustrated
when we’re in back-to-back global crises
COVID-19, Black Lives Matter, femicide,
failing in class, time wasting, without the right visas,
the right accents; Black, white, homeless, in poverty,
women, trans, when we’re not A-Grade students, when we don’t
have the right last name; when we’re suicidal
when people are anxious, depressed, autistic
tick-box statistics within unprotected characteristics
all permeates through workers’ and student rights
When you see staff on strike now,
we’re protesting things related to jobs yes,
but also, the after-effects
as institutions always protect themselves
so sometimes I think about
when senior management vote on policies…
if there’s a difference between the nice ones ticking boxes
and the other ones that scatter white supremacy?
I wonder if it’s about diversity, inclusion, and equality [DIE],
how come they discriminate in the name of transforming lives
how come Black students are questioned (under caution) in disciplinaries
like this is the London Met maintaining law and order …
upholding canteen cultures of policing
Black and Brown bodies. Decolonisation is more
than the curriculum; Tuck and Yang
tell us decolonisation is not a metaphor,
so why is it used in meetings as lip service –

why aren’t staff hired in
in critical race studies, whiteness studies, decolonial studies
why is liberation politics and anti-racism not at the heart of this
why are mediocre white men failing upwards,
they tell me we have misunderstood
but promotion based on merit doesn’t exist
bell hooks called this
imperialist heteropatriarchal white supremacy
you know Free Palestine, Black Lives Matter, and the rest
we must protest how we want to protest
we must never be silenced; is this being me radical, am I radical
Cos I’m tired of being called a “millennial lefty snowflake”, when I’m just trying not to DIE?!
Further Reading
Ahmed, Sara (2012) On Being Included: Racism and Diversity in Institutional Life. London: Duke.
Ahmed, Sara (2021) Complaint. London: Duke.
Bhanot, Kavita (2015) Decolonise, Not Diversify. Media Diversified [online].
Double Down News (2021) This Is England: Ash Sakar’s Alternative Race Report. YouTube.
Chen, Sophia (2020) The Equity-Diversity-Inclusion Industrial Complex Gets a Makeover. Wired [online].
Puwar, Nirmal (2004) Space Invaders: Race, Gender and Bodies Out of Place. Oxford: Berg.
Read, Bridget (2021) Doing the Work at Work What are companies desperate for diversity consultants actually buying? The Cut [online].
Ventour, Tré (2021) Telling it Like it is: Decolonisation is Not Diversity. Diverse Educators [online].
If we could empathize with all life, we… [fill in the blank]
In Honour of my two teachers’ passing (seen together here). Rest In Power, bell hooks (d. 15/12/21) and Thich Nhat Hanh (d. 22/01/22).

If we could empathize with all life, we…
… wouldn’t treat all animals as either food or fodder.
… wouldn’t develop nuclear technology into bombs.
…would never show an interest in making so many guns and ways of destroying life.
…would more genuinely aim to achieve mutual understanding between individuals.
…wouldn’t have so much intergenerational trauma within families, communities, nations.
…would be more neighborly in all our affairs.
…wouldn’t treat trade like a sport, a winner-takes-all competition over natural resources.
…would harness the power of the sun for it shines on all life collectively.
…would cultivate care, and be kinder as a general rule.
… would teach kindness in school, a required class on every campus.
…would not build entire ideologies, systems of government, religions, arts, and culture around patriarchy.
… would not be reduced to binaries, not just in gender, but ‘black or white’ in our overall thinking, because that’s where it came from: A false yet powerful and enduring dichotomy.
Binary thinking produced gender binaries, not the other way around. Knowing this is key to its undoing. Please know that capitalism produced racism, and greed crafted classism. A2 + B2 = C2, still. Racism is exponentially untamed greed; and patriarchy an inferiority complex run rampant and amok. Such cultures of greed can’t be conquered by competition; greed can’t be beat! We need a new dimension.
If we could empathize with all life, we would aspire to be far more fair.
If we could empathize with all life, we would love more.
Your turn.
Fill in the blank.
#CriminologyBookClub: Dying in Brighton
As you know by now, a small group of us decided the best way to thrive in lockdown was to seek solace in reading and talking about books. Hence the creation of #CriminologyBookClub! Building on on what has quickly become standard practice, we’ve decided to continue with all eight bloggers contributing! This title was the second chosen by @manosdaskalou and is our 14th book. Read on to find out what we thought….

I have no profound objection to self-published books but have read only one other. The rationale for reading the first one was to proof-read/copy edit for the author. That can’t really be called reading, because you miss the story by studying the text so closely. However, I digress. The blurb for this book sounded fascinating, individual narratives heading toward one place: Brighton. Unfortunately, whilst the idea for the book was clever, the writing was overly descriptive and at times, turgid. There is no space for the reader to imagine the characters or the places, everything is told in minute detail. There is a clear attempt to be inclusive with the choice of characters, but they are largely one-dimensional and lack authenticity. The final character talks about his supposed lack of representation as a white man in Brighton (with a white population of 90%) and at that point, I lost what little interest remained. In feminist circles, the question “what would a mediocre white man do?” is prevalent, a possible response could be; write this book. The only positive I have to offer is the support offered by sales to Shelter.
@paulaabowles
The format and style of the book was unlike anything I had read before: and I really liked it. The characters were full of life: a life riddled with inequalities, harm and pain. Unlike other reads where I have failed to feel anything for the characters (or anything other than a serious dislike), Dying in Brighton evoked a number of emotions from myself towards the people in the book. However these emotions were left in a sort of vacuum, with myself feeling very ‘meh’ at the end of the book. I was disappointed with the final chapter. Whilst I can appreciate the ending and the manner in which it is told, I did not like it. I wanted to know more about how Akeem, Nicola, Wasim, Lori and Paul got to the end they got to. Considering the ‘end result’ and my emotions from the previous chapters, I feel I should have had a more powerful response to the end: but I did not. The short snippets were not enough for me: and I feel that the last chapter does not do their stories or their lives justice. Despite this, I would recommend!
@jesjames50
The title Dying in Brighton does not leave much to the imagination. I am glad that the purchase of this book supports a charity. Unfortunately, I found this book to be problematic. I did not understand his selection of characters or how their stories linked. The book reads as though a heterosexual white man who is not disabled is congratulating the white men characters within the book for being friends with people who are migrants or LGBT. There is even a point where a character feels ‘underrepresented’ as a white man…I skimmed the book as I am sick of hearing similar to this in reality.
@haleysread
This is a book that definitely divided the book club and I have to say the comments were by far more negative than positive. For my part, I found the narrative interesting in a strange sort of way. I didn’t find myself labouring on the description and attributes of the characters but rather took in an overall sense of ordinary people that were troubled and in trouble for some reason or another and therefore found themselves gravitating to Brighton; in fairness they could have gone anywhere. The book didn’t take long to read, and the narrative ends rather abruptly but I think that is probably the point. The book left me with a sense of sadness, and it reminded me that homeless people are real people with real lives and yet are very often invisible in our society. Would I read something from the same author again, probably not? Would I recommend the book, probably not, but it did hit a mark somewhere along the line?
@5teveh
This book was a very quick read. Each chapter presented a very stereotypical view of a member of every marginalised group you can think of – a refugee, a trans woman, a troubled teenage girl. The book ended with a chapter about a rich white man with houses all over the world, finding himself feeling like he wasn’t represented. It turns out – spoiler alert – that all the marginalised people went to Brighton, became homeless and died. At the end a woman was selling craftwork with each of the dead, marginalised homeless person’s face. Now I can see how, to a critical criminologist, all this is problematic to say the least. However, the book carried a message that homeless people are invisible. People walk past them every day without a second glance. The author also donated profits of the book to Shelter so it was for a good cause. So, although the book was heavily criticised during our discussion, for people in many walks of life I’d like to think the book would quite literally open their eyes and say hello to a person living on the streets.
@amycortvriend
This book centres around 5 different characters and their life experiences and choices that lead them to Brighton. When I first read the blurb, I assumed this book would take me on a thought-provoking journey about individuals that could be seen as outsiders within society, and how their stories are interwoven. What was thought provoking for me was how the representation of individuals can be so wrong. Throughout the book I was distracted by the problematic ways in which the characters were portrayed. I didn’t like the hyper sexualisation of Lori, I felt like this was an attempt to explore transgender issues without any understanding of transgender issues… it was tasteless and done from a male gaze. I also didn’t like the lack of context and understanding of refugees, this exploration was very tone deaf and seemed informed by how the ‘Western world’ views refugees. Usually when reading a book I have some emotion to the characters, however I felt far removed from all the characters and their stories. At the end of the book I also felt like the stories of the five individuals were rushed, there was no back story to why or how they had died in Brighton just that they were dead. I don’t know what angle the author was going for but for me the ending fell flat.
@svr2727
This book sounded very promising and I usually really enjoy short stories about very different characters and their experiences and how they converge but this book was disappointing in so many ways. Obviously being self-published meant that it wasn’t as polished as it could’ve been and I find little mistakes to spelling and punctuation really distracting from a story. I wish this was my only complaint! The characters were badly written caricatures – you got the sense that the author had never spent any time with anyone from those backgrounds and that perhaps he wasn’t the right person to be telling these stories. The most authentic chapter of the book was the final one where the narrator (a successful white man) feels that he isn’t represented! Easily the worst book I’ve ever read.
@saffrongarside
This is an anthology of different stories of people in very adverse circumstances all of whom are heading to Brighton. In most cases it is not clear why they are heading that way and what they hope from their move there. The short stories are independent from each other and there is no obvious connection between them. Each story explores a different character faced with different issues from abuse, sexuality and substance use. It sends out a signal of some of the social vulnerabilities people are exposed; this however is done as a matter of fact not exploring the social dimensions of the situation. The end brings the stories together but for me this was unsatisfactory. This book has a great idea, an interesting layout but its execution does not meet the goal. The stories are interesting but some of them feel a bit rushed; more character development would have allowed the reader to get closer to the situation and the social issues the author wants to alert people to. As I read it, I thought that some of the stories read more like vignettes that we use in exercises or training for making people aware of certain problems. In terms of literary merit, these are not quite there.
@manosdaskalou

Kisses from Granny Don’t Count! #BlackenAsiaWithLove #ShortStory
In America, and most certainly in the land of Dixie and cotillions, at the end of junior high school year we have a tradition of getting our senior class rings. By “getting,” I mean individually buying a ring from the same one or two companies in our city who cash in on this ritual annually. We knew that many of us had to foot the bill with our own after-school jobs, while others’ parents could virtually write a blank check! (Hopefully, at least, or perhaps most assuredly, somebody in the school system gets a kickback from all this cash flow.)
While class rings appeared personalized, the rings – and the ritual – were effectively mass manufactured, complete with standardized shapes and design features: school’s name and mascot – in our case a bear – class year (1993!), and maybe our initials inscribed inside. Oh, and a heteronormative adolescent sexualized ritual to which I shall return shortly.
Rings are generally presented at a school ceremony. Until graduation, class rings are worn facing the wearer as motivation towards the ultimate achievement, after which it is worn outward as a badge of pride and honor. A graduating class could all agree to the same design – usually the school colors – which I believe the majority of my class did. While I prefer the look of silver against my dark skin, our school colors were royal blue and gold, so classes at our school often got blue sapphire set in the lowest Karat gold available that didn’t look cheap. For such a notoriously liberal school (i.e., gender and racially/geographically* integrated by design), this was one of the few explicit acts of conformity.
‘You Wear it Well’ – DeBarge, 1985
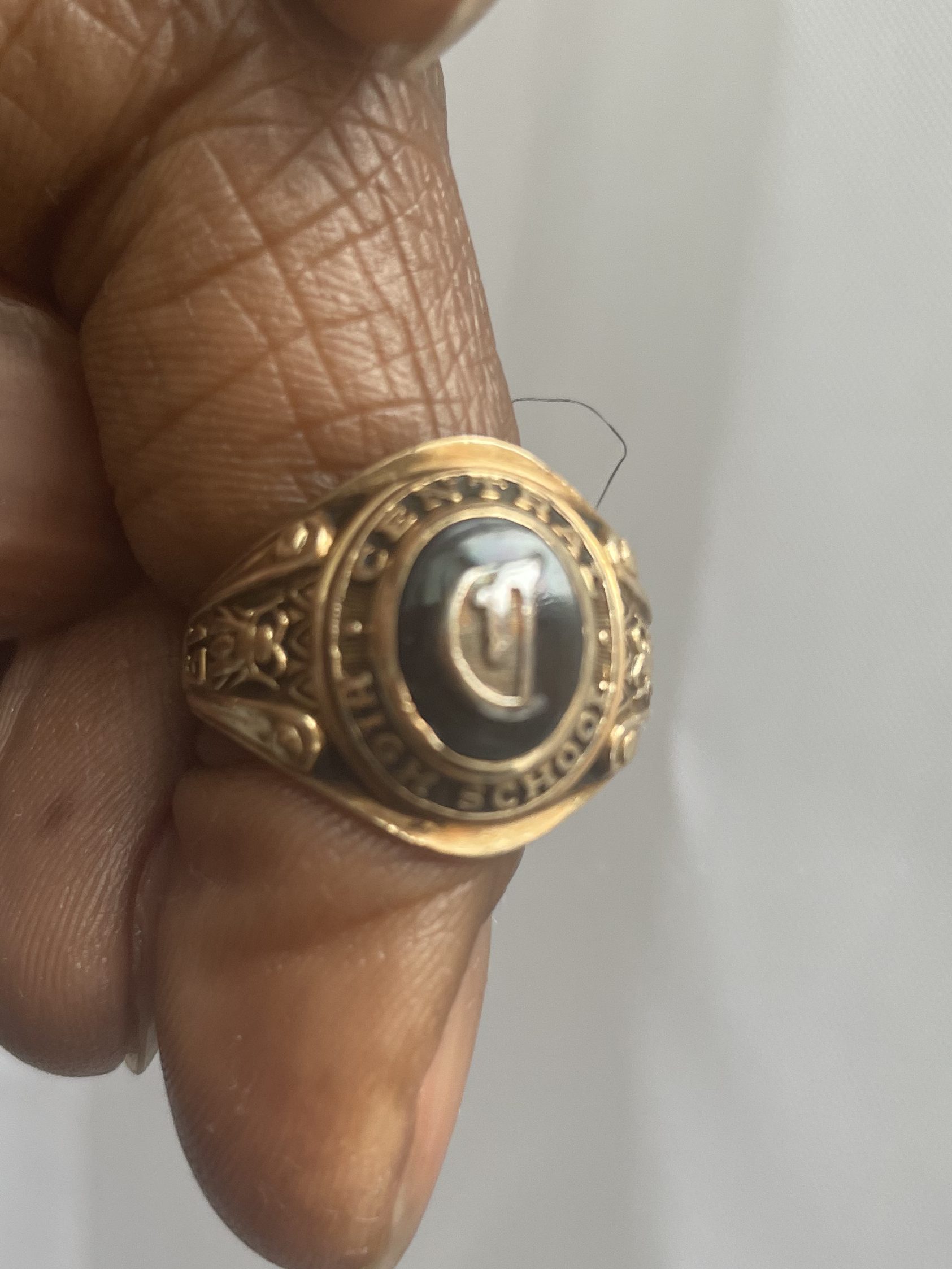

The next part of the tradition is having 100 different people turn the ring, as sort of an acknowledgement of becoming a senior. The first 99 turn it in one direction, while the final person reverses the order. This clockwise/counter-clockwise turn seals the deal. Yet get this, you’re supposed to kiss the hundredth person who turns the ring. You say the word “kiss” in front of most any group of adolescents and they’ll giggle. We knew what kind of kiss was meant. FRENCH like fries! Somehow becoming a senior in high school had been coopted by this hetero-ritual, a hetero-rite of passage (het-or-no-rites!).
I am troubled that this academic milestone is linked to gender. Worse, the ritual is predictably a performance act that fixes gender to normative sexual roles; yes, heteropatriarchy. Worse still, this binary gender performance is discrete, couched in achieving a basic education.
The ring dealer comes to school and makes a sales pitch to the class, and sets up a booth in the lobby after school. In his pitch, he promises a ‘free’ glossy little form to collect all the signatures. It was a bait and switch. These dealers sold us the rings but gave us the forms, the evidence we needed to prove we’d passed another stage towards adulthood. And what were we supposed to do with the blank glossy forms? Come back to school and boast?
The first 50 or so signatures were just us. Our own schoolmates turning each other’s rings, filling in each other’s forms on the very day the rings arrived. Family filled in a lot, too. I distinctly remember a teacher or two requesting to be excluded from the tradition, or take part in the ring ritual of becoming a senior, else we whittle their fingers away.
We all know everybody only wanted to see who signed the final line – a prompt to incite heteronormalizing speech-acts. Well, a few folks weren’t single and already had that 100th spot reserved and filled by sundown. Needless to say, kisses from granny don’t count! I’m pretty sure this wasn’t written on the dealer’s well-crafted sheet. Our market dominated, heteronormative introduction to adulthood for all to see.
I’d attended the same school since second grade so I’d seen people celebrate this class ring ritual for years, and even attended several graduations. I’d watched the “Senior run” year after year – a day at the end of school, when the graduating class runs through all the halls, cheering, banging on lockers as all the kids in all the classes rush out to line the hallways and egg them on. I loved school, adored our school, adored my classmates, and even looked forward to our turn, though parting so bittersweet.
At 16, I was only starting to be able to fully disidentify with the barrage of heterosexualized norms that engulfed me. I had to disentangle heterosexuality from virtually every facet of life – even finishing high school, a normal step we’re all expected to take. It’s as if to gain access to what bell hooks calls ‘the good life’ one had to signify alignment with compulsory heterosexuality.
I knew that I could not even turn my ring 100 times without kissing a girl. No way I’d risk putting a guy’s name at the end of that glossy list – someone I’d actually dreamt of French-kissing. Not like I knew any guy who’d be game. Damn. This was a lot of pressure. This junior prom was forcing me to make all kinds of adult decisions.
“The more I get of you, the stranger it feels…”
I was 16, and wasn’t out yet. Unlike at twelve when these feelings first bubbled over, by 16 I was on the cusp of self-acceptance, and preparing to face this possibility that I was gay. Perhaps it was pure timing. By the 11thgrade I knew for sure I’d be leaving home months after graduation, which was suddenly within reach. I could chart my own homo path. But still, at that age, I had doubts. I tried seriously dating a young woman as my last-ditch effort to see if I was straight or (at least) bisexual.
Kaye wasn’t a classmate, which wouldn’t have worked anyway because in retrospect all my classmates already knew, and had decided to accept me without question. Kaye attended an all-girls’ school, so we’d met through an extracurricular, Black youth empowerment program. Kaye was clearly college bound. She had her own dreams and ambitions, and pursued them – an ideal mate for me. She was the most attractive woman I knew, both inside and out, both to me and others. Yes, THAT sister who is not invulnerable, but has it all together. If she didn’t do, then dammit I was gay!
Fortunately, my girl was smart. And by smart, I mean that she was intelligent, real smart as in NOT clueless at all. We agreed to a kiss on the cheek, and she’d sign the last line on my glossy form. And by ‘agreed to’, I mean that this is what Kaye put on the table as her firm and final offer. She also had the good sense to let me turn her ring, too, but she reserved the 100th signature for someone special. I respected that. This clarified our plutonic status – no Facebook updates needed: I’m gay.
“Gotta find out what I meant to you…You were sweet as cheery pie/ Wild as Friday night”
What about women?

This month marks Women’s History Month. It’s a time where I reflect on how privileged I am to be surrounded by a group of women who have added so much to my life just by being in it.
I am also reminded of writers and poets (both past and present) like Woolf, De Beauvoir, Lorde, Walker, Kaur, Attwood and Evaristo whose words have not only added so much to my outlook on life but they also continue to remind me that as a woman I need to continue to listen, provide support and uplift other women. It is incredibly sad but necessary that we need to be reminded of the need to support one another.
Women’s History Month has coincided with the murder of Sarah Everard, another of the many women who have been murdered by men whilst walking home alone. The policing and arresting of women at Sarah’s vigil, the justifications for such arrests and the events themselves are now being reported as false. Followed by the government’s predictable draconian response to silence and restrict protesting rights is maddening. And more importantly, the solidarity illustrated with women gathering to pay their respects to Sarah has now been spoilt due to these damaging enforcement responses.
I find it so sad that commentary by some women surrounding the murder of Sarah had taken the stance of defending men. There are so many very good men in this world, and it is true that not all men are bad, but the reality is that men tend to be the perpetrators when other men, women and children are murdered.
We live in a society which reinforces gender inequality, oppression and stereotypes about women to the point that women internalise misogyny. As a result, some women are quick to defend men to the point that, in some cases, men who are the perpetrators are presented as the victims. And the women who are actual victims are blamed for their own victimisation.
This attitude towards women comes at the detriment of not allowing the space for people to begin to consider that femicide and gendered violence are the damaging consequences of living in an unequal society. The pain caused to the victims also becomes either diluted or made invisible. This is especially the case with Asian or Black women’s victim experiences, as these are rarely found within the news, and if shown, are rarely believed.
There are many obstacles faced by women who attempt to flee routine gendered violence. Attempts to seek support can result in many women losing their homes, jobs and contact with their friends and families. As well as this, women who intend to report being victims of gender-based violence may battle to overcome the stigma that is attached to being a victim. For women with visas that state that there is ‘no recourse to public funds’ escaping violence becomes even more difficult, post Brexit, this now also applies to women from the EU.
Whilst online debates occur surrounding Sarah Everard’s case, the reality is that many women are scared to walk alone. Many are also scared to live within their own homes due to the fear of violence. If we are quick to defend men in light of such tragic events how will we ever be able to support these women? How will they ever feel empowered to report being victims of crime? Yes, not all men are bad, but when a case like Sarah’s is publicised perhaps our first response should be empathising with other women.
The Case of Mr Frederick Park and Mr Ernest Boulton
As a twenty-first century cis woman, I cannot directly identify with the people detailed below. However, I feel it important to mark LGBT+ History Month, recognising that so much history has been lost. This is detrimental to society’s understanding and hides the contribution that so many individuals have made to British and indeed, world history. What follows was the basis of a lecture I first delivered in the module CRI1006 True Crimes and Other Fictions but its roots are little longer
Some years ago I bought a very dear friend tickets for us to go and see a play in London (after almost a year of lockdowns, it seems very strange to write about the theatre).. I’d read a review of the play in The Guardian and both the production and the setting sounded very interesting. As a fan of Oscar Wilde’s writing, particularly The Ballad of Reading Gaol and De Profundis (both particularly suited to criminological tastes) and a long held fascination with Polari, the play sounded appealing. Nothing particularly unusual on the surface, but the experience, the play and the actors we watched that evening, were extraordinary. The play is entitled Fanny and Stella: The SHOCKING True Story and the theatre, Above the Stag in Vauxhall, London. Self-described as The UK’s LGBTQIA+ theatre, Above the Stag is often described as an intimate setting. Little did we know how intimate the setting would be. It’s a beautiful, tiny space, where the actors are close enough to just reach out and touch. All of the action (and the singing) happen right before your eyes. Believe me, with songs like Sodomy on the Strand and Where Has My Fanny Gone there is plenty to enjoy. If you ever get the opportunity to go to this theatre, for this play, or any other, grab the opportunity.
So who were Fanny and Stella? Christened Frederick Park (1848-1881) and Ernest Boulton (1848-1901), their early lives are largely undocumented beyond the very basics. Park’s father was a judge, Boulton, the son of a stockbroker. As perhaps was usual for the time, both sons followed their respective fathers into similar trades, Park training as an articled clerk, Boulton, working as a trainee bank clerk. In addition, both were employed to act within music halls and theatres. So far nothing extraordinary….
But on the 29 April 1870 as Fanny and Stella left the Strand Theatre they were accosted by undercover police officers;
‘“I’m a police officer from Bow Street […] and I have every reason to believe that you are men in female attire and you will have to come to Bow Street with me now”’
(no reference, cited in McKenna, 2013: 7)
Upon arrest, both Fanny and Stella told the police officers that they were men and at the police station they provided their full names and addresses. They were then stripped naked, making it obvious to the onlooking officers that both Fanny and Stella were (physically typical) males. By now, the police had all the evidence they needed to support the claims made at the point of arrest. However, they were not satisfied and proceeded to submit the men to a physically violent examination designed to identify if the men had engaged in anal sex. This was in order to charge both Fanny and Stella with the offence of buggery (also known as sodomy). The charges when they came, were as follows:
‘they did with each and one another feloniously commit the abominable crime of buggery’
‘they did unlawfully conspire together , and with divers other persons, feloniously, to commit the said crimes’
‘they did unlawfully conspire together , and with divers other persons, to induce and incite other persons, feloniously, to commit the said crimes’
‘they being men, did unlawfully conspire together, and with divers others, to disguise themselves as women and to frequent places of public resort, so disguised, and to thereby openly and scandalously outrage public decency and corrupt public morals’
Trial transcript cited in McKenna (2013: 35)
It is worth noting that until 1861 the penalty for being found guilty of buggery was death. After 1861 the penalty changed to penal servitude with hard labour for life.
You’ll be delighted to know, I am not going to give any spoilers, you need to read the book or even better, see the play. But I think it is important to consider the many complex facets of telling stories from the past, including public/private lives, the ethics of writing about the dead, the importance of doing justice to the narrative, whilst also shining a light on to hidden communities, social histories and “ordinary” people. Fanny and Stella’s lives were firmly set in the 19th century, a time when photography was a very expensive and stylised art, when social media was not even a twinkle in the eye. Thus their lives, like so many others throughout history, were primarily expected to be private, notwithstanding their theatrical performances. Furthermore, sexual activity, even today, is generally a private matter and there (thankfully) seems to be no evidence of a Victorian equivalent of the “dick pic”! Sexual activity, sexual thoughts, sexuality and so on are generally private and even when shared, kept between a select group of people.

This means that authors working on historical sexual cases, such as that of Fanny and Stella, are left with very partial evidence. Furthermore, the evidence which exists is institutionally acquired, that is we only know their story through the ignominy of their criminal justice records. We know nothing of their private thoughts, we have no idea of their sexual preferences or fantasies. Certainly, the term ‘homosexual’ did not emerge until the late 1860s in Germany, so it is unlikely they would have used that language to describe themselves. Likewise, the terms transvestite, transsexual and transgender did not appear until 1910s, 1940s and 1960s respectively so Fanny and Stella could not use any of these as descriptors. Despite the blue plaque above, we have no evidence to suggest that they ever described themselves as ‘cross-dressers’ In short, we have no idea how either Fanny or Stella perceived of themselves or how they constructed their individual life stories. Instead, authors such as Neil McKenna, close the gaps in order to create a seamless narrative.
McKenna calls upon an excellent range of different archival material for his book (upon which the play is based). These include:
- National Archives in Kew
- British Library/British Newspaper Library, London
- Metropolitan Police Service Archive, London
- Wellcome Institute, London
- Parliamentary Archives, London
- Libraries of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons, London and Edinburgh
- National Archives of Scotland
Nevertheless, these archives do not contain the level of personal detail, required to tell a fascinating story. Instead the author draws upon his own knowledge and understanding to bring these characters to life. Of course, no author writes in a vacuum and we all have a standpoint which impacts on the way in which we understand the world. So whilst, we know the institutional version of some part of Fanny and Stella’s life, we can never know their inner most thoughts or how they thought of themselves and each other. Any decision to include content which is not supported by evidence is fraught with difficulty and runs the risk of exaggeration or misinterpretation. A constant reminder that the two at the centre of the case are dead and justice needs to be done to a narrative where there is no right of response.
It is clear that both the book and the play contain elements that we cannot be certain are reflective of Fanny and Stella’s lives or the world they moved in. The alternative is to allow their story to be left unknown or only told through police and court records. Both would be a huge shame. As long as we remember that their story is one of fragile human beings, with many strengths and frailties, narratives such as this allow us a brief glimpse into a hidden community and two, not so ordinary people. But we also need to bear in mind that in this case, as with Oscar Wilde, the focus is on the flamboyantly illicit and tells us little about the lived experience of some many others whose voices and experiences are lost in time..
References
McKenna, Neil, (2013), Fanny and Stella: The Young Men Who Shocked Victorian England, (London: Faber and Faber Ltd.) Norton, Rictor, (2005), ‘Recovering Gay History from the Old Bailey,’ The London Journal, 30, 1: 39-54 Old Bailey Online, (2003-2018), ‘The Proceedings of the Old Bailey,’ The Old Baily Online, [online]. Available from: https://www.oldbaileyonline.org/ [Last accessed 25 February 2021]