Home » Nigeria (Page 2)
Category Archives: Nigeria
Visa by Impression, Atavism or Exploitation?
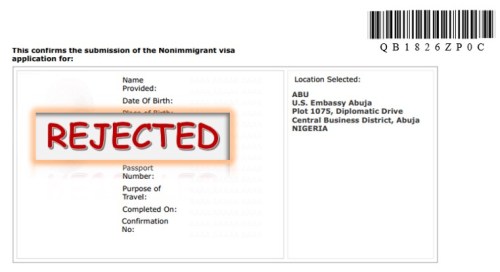
My paper, ‘beyond institutional autonomy: a quadrumvirate interaction theory of civil-military relations’ was accepted for presentation at the 2019 Biennial International Conference of the Inter-University Seminar on Armed Forces and Society scheduled for November 8-10, 2019 at the Hyatt Regency, Reston, Virginia. However, I am unable to attend the conference because I was denied visa at the US Embassy in Abuja, Nigeria. In this entry, I wish to highlight and add my voice to the concerns academics and non-academics, especially those from the ‘Global South’ face in securing visas to enable them attend conferences in the supposed ‘developed world.’ Hence, this entry is a personal reflection on the US visa regime in Nigeria, and its nexus with criminology.
Individual visas are often issued based on the merit of an application and the adequacy of the supporting documents submitted by applicants who are also required to pay certain fees and charges for the application. The issuing authorities would normally consider the criminal background record of an applicant, their previous travel history and the adequacy of funds to cover for the cost of the trip. In some cases, as typical with the US visa regime in Nigeria, applicants are required to present themselves before a consular officer for a visa interview and the decision to issue a visa is at the discretion of the consular officer.
Given this, one would expect that the consular officer would in the least, view/review the supporting documents of an applicant, in addition to asking some pertinent questions. The rationale being that the US visa web-application platform does not provide a link/option for submitting the supporting system prior to the interview. However, this was not the case when I was denied a visa. In fact, the interview barely lasted two minutes, and the following was the ‘interview’ conversation I had with the male consular officer:
Why do you want to go to Reston Virginia? To attend a conference.
What do you intend to do in the conference? I will be presenting a paper, a theory from my PhD research.
Who would pay for the conference and travel fee? The conference organisers and (he interjects with the next question, but I told him I still have another source of income, but he replied saying I had told him enough and that I should answer the next question).
What is your highest academic qualification? A PhD from the University of Stellenbosch, South Africa, I just concluded last December.
What do you do for a living? I just concluded a Postdoctoral Fellowship with the University of Stellenbosch and I have just accepted an appointment with the University of Jos as a Lecturer.
Do you have a family? Yes, a wife and a child, and we are expecting another.
For how long have you been married? 3 years
How old is your child? 1 year and 8 months
What does your wife do for a living? She is a housewife, she looks after the family
Are you travelling alone? Yeah (At this point, he faced his computer keyboard, typed some few words, then turned to me and told me, unfortunately we cannot issue you the visa while handing over a pre-printed form containing the reasons for visa denials).
From this ‘interview’ conversation, two things stood out for me. One is the fact that the consular officer made his decisions without viewing or considering any of my supporting documents and the second was the question, what did I do, say, or answer wrongly?
In terms of the latter, I found nothing wrong with my responses, but I found a huge systemic fault with regards to the former. The internet is rife with complaints from individuals, organisations and recently countries accusing the US of implementing a harsh visa regime which deliberately frustrates and traumatises visa applicants. My web application process in Nigeria is nothing short of this, in fact, I thought it was easier to make heaven than to obtain the US visa from Nigeria.
Having carefully thought about the visa regime in the light of my ‘interview,’ I concluded that the US visa regime is anachronistically atavistic, an exploitative business strategy, or both. My opinion is simply that I was denied visa not because of my responses to the questions but because the consular officer found a questionable impression through observing my face as he had not viewed or considered my supporting documents. For this, I appreciate Cesare Lombroso and one needs not be a Criminologist before knowing that facial impression and appearance are never better yardstick than considering the merits of the supporting documents.
A fair and equitable visa system will consider the merit of an application, the travel history of an applicant (which I have a reasonable one), whether the supporting documents are convincing, the criminal record background, purpose of travel, sufficiency of funds, and the existence of a strong tie with one’s origin. However, this was not the case, and this led me to the business exploitation opinion.
Customarily, when one pays for a service, the norm is to provide quality and effective service worth the value of the money paid or promised, anything short of this is clear exploitation – unfortunately, this is how the US visa regime operates in Nigeria. On the day of my interview, there were at least seventy (70) persons queuing up for theirs early in the morning, but it is not my intention to analyse how much income the US derives from this.
When the Police takes to Tweeter HashTags to Seek ‘Justice’

https://twitter.com/PoliceNG/status/1159548411244371969?s=20)
I am tempted to end this blog in one sentence with the famous Disney lyrics, “disaster is in the air” but this may do no justice to the entry as it lacks a contextual background. So last week, Nigerian Twitter was agog with numerous tweets, retweets, comments, and reactions following the news that soldiers of the Nigerian Army had allegedly killed one civilian and three police personnel in the line of duty. A brief summary of the case is that the killed police personnel had arrested an alleged notorious and ‘wanted’ kidnaper and were transporting him to a command headquarters when they ran into a military checkpoint. Soldiers at the checkpoint allegedly opened fire at close range, killed the police who were said to have attempted identifying themselves, and freed the handcuffed ‘kidnapper.’
In a swift reaction, a Joint Investigation Panel comprised of the Police and the Army was constituted to investigate the incident. Notwithstanding this, the Police took to their Twitter handle @PoliceNG calling out for justice and expressing dissatisfaction and concerns in what metamorphosed into series of threads and hashtags – #WhereIsEspiritDCorp and #ProvideAnswersNigerianArmy. Ordinarily, this should have aroused and generated wide condemnation and national mourning, but, the comments, tweets and reactions on twitter suggests otherwise. While Nigerians expressed sympathy to the victims of the unfortunate incident, they also took to the social media platform to unravel their anger with many unleashing unsympathetic words and re-stating their distrust in the Police. In fact, it was the strong opinion of many that the incident was just a taste of their medicine as they often infringe on the rights of civilians daily, and are notoriously stubborn and predatory.
Certainly, this issue has some criminological relevance and one is that it brings to light the widely debated conversation on the appropriateness and the potency of deploying the military in society for law enforcement duties which they are generally not trained to do. Hence, this evokes numerous challenges including the tendency for it to make civilians loathe to interact with the military. I have previously argued that the internal use of the Nigerian military in law enforcement duties has exacerbated rather than ameliorated insecurity in several parts of the country. As with this instance, this is due to the penchant of the military to use force, the unprofessional conduct of personnel, and a weak system of civil control of the military to hold personnel accountable for their actions.
Similarly, this issue has also raised concerns on the coordination of the security forces and the need for an active operational command which shares security information with all the agencies involved in internal security. However, the reality is that interagency feud among the numerous Nigerian security agencies remains a worrying concern that not only undermine, but hinders the likelihood for an effective coordination of security activities.
Another angle to the conversation is that the social media provides a potent weapon for citizens to compel response and actions from state authorities – including demanding for justice. However, when the police is crippled and seemingly unable to ensure the prosecution of rights violations and extrajudicial killings, and they resort to twitter threads and hashtags to call out for justice, overhauling the security architecture is extremely necessary.
A Failing Cultural or Criminal Justice System?

Sallek is a graduate from the MSc Criminology. He is currently undertaking doctoral studies at Stellenbosch University, South Africa.
In this piece, I reflect on the criminal justice system in Nigeria showing how a cultural practice evoked a social problematique, one that has exposed the state of the criminal justice system of the country. While I dissociate myself from the sect, I assume the place of the first person in contextualizing this discourse.
In line with the norm, our mothers were married to them. Having paid the bride wealth, even though they have no means, no investment and had little for their upkeep, they married as many as they could satisfy. In our number, they birth as many as their strength could allow, but, little did we know the intention is to give us out to tutelage from religious teachers once we could speak. So, we grew with little or no parental care, had little or no contact, and the street was to become our home where we learnt to be tough and strong. There we learnt we are the Almajiri (homeless children), learning and following the way and teaching of a teacher while we survived on alms and the goodwill of the rich and the sympathetic public.
As we grew older, some learnt trades, others grew stronger in the streets that became our home, a place which toughened and strengthened us into becoming readily available handymen, although our speciality was undefined. We became a political tool servicing the needs of desperate politicians, but, when our greed and their greed became insatiable, they lost their grip on us. We became swayed by extremist teachings, the ideologies were appealing and to us, a worthy course, so, we joined the sect and began a movement that would later become globally infamous. We grew in strength and might, then they coerced us into violence when in cold blood, their police murdered our leader with impunity. No one was held responsible; the court did nothing, and no form of judicial remedy was provided. So, we promised full scale war and to achieve this, we withdrew, strategized, and trained to be surgical and deadly.
The havoc we created was unimaginable, so they labelled us terrorists and we lived the name, overwhelmed their police, seized control of their territories, and continued to execute full war of terror. We caused a great humanitarian crisis, displaced many, and forced a refugee crisis, but, their predicament is better than our childhood experience. So, when they sheltered these displaced people in camps promising them protection, we defiled this fortress and have continued to kill many before their eyes. The war they waged on us using their potent monster, the military continuous to be futile. They lied to their populace that they have overpowered us, but, not only did we dare them, we also gave the military a great blow that no one could have imagined we could. The politicians promised change, but we proved that it was a mere propaganda when they had to negotiate the release of their daughters for a ransom which included releasing our friends in their custody. After this, we abducted even more girls at Dapchi. Now I wonder, these monsters we have become, is it our making, the fault of our parents, a failure of the criminal justice system, or a product of society?
A Troubling Ambiguous Order?

Sallek is a graduate from the MSc Criminology. He is currently undertaking doctoral studies at Stellenbosch University, South Africa.
Having spent the early years of my life in Nigeria, one of the first culture shock I experienced in the UK was seeing that its regular police do not wield arms. Unsurprising, in my lecture on the nature and causes of war in Africa, a young British student studying in Stellenbosch University also shared a similar but reverse sentiment – the South African police and private security forces wield arms openly. To her, this was troubling, but, even more distressing is the everyday use of most African militaries in society for internal security enforcement duties. This is either in direct conflict to the conventional understanding on the institutions involved in the criminal justice system, or African States have developed a unique and unconventional system. Thus, this raises a lot of questions needing answers and this entry is an attempt to stimulate further, thoughts and debate on this issue.
Conventionally, two spheres make up state security, the internal sphere of policing and law enforcement and the external sphere of defence and war-fighting. However, since the end of the Cold War, distinguishing between the two has become particularly difficult because of the internal involvement of the military in society. Several explanations explain why the military has become an active player in the internal sphere doing security enforcement duties in support of the police or as an independent player. Key among this is the general weakness and lack of legitimacy of the police, thus, the use of the military which has the capacity to suppress violence and ‘insurgence.’ Also, a lack of public trust, confidence, and legitimacy of the government is another key reason States resort to authoritarian practices, particularly using the military to clamp down civil society. The recent protests in Togo which turned ‘bloody’ following violent State repression presents a case in point. The recent carnage in Plateau State, Nigeria where herdsmen of similar ethnic origin as the President ‘allegedly’ killed over fifty civilians in cold blood also presents another instance. The President neither condemned the attacks nor declared a national mourning despite public outcry over the complicity of the military in the massacre.
Certainly, using the military for internal security enforcement otherwise known as military aid to civil authority in society comes with attendant challenges. One reason for this is the discrepancy of this role with its training particularly because military training and indoctrination focuses extensively on lethality and the application of force. This often results to several incidences of human rights abuses, the restriction of civil liberty and in extreme cases, summary extrajudicial killings. This situation worsens in societies affected by sectarian violence where the military assumes the leading role of law enforcement to force the return to peace as is the case in Plateau State, Nigeria. The problem with this is, in many of these States, the criminal justice system is also weak and thereby unable to guarantee judicial remedy to victims of State repression.
Consequently, citizens faced by the security dilemma of State repression and violence from armed groups may be compelled to join or seek protection from opposition groups thereby creating further security quandary. In turn, this affects the interaction of the citizenry with the military thereby straining civil-military relations in the State with the end result been the spinning of violence cycle. It also places huge economic burden with lasting impact on State resources, individuals, and corporate bodies and where the military is predatory, insecurity could worsen. The sectarian violence in Plateau State and the Niger Delta region in Nigeria where such military heavy-handedness remains the source of (in)security shows the weakness of this approach, and unless reconsidered, peace could remain elusive. Thus, now more than ever, this ambiguous (dis)order requires reconsideration for a civil approach to security in Africa.

Life in the UK: Nigerians migrating from the other side
Damilola is a 2017 graduate having read BA Criminology with Sociology. Her blog entry reflects on the way in which personal experience can inform and be informed by research. Her dissertation is entitled Life in the UK: The individual narratives of Nigerians living in the United Kingdom and the different problems they faced during their integration into the UK
During my research on the topic of migration and integration, it was important to me, to make the individuals the focal point. This is because the majority of research in this area, depicts a holistic perspective. Therefore, understanding each individual story was vital during my research. It enabled an insight into the different coping mechanisms the Nigerian migrants used, to compensate for the sense of othering they often felt.
One of the most eye opening stories was that of a woman who had bleached her skin to become lighter. She felt this would encourage others to accept her and also, make her more appealing to prospective employers in the UK. Nigerian women bleaching their skin is not a new phenomena. According to the World Health Organisation, Nigerian women are the largest consumers of bleaching creams. This was a very important aspect because it highlighted that, Nigerian women both home and abroad often feel inferior because of the colour of their skin. These bleaching creams can cause serious damages to the skin, however these women and others alike are still willing to compromise their health because, they believe it will increase their likelihood of success.
Here is a blog post that goes into further details about the side effects of bleaching:
When migration is spoken about, it is almost always portrayed as an ‘issue’, something negative that needs to be dealt with. This is particularly evident with the campaigns during BREXIT of 2016. A lot of times, this encourages a negative stigma of migrants, both internationally and those from neighbouring European countries. This is not only damaging to the potential relationship between countries, it also creates a divide, a sense of ‘us against them’. Amidst of it all, are the most sensitive victims, the children of these migrants. A Participant during my research mentioned her children learning slangs such as “init” to fit in with the other kids at school. She also made mention of shortening the names of her children to accommodate the English tongue of their peers and teachers. For her the mental wellbeing of her children was more important, than a proper vocabulary or the right pronunciation of their names.
Moreover this also leads to another misconception about migrants. The common viewpoint proposed by earlier research is that the lack of understanding of the English language is the barrier that most migrants face. However the results from my research propose a different argument. I found that, it was the foreign African accent that most participants felt others had an issue with. For most participants their accent was the most difficult thing to loose. This often proved to be a problem. This is because it made them stand out and, was a universal stamp that highlighted “I AM NOT FROM HERE” in a country that encourages everyone to blend in.
Once again, this illustrates the real issue with migration, for many migrants the sense of belonging is never present. As a participant pointed out “even after getting my British passport, I am still not like them. I will always be Nigerian, I know that now”.
In relation to the interviewing of the participants, this proved to be the most difficult part of my research. This is because the women often drifted away from questions being asked and told tales of people who had similar experiences to them. Nonetheless it was also the most rewarding experience because these different tales were embedded with deeper meanings. The meanings that would later encourage a better understanding, of the way the women coped with integrating into a new country. Moreover, as a migrant myself it was interesting to see the changes that had occurred over time and, also a lot of what has remained the same. This is because despite coming to the country at a young age, I was able to relate to some of the coping mechanisms, such as the shortening of my name to accommodate the English tongue.
As a recent criminology graduate, my dissertation on migration and integration was one of the most eyeopening experiences of my life. I have learnt so much through this process, not only about the topic but also about myself. I am grateful for this experience because it has prepared me for what to expect for my postgraduate degree. A friendly advice from me, to anyone writing their dissertation would be to START EARLY!! It may seem impossible to start with but it will all be worth it in the end.
GOOD LUCK !!







