Home » Justice (Page 5)
Category Archives: Justice
Thinking “outside the box”

Having recently done a session on criminal records with @paulaabowles to a group of voluntary, 3rd sector and other practitioners I started thinking of the wider implications of taking knowledge out of the traditional classroom and introducing it to an audience, that is not necessarily academic. When we prepare for class the usual concern is the levelness of the material used and the way we pitch the information. In anything we do as part of consultancy or outside of the standard educational framework we have a different challenge. That of presenting information that corresponds to expertise in a language and tone that is neither exclusive nor condescending to the participants.
In the designing stages we considered the information we had to include, and the session started by introducing criminology. Audience participation was encouraged, and group discussion became a tool to promote the flow of information. Once that process started and people became more able to exchange information then we started moving from information to knowledge exchange. This is a more profound interaction that allows the audience to engage with information that they may not be familiar with and it is designed to achieve one of the prime quests of any social science, to challenge established views.
The process itself indicates the level of skill involved in academic reasoning and the complexity associated with presenting people with new knowledge in an understandable form. It is that apparent simplicity that allows participants to scaffold their understanding, taking different elements from the same content. It is easy to say to any audience for example that “every person has an opinion on crime” however to be able to accept this statement indicates a level of proficiency on receiving views of the other and then accommodating it to your own understanding. This is the basis of the philosophy of knowledge, and it happens to all engaged in academia whatever level, albeit consciously or unconsciously.
As per usual the session overran, testament that people do have opinions on crime and how society should respond to them. The intriguing part of this session was the ability of participants to negotiate different roles and identities, whilst offering an explanation or interpretation of a situation. When this was pointed out they were surprised by the level of knowledge they possessed and its complexity. The role of the academic is not simply to advance knowledge, which is clearly expected, but also to take subjects and contextualise them. In recent weeks, colleagues from our University, were able to discuss issues relating to health, psychology, work, human rights and consumer rights to national and local media, informing the public on the issues concerned.
This is what got me thinking about our role in society more generally. We are not merely providing education for adults who wish to acquire knowledge and become part of the professional classes, but we are also engaging in a continuous dialogue with our local community, sharing knowledge beyond the classroom and expanding education beyond the campus. These are reasons which make a University, as an institution, an invaluable link to society that governments need to nurture and support. The success of the University is not in the students within but also on the reach it has to the people around.
At the end of the session we talked about a number of campaigns to help ex-offenders to get forward with work and education by “banning the box”. This was a fitting end to a session where we all thought “outside the box”.
Documenting inequality: how much evidence is needed to change things?
In our society, there is a focus on documenting inequality and injustice. In the discipline of criminology (as with other social sciences) we question and read and take notes and count and read and take more notes. We then come to an evidence based conclusion; yes, there is definite evidence of disproportionality and inequality within our society. Excellent, we have identified and quantified a social problem. We can talk and write, inside and outside of that social problem, exploring it from all possible angles. We can approach social problems from different viewpoints, different perspectives using a diverse range of theoretical standpoints and research methodologies. But what happens next? I would argue that in many cases, absolutely nothing! Or at least, nothing that changes these ingrained social problems and inequalities.
Even the most cursory examination reveals discrimination, inequality, injustice (often on the grounds of gender, race, disability, sexuality, belief, age, health…the list goes on), often articulated, the subject of heated debate and argument within all strata of society, but remaining resolutely insoluble. It is as if discrimination, inequality and injustice were part and parcel of living in the twenty-first century in a supposedly wealthy nation. If you don’t agree with my claims, look at some specific examples; poverty, gender inequality in the workplace, disproportionality in police stop and search and the rise of hate crime.
- Three years before the end of World War 2, Beveridge claimed that through a minor redistribution of wealth (through welfare schemes including child support) poverty ‘could have been abolished in Britain‘ prior to the war (Beveridge, 1942: 8, n. 14)
- Yet here we are in 2019 talking about children growing up in poverty with claims indicating ‘4.1 million children living in poverty in the UK’. In addition, 1.6 million parcels have been distributed by food banks to individuals and families facing hunger
- There is legal impetus for companies and organisations to publish data relating to their employees. From these reports, it appears that 8 out of 10 of these organisations pay women less than men. In addition, claims that 37% of female managers find their workplace to be sexist are noted
- Disproportionality in stop and search has long been identified and quantified, particularly in relation to young black males. As David Lammy’s (2017) Review made clear this is a problem that is not going away, instead there is plenty of evidence to indicate that this inequality is expanding rather than contracting
- Post-referendum, concerns were raised in many areas about an increase in hate crime. Most attention has focused on issues of race and religion but there are other targets of violence and intolerance
These are just some examples of inequality and injustice. Despite the ever-increasing data, where is the evidence to show that society is learning, is responding to these issues with more than just platitudes? Even when, as a society, we are faced with the horror of Grenfell Tower, exposing all manner of social inequalities and injustices no longer hidden but in plain sight, there is no meaningful response. Instead, there are arguments about who is to blame, who should pay, with the lives of those individuals and families (both living and dead) tossed around as if they were insignificant, in all of these discussions.

As the writer Pearl S. Buck made explicit
‘our society must make it right and possible for old people not to fear the young or be deserted by them, for the test of a civilization is in the way that it cares for its helpless members’ (1954: 337).
If society seriously wants to make a difference the evidence is all around us…stop counting and start doing. Start knocking down the barriers faced by so many and remove inequality and injustice from the world. Only then can we have a society which we all truly want to belong to.
Selected bibliography
Beveridge, William, (1942), Report of the Inter-Departmental Committee on Social Insurance and Allied Services, (HMSO: London)
Buck, Pearl S. (1954), My Several Worlds: A Personal Record, (London: Methuen)
Lammy, David, (2017), The Lammy Review: An Independent Review into the Treatment of, and Outcomes for, Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic Individuals in the Criminal Justice System, (London: Ministry of Justice)
Who cares what I think?

Erzsébet Korb (1923) Girl’s Portrait (Thinker; Contemplation)
The other week, I went for a meal with a friend. The food was lovely, the staff and environment welcoming and friendly and company, fabulous. A couple of days later I was thinking about that evening and I wondered why I had not felt the need to write some positive feedback on google, or similar. The answer was because I felt that I and my dining companion, had expressed our pleasure both in word and deed (the plates were clean!). Thus, the relationship between diners and restaurant staff had been overwhelmingly positive and this had been expressed by both.
However, wherever we go nowadays, we are regularly confronted by requests for feedback; “how is my driving?”, “did you enjoy your meal?” “would you recommend our services to others”? Often these questions are accompanied by Likert scales, so we can record our opinion on almost everything. Sometimes we might take some time to consider the options, other times we might just tick random boxes, more usually (if I’m anything to go by) I just don’t engage with such requests. Despite their often-jolly appearance, these questions are not harmless, they have an impact, most usually to measure individuals’ performances.
Whether we engage with such requests or not, we do not question whether we are well-placed to judge. So, for instance, as a driver of probably one of the smallest cars on the market (that’s me!), I’m expected to be able to mark the driver of a lorry. Or someone, who has the cooking know-how of a small child (I speak for myself again!) is expected to form an opinion on a dish prepared by a trained chef, these questions are hardly fair. More importantly, my answers are meaningless; whilst I might respond “the lorry appeared to take the corner a bit wide”, I have neither knowledge or understanding of the turning circle of a 32-tonne lorry. Similarly, my thoughts about the heat of a Bangladeshi biryani or the sweetness of a mille-feuille is neither here nor there. Given I can neither drive a lorry nor cook these wonderful dishes, who am I to voice an opinion?
Of course, there are times when it is necessary to voice an opinion, the lorry driver is behaving in a dangerous manner liable to cause an accident, or the restaurant is serving rancid or rotten food; both scenarios likely to involve serious harm. However, these concerns would need to be raised immediately, either by alerting the police (in the case of the lorry) or the management of the restaurant. In the case of the latter, you may also feel it necessary to contact environmental health if you felt that your complaint had not been addressed or you had concerns about the hygiene of the restaurant in general. However, these types of problems are largely outside the feedback requested.
In many of the scenarios/environments we are asked to comment on, we are in a relationship with the other party. Take the restaurant; if I am friendly and polite to the staff, I can expect a reciprocal relationship. If I am rude and aggressive, is it any wonder staff behave in a different way. They are constrained by their professions to focus on customer service, but this should not lay them open to abuse. Whilst the old adage “the customer is always right” might be an excellent baseline, it is not possible for this always to be the case. As someone who has spent a previous lifetime working in retail, sometimes the customer can be obtuse, rude or even downright, ignorant and abusive. Adherence to such an adage, at all costs, can only open the way for abuse.
But what about those feedback forms? On a bad day, in a rash moment, or because I’m bored, I decide to complete one of these forms. The waiter kept me waiting, the food was too spicy, I didn’t like the feedback I was given on my job application, my essay was critiqued, my teeth haven’t been flossed regularly, I didn’t like the book recommended to me by the librarian or the book seller, I can’t believe my line manager has turned down my application for annual leave. I can easily demonstrate my unhappiness with the situation with a few judiciously placed ticks, circles or smiley/sad faces. Can I say the waiter, the chef, the HR professional, the lecturer, the dentist, the librarian, the book seller and my line manager are performing poorly? Can I say they are unprofessional, unprepared, untrained, lacking in knowledge or skills or just plain wrong? And if I do, is that fair or just? Furthermore, am I happy to be subject to the same judgement from people who do not share my experiences; professional or otherwise? Remember too much of this bad feedback, however flippant and lacking in evidence it may be, may lead to disciplinary action, including dismissal.
There is an oft-cited, albeit crude, truth: “Opinions are like arseholes; everyone has one”! Ultimately, whether we choose to share (either) in public is up to us! Think carefully before ticking those boxes and encourage others to do the same. Who knows, someone may well be ticking boxes about you!
Celebrations and Commemorations: What to remember and what to forget

Today is Good Friday (in the UK at least) a day full of meaning for those of the Christian faith. For others, more secularly minded, today is the beginning of a long weekend. For Blur (1994), these special days manifest in a brief escape from work:
Bank holiday comes six times a year
Days of enjoyment to which everyone cheers
Bank holiday comes with six-pack of beer
Then it’s back to work A-G-A-I-N
(James et al., 1994).
However, you choose to spend your long weekend (that is, if you are lucky enough to have one), Easter is a time to pause and mark the occasion (however, you might choose). This occasion appears annually on the UK calendar alongside a number other dates identified as special or meaningful; Bandi Chhorh Divas, Christmas, Diwali, Eid al-Adha, Father’s Day, Guys Fawkes’ Night, Hallowe’en, Hanukkah, Hogmanay, Holi, Mothering Sunday, Navaratri, Shrove Tuesday, Ramadan, Yule and so on. Alongside these are more personal occasions; birthdays, first days at school/college/university, work, graduations, marriages and bereavements. When marked, each of these days is surrounded by ritual, some more elaborate than others. Although many of these special days have a religious connection, it is not uncommon (in the UK at least) to mark them with non-religious ritual. For example; putting a decorated tree in your house, eating chocolate eggs or going trick or treating. Nevertheless, many of these special dates have been marked for centuries and whatever meanings you apply individually, there is an acknowledgement that each of these has a place in many people’s lives.
Alongside these permanent fixtures in the year, other commemorations occur, and it is here where I want to focus my attention. Who decides what will be commemorated and who decides how it will be commemorated? For example; Armistice Day which in 2018 marked 100 years since the end of World War I. This commemoration is modern, in comparison with the celebrations I discuss above, yet it has a set of rituals which are fiercely protected (Tweedy, 2015). Prior to 11.11.18 I raised the issue of the appropriateness of displaying RBL poppies on a multi-cultural campus in the twenty-first century, but to no avail. This commemoration is marked on behalf of individuals who are no longing living. More importantly, there is no living person alive who survived the carnage of WWI, to engage with the rituals. Whilst the sheer horror of WWI, not to mention WWII, which began a mere 21 years later, makes commemoration important to many, given the long-standing impact both had (and continue to have). Likewise, last year the centenary of (some) women and men gaining suffrage in the UK was deemed worthy of commemoration. This, as with WWI and WWII, was life-changing and had profound impact on society, yet is not an annual commemoration. Nevertheless, these commemoration offer the prospect of learning from history and making sure that as a society, we do much better.
Other examples less clear-cut include the sinking of RMS Titanic on 15 April 1912 (1,503 dead). An annual commemoration was held at Belfast’s City Hall and paying guests to the Titanic Museum could watch A Night to Remember. This year’s anniversary was further marked by the announcement that plans are afoot to exhume the dead, to try and identify the unknown victims. Far less interest is paid in her sister ship; RMS Lusitania (sank 1915, 1,198 dead). It is difficult to understand the hold this event (horrific as it was) still has and why attention is still raised on an annual basis. Of course, for the families affected by both disasters, commemoration may have meaning, but that does not explain why only one ship’s sinking is worthy of comment. Certainly it is unclear what lessons are to be learnt from this disaster.
Earlier this week, @anfieldbhoy discussed the importance of commemorating the 30th anniversary of the Hillsborough Disaster. This year also marks 30 years since the publication of MacPherson (1999) and Monday marks the 26th anniversary of Stephen Lawrence’s murder. In less than two months it will two years since the horror of Grenfell Tower. All of these events and many others (the murder of James Bulger, the shootings of Jean Charles de Menezes and Mark Duggan, the Dunblane and Hungerford massacres, to name but a few) are familiar and deemed important criminologically. But what sets these cases apart? What is it we want to remember? In the cases of Hillsborough, Lawrence and Grenfell, I would argue this is unfinished business and these horrible events remind us that, until there is justice, there can be no end.
However, what about Arthur Clatworthy? This is a name unknown to many and forgotten by most. Mr Clatworthy was a 20-year-old borstal boy, who died in Wormwood Scrubs in 1945. Prior to his death he had told his mother that he had been assaulted by prison officers. In the Houses of Parliament, the MP for Shoreditch, Mr Thurtle told a tale, familiar to twenty-first century criminologists, of institutional violence. If commemoration was about just learning from the past, we would all be familiar with the death of Mr Clatworthy. His case would be held up as a shining example of how we do things differently today, how such horrific events could never happen again. Unfortunately, that is not the case and Mr Clatworthy’s death remains unremarked and unremarkable. So again, I ask the question: who decides what it is worthy of commemoration?
Selected Bibliography:
James, Alexander, Rowntree, David, Albarn, Damon and Coxon, Graham, (1994), Bank Holiday, [CD], Recorded by Blur in Parklife, Food SBK, [RAK Studios]
Hillsborough 30 years on. A case study in liberating the truth

Dr Stephen O’Brien is the Dean for the Faculty of Health and Society at the University of Northampton
Before I start this blog, it is important to declare my personal position. I am a lifelong supporter of Liverpool Football Club (LFC) and had I not been at a friend’s wedding on that fatal Saturday in April 1989, I may well have been in the Leppings Lane end of the Hillsborough stadium in Sheffield. I have followed the unfolding Hillsborough phenomenon for 30 years now and like the football club itself, it is an integral part of my life. To all caught up in the horrific events of Hillsborough, I echo a phrase synonymous with LFC and say; “You’ll Never Walk Alone”.
On April 15th, 1989 ninety-six men, women and children, supporters of Liverpool Football Club, died in a severe crush at an FA Cup semi-final at the Hillsborough Stadium, Sheffield. Hundreds were injured, and thousands traumatised. Within hours, the causes and circumstances of the disaster were being contested. While an initial judicial inquiry found serious institutional failures in the policing and management of the capacity crowd, no criminal prosecutions resulted, and the inquests returned ‘accidental death’ verdicts. Immediately, the authorities claimed that drunken, violent fans had caused the fatal crush. In the days and weeks following the disaster, police fed false stories to the press suggesting that hooliganism and drunkenness by Liverpool supporters were the root causes of the disaster. The media briefing was most significantly demonstrated in the headline “THE TRUTH” which appeared in The Sun newspaper immediately after the event devoting its front page to the story and reporting that: ‘Some fans picked pockets of victims; Some fans urinated on the brave cops; Some fans beat up PC giving life kiss’. What of course we appreciate now is that this headline was far from truth, however the blame narrative was already being set. For example, Chief Superintendent David Duckenfield, the match commander on the day, misinformed senior officials from the Football Association that fans had forced entry causing an inrush into already packed stadium pens. Yet it was Duckenfield who had ordered the opening of the gates to relieve the crush at the turnstiles. Within minutes the lie was broadcast internationally.
Blaming of Liverpool fans persisted even after the Taylor Report of 1990, which found that the main cause of the disaster was a profound failure in police control. While directing its most damning conclusions towards the South Yorkshire Police, it also criticised Sheffield Wednesday Football Club, its safety engineers and Sheffield City Council. However, following the Taylor Report, the Director of Public Prosecutions (DPP) ruled there was no evidence to justify prosecution of any individuals or institutions. On a more positive note, the disaster did lead to safety improvements in the largest English football grounds, notably the elimination of fenced terraces in favour of all seated stadiums.With the media allegations unchallenged and in the absence of any imminent prosecutions the families of the 96 hugely supported by the people of the City of Liverpool and it’s two football clubs began an exerted and prolonged campaign for truth and justice. In late June 1997, soon after the election of the Labour Government and following a concerted campaign by families, the Home Secretary Jack Straw proposed an unprecedented judicial scrutiny of any new evidence and appointed senior appeal court judge and former MI6 Commissioner Lord Justice Stuart-Smith to review further material that interested parties wished to submit. A large volume of new material was presented. However, Stuart-Smith rejected the new evidence concluding that there was no basis for a further public inquiry or new material of interest to the DPP or police disciplinary authorities. Undeterred by such a devastating outcome the families undertook a series of private prosecutions again to no avail.
It is important to note that public inquiries, convened in the aftermath of major incidents such as Hillsborough or to address alleged irregularities or failures in the administration of justice, should not be considered a panacea but provide an opportunity to speedily ensure that management failings are exposed to public scrutiny. They are popularly perceived to be objective and politically independent. On the other hand, they also have the potential to act as a convenient mechanism of legitimation for the state. It appeared to the families that the various inquiries that followed Hillsborough were incapable of surfacing the truth as the cards were stacked in favour of the state.
Roll forward to 2009. On the 20th anniversary, invited by the Hillsborough Family Support Group, Minister for Health Andy Burnham MP addressed over 30,000 people attending the annual memorial service at Liverpool FC’s Anfield stadium. Whilst acknowledging the dignity, resolve and courage they had exhibited in all the events of the previous 20 years he offered support and hope that their struggle would be further supported by the MPs in Liverpool as a whole. The cries of “Justice for the 96” that rang out that day heralded a turning point. Consequently, in December 2009, following the families unrelenting campaign, the Bishop of Liverpool, James Jones, was appointed to chair the Hillsborough Independent Panel. It was given unfettered access to all the documentation that had been generated in all the enquiries and investigations to date. The outcomes of their deliberations were presented in closed session to the bereaved families at Liverpool’s Anglican Cathedral on 12 September 2012, the report concluded that there was no evidence among the vast documentation to support or verify the serious allegations of exceptional levels of drunkenness, fans with no tickets or violence. The bereaved families and survivors were overwhelmed by the unqualified exoneration of those who died and survived. Shortly after, the Prime Minister David Cameron responded in detail to a packed House of Commons. He made a proper apology to the families of the 96 for all they have suffered over the past 23 years. In April 2016, a special Coroner’s Court ruled that the Hillsborough dead had been unlawfully killed and a campaign for justice that had run for well over two decades was concluded.
This year will be the 30th anniversary of that tragic event and I believe it is fair to say that the ensuing years have provided us with a troubling case study with features of institutional cover up, the power of the state, the Establishment, the resilience of the victim’s families, community and a social movement which Scraton (1999, 2013) refers to as an alternative method for liberating truth, securing acknowledgement and pursuing justice. Scraton has written extensively on the disaster and the subsequent events. He draws on human rights discourse to show how ‘regimes of truth’ operate to protect and sustain the interests of the ‘powerful’. He examined in detail the formal legal processes and their outcomes regarding Hillsborough and demonstrated how they were manipulated to degrade the truth and deny justice to the bereaved. He exposed the procedural and structural inadequacies of these processes and raised fundamental questions about the legal and political accountability of the instruments of authority. The broader socio/legal policy question that emerges from Hillsborough is whether ‘truth’ can ever be acknowledged and institutionalized injustices reconciled in a timely fashion when the force of the state apparatus works to differing ends. Time will only tell. In 2019 there are many other tragic examples where we could replace Hillsborough with Orgreave, Lawrence, Windrush, Grenfell. Let’s hope that it doesn’t take 30 years for truth and justice to emerge in the future.
References
Scraton P., (1999) Policing with Contempt: The Degrading of Truth and Denial of Justice in the Aftermath of the Hillsborough Disaster. Journal of Law and Society 26, 3, p273-297
Scraton P., (2013) The Legacy of Hillsborough: liberating truth, challenging power Race and Class, 55, 2, p1-27
The lone wolf: a media creation or a criminological phenomenon?

In a previous blog post, I spoke how the attention of the public is captivated by crime stories. Family tragedies, acts of mindless violence and other unusual cases, that seem to capture the Zeitgeist, with public discussion becoming topics in social situations. It happened again; Friday March 15 after 1:00 local time, a lone gunman entered the local Mosque in Christchurch and started shooting indiscriminately, causing the death of 50 and injuring as many, entering what the New Zealand Prime Minister would later call, in a televised address, one of NZ’s darkest days.
The singular gunman entering a public space and using a weapon/or weaponised machine (a car, nail bomb) is becoming a familiar aberration in society that the media describe as the “lone wolf”. A single, radicalised individual, with or without a cause, that leaves a trail of havoc described in the media using the darkest shades, as carnage or massacre. These reports focus on the person who does such an act, and the motivations behind it. In criminology, this is the illusive “criminal mind”. A process of radicalisation towards an ideology of hate, is usually the prevailing explanation, combined with the personal attributes of the person, including personality and previous lifestyle.
In the aftermath of such attacks, communities go through a process of introspection, internalising what happened, and families will try to come together to support each other. 23 years ago, a person entered a school in Dunblane, Scotland and murdered 16 children and their teacher. The country went into shock, and in the subsequent years the gun laws changed. The community was the focus of national and international attention, until the lights dimmed, the cameras left, and the families were left alone in grief.
Since then numerous attacks from little people with big weapons have occurred from Norway to USA, France to Russia and to New Zealand, as the latest. And still, we try to keep a sense of why this happened. We allow the media to talk about the attacker; a lone wolf is always a man, his history the backstory and his victims, as he is entitled to posthumous ownership of those he murdered. The information we retain in our collective consciousness, is that of his aggression and his methodology of murder. Regrettably as a society we merely focus on the gun and the gunman but never on the society that produces the guns and raises gunmen.
At this point, it is significant to declare that I have no interest in the “true crime” genre and I find the cult of the lone wolf, an appalling distraction for societies that feed and reproduce violence for the sake of panem et circenses. Back in 2015, in Charleston another gunman entered a church and murdered another group of people. Families of the victims stood up and court and told the defendant, that they would pray for his soul and forgive him for his terrible act. Many took issue, but behind this act, a community took matters into their own hands. This was not about an insignificant person with a gun, but the resilience of a community to rise above it and their pain. A similar response in the aftermath of the shooting in Orlando in 2016, where the LGBTQ+ community held vigils in the US and across the world (even in Northampton). In New Zealand, the Prime Minister, Jacinda Ardern was praised for her sombre message and her tribute to the community, not mentioning the gunman by name, not even once. This is not a subject that I could address in a single blog post (I feel I should come back to it in time) but there is something quite empowering to know the person who did the act, but to deliberately and publicly, ignore him. We forget the importance celebrity plays in our culture and so taking that away, from whomever decides to make a name for themselves by killing, is our collective retribution. In ancient Egypt they rubbed off the hieroglyphs of the columns. Maybe now we need to take his name from the newspaper columns, do not make the story about him, but reflect instead, on the way we live as a community and the people who matter.
Majority Verdicts and Reasonable Doubt

Recently I attended an Inside Justice Live Crime event hosted by Anglia Law School at Anglia Ruskin University. The last speaker for the evening was Kevin Lane who is trying to have his wrongful conviction overturned, during his discussion he mentioned that he was found guilty of murder by a 10-2 majority verdict. It came as quite a shock to me to hear that majority verdicts are used for murder charges in England.
In 1994 Robert Magill was shot dead by a hitman while walking his dog in Hertfordshire, two men fled the scene in a BMW car. In 1995 Lane and a co-accused were charged with the murder of Magill. The prosecution alleged that Lane had received payment for this murder and submitted that fingerprints were found in bin liners in the car. Police were unable to link Lane to the scene of the crime, were unable to prove he had received payment, and he has always maintained his innocence.
There were a number of limitations and concerns in this case – the murder weapon was never recovered, two prime suspects who were brought to the police’s attention soon after the murder were not properly investigated and were later found to have an inappropriate relationship with the investigating police officer, and there were on going disclosure problems. Further, in 2002 the investigating officer was sent to prison for four years of conspiracy to steal £160,000 from the Hertfordshire Police and misconduct in a public office. (This is a very brief summary of a complicated case).
A majority verdict is used when the jury cannot reach a unanimous verdict and where the jury consists of usually 12 jurors and at least 10 or 11 agree (depending on the jurisdiction) – under certain conditions the judge is able to accept the jury’s verdict. The provision of a majority verdict is generally used when a prescribed period of time has elapsed, and the judge is satisfied that the jury are unlikely to reach a unanimous verdict after further deliberation. Majority verdicts have been used in England since 1974 and were originally introduced to prevent the intimidation or bribing of jurors.
While I am aware of majority verdicts, as they are used in Queensland, Australia (where I completed my legal education). Majority verdicts cannot be used for murder trials, for an offence which has mandatory life imprisonment as a penalty, and Commonwealth offences. The overall concern with majority verdicts is that if the jury is unable to reach a unanimous decision then they cannot be said to have reached a decision ‘beyond a reasonable doubt’ which is the standard of proof for criminal matters, and as a consequence have demonstrated reasonable doubt.
Unanimous jury verdicts have been part of the common law since the 14thcentury. Prior to 1866, if a jury could not reach an agreement they could be ‘carried around in a wagon with the court without meat or drink, fire or candle until they were starved or frozen into agreement.’ We have obviously come a long way since the days of locking jurors up and separating them from their family and friends until they reached a decision.
Using unanimous verdicts is argued to reduce the risk of convicting an innocent person, that unanimity is a fundamental feature of a jury trial, it leads to better deliberation, and that disagreement in a jury is not unreasonable. When considering the issue from the perspective of the accused, majority verdicts place them at a great disadvantage when one considers that the prosecution has much more resources. There are already a number of contributors to wrongful convictions which the accused needs to contest with, and the fact that appeals are very difficult.
It can be argued there are benefits for majority verdicts – they reduce the instance of a hung jury (where the accused is neither acquitted or convicted) and the potential for a retrial (and the economic cost associated for a criminal justice system which is already overloaded). Majority verdicts are said to overcome problems with ‘rogue’ jurors, bribery and intimidation. The use of majority verdicts allows there to be finality in the case for the victim/s, the accused, the family and friend of the victim/s and accused, and the community.
Personally, I believe that in the interest of justice majority verdicts should not be used in serious criminal cases – such as murder and offences which carry mandatory life imprisonment penalty. These cases are much too serious and if reasonable doubt is present then this should be recognised. In Kevin Lane’s case he would not have been convicted, served 18 years in prison, and still be trying to overturn his conviction.
Further reading
Cowdery, N. (2007). Majority jury verdicts. Reform Issue. 90, 18-19.
Garrett, B.L. & Neufeld, P.J. (2009). Invalid forensic science testimony and wrongful convictions. Virginia Law Review. 95(1), 1-97.
Gray, A. (2009). A guarantee right to trial by jury at state level? Australian Journal of Human Rights. 15(1), 97-125.
Roberts, S. & Weathered, L. (2009). Assisting the factually innocent: The contradictions and compatibility of Innocence Projects and the Criminal Cases Review Commission. Oxford Journal of Legal Studies. 29(1), 43-70.
Sankoff, P. (2006). Majority jury verdicts and the Charter of Rights and Freedoms. UBC Law Review. 39(2), 333-369.
The roots of criminology; the past in the service of the future;
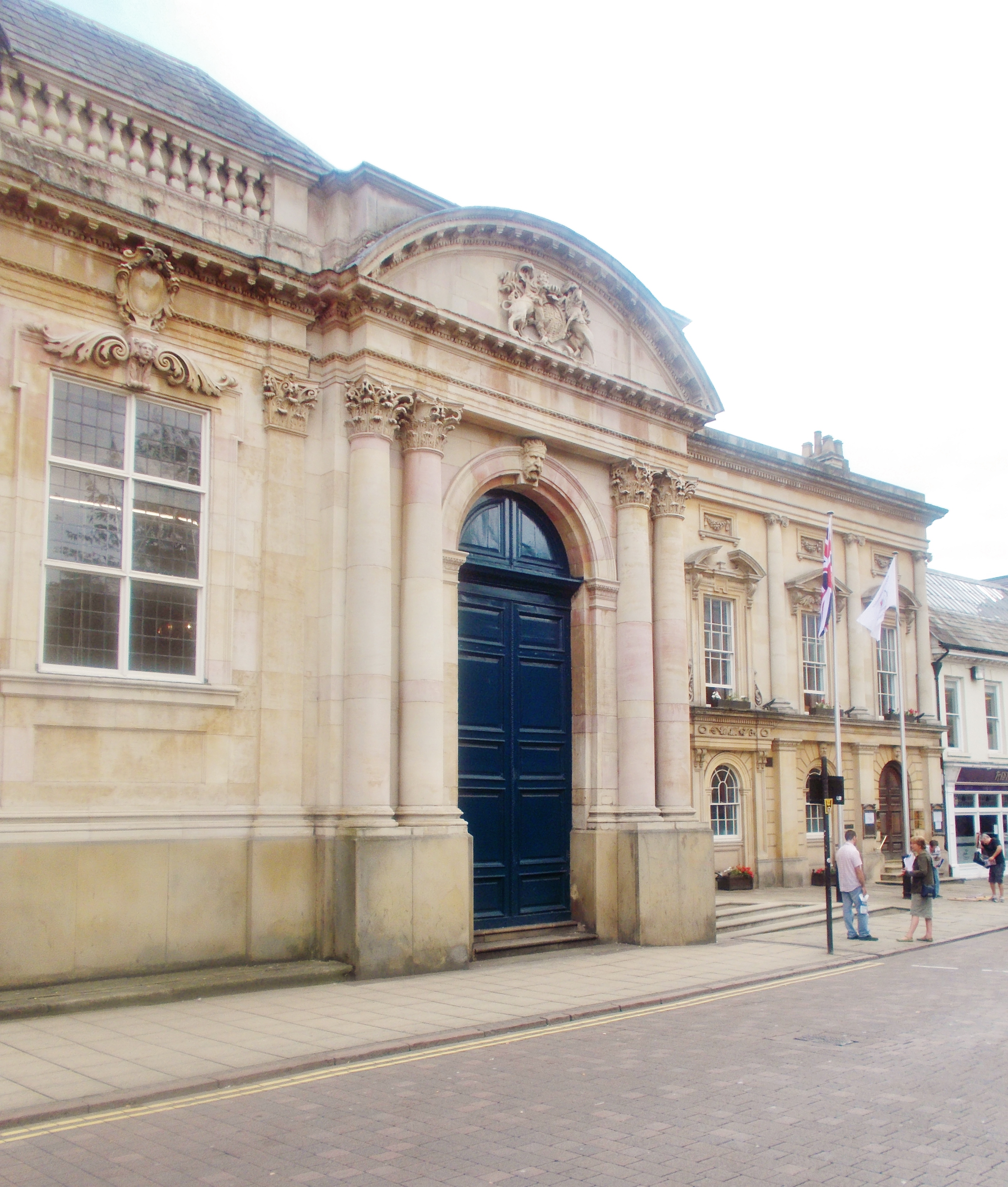

In a number of blog posts colleagues and myself (New Beginnings, Modern University or New University? Waterside: What an exciting time to be a student, Park Life, The ever rolling stream rolls on), we talked about the move to a new campus and the pedagogies it will develop for staff and students. Despite being in one of the newest campuses in the country, we also deliver some of our course content in the Sessions House. This is one of the oldest and most historic buildings in town. Sometimes with students we leave the modern to take a plunge in history in a matter of hours. Traditionally the court has been used in education primarily for mooting in the study of law or for reenactment for humanities. On this occasion, criminology occupies the space for learning enhancement that shall go beyond these roles.
The Sessions House is the old court in the centre of Northampton, built 1676 following the great fire of Northampton in 1675. The building was the seat of justice for the town, where the public heard unspeakable crimes from matricide to witchcraft. Justice in the 17th century appear as a drama to be played in public, where all could hear the details of those wicked people, to be judged. Once condemned, their execution at the gallows at the back of the court completed the spectacle of justice. In criminology discourse, at the time this building was founded, Locke was writing about toleration and the constrains of earthy judges. The building for the town became the embodiment of justice and the representation of fairness. How can criminology not be part of this legacy?
There were some of the reasons why we have made this connection with the past but sometimes these connections may not be so apparent or clear. It was in one of those sessions that I began to think of the importance of what we do. This is not just a space; it is a connection to the past that contains part of the history of what we now recognise as criminology. The witch trials of Northampton, among other lessons they can demonstrate, show a society suspicious of those women who are visible. Something that four centuries after we still struggle with, if we were to observe for example the #metoo movement. Furthermore, from the historic trials on those who murdered their partners we can now gain a new understanding, in a room full of students, instead of judges debating the merits of punishment and the boundaries of sentencing.
These are some of the reasons that will take this historic building forward and project it forward reclaiming it for what it was intended to be. A courthouse is a place of arbitration and debate. In the world of pedagogy knowledge is constant and ever evolving but knowing one’s roots allows the exploration of the subject to be anchored in a way that one can identify how debates and issues evolve in the discipline. Academic work can be solitary work, long hours of reading and assignment preparation, but it can also be demonstrative. In this case we a group (or maybe a gang) of criminologists explore how justice and penal policy changes so sitting at the green leather seats of courtroom, whilst tapping notes on a tablet. We are delighted to reclaim this space so that the criminologists of the future to figure out many ethical dilemmas some of whom once may have occupied the mind of the bench and formed legal precedent. History has a lot to teach us and we can project this into the future as new theoretical conventions are to emerge.
Locke J, (1689), A letter Concerning Toleration, assessed 01/11/18 https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/A_Letter_Concerning_Toleration












