Home » Criminologist (Page 2)
Category Archives: Criminologist
Covid-Universities and what if

Over the past week or so there have been some mutterings about whether it is safe to open up universities. There is the advice from the scientific advisors (Universities get some Indie SAGE advice on reopening campuses in September) and some thoughts from academics ‘Why universities must move all teaching online this autumn’.
As we move closer to the start of term, so my dread of what is ahead comes into sharper focus. I try to imagine what it would be like and try to reassure myself that the risk assessments have been done and the reassurances that the universities are Covid safe are true rather than simply fantasy and wishful thinking.
In this safe environment I imagine that the number of students and staff on campuses will be carefully managed as it is with many large stores.
I imagine that all staff and students will be wearing face coverings. This is not for protection of themselves, as the use of coverings is a somewhat altruistic venture, I cover my face and protect you and you cover yours and protect me.
I imagine that all thoroughfares will be marked and monitored. Social distancing is important, and we need to be at least a metre apart.
I imagine that the classrooms will be laid out in such a way that social distancing can be maintained and that the classrooms will be well ventilated, even in the middle of winter. I imagine all the chairs and desks and any other equipment will be wiped down after each session.
I imagine that face to face teaching will be limited and interactions with multiple groups of students will be severely curtailed to ensure lecturers are not put at unnecessary risk. I imagine each class will comprise only a few students to minimise risk.
I imagine that anyone who is symptomatic will not attend a university and will after being tested self-isolate. I imagine that all the people they have been in contact with will do the same for a whole, boring, 14 days.
I imagine that the universities’ management will be at each university, leading from the front. They will be checking to ensure the safety of students and staff. They will be mixing with staff and students, receiving feedback and continuously monitoring. I imagine the safety of the students and staff is paramount.
And then I think, what if…
What if campuses are a free for all. Students can come and go as they please, there is no monitoring of volumes. Or what if there is, but it is impossible to enforce with limited staff to do so. And those staff tasked with this endeavour are at greater risk due to the proximity with large volumes of students.
What if people decide not to wear face coverings or having got into the building decide to take them off or several people are exempt for some reason or another. Altruism has gone out of the window. I’m a criminologist and I know that people break the rules for all sorts of reasons and the only certainty is that some people will break the rules.
What if social distancing becomes all too difficult. Many of us have experienced it in stores. A one-way system works for most, but a significant number just don’t abide by it, for whatever reason. People break rules.
What if the social distancing in classes is impossible, there just isn’t enough classes to maintain it with the volume of students on the course. What if ventilation is impossible, other than air conditioning, some classes are in the middle of buildings. Who will clean the chairs and equipment after each class? Go to a restaurant and tables and chairs are wiped down after each use so who will do it at a university?
What if lecturers have to teach multiple groups face to face as there are not enough staff to spread the load. Teaching in a classroom for two hours multiple times in a day with different groups each time must surely expose lecturers to much greater risk.
What if students are of the age group where they are more likely to be asymptomatic? How many that are infected might be at a university, spreading the virus around campus and around the locality. Even if they are symptomatic, how likely are they to self-isolate? Judging by the street parties and illegal raves reported on the news, there is a good chance that some will break the rules. Let’s be realistic, if you are only likely to suffer affects akin to a cold, why would you be that bothered about social distancing or self-isolation?
And finally, what if all managers avail themselves of the much-vaunted government advice, work from home if you can. Leadership from the rear, the bottom line is more important than the safety of others. We can of course dress this up in management psychobabble about what the students need.
Never mind, ‘Tally ho and all of that sort of thing and over the top we go’*.
* For those of you that are lost at this point it might be worth a visit to the last episode of Blackadder Goes Forth.
How I became an evil man

My love of poetry came in my sleep like a dream, a fever I could not escape and in little hours of the day I would read some poetry from different people who voice the volume of their emotions with words. In one of those poems by Elleni Vakalo How he became a bad man, she introduced me to a new understanding of criminological thinking. The idea of consequences, that lead a seemingly good person to become bad, without the usual motivational factors, other than fear. This was the main catalyst that became the source of this man’s turn to the bad.
This almost surrealistic description of criminal motivation has since fascinated me. It is incredibly focused, devoid of social motivations and personal blame. In fact, it demonstrates a social cognition that once activated is powerful enough to lead a seemingly decent person to behave in uncharacteristic moves of violence. This interesting perspective was forged during the war and the post war turmoil experienced. Like Camus, the act of evil is presented as a matter of fact and the product of thoughts that are originally innocent and even non-threatening.
The realisation in this way of thinking, is not the normalisation of violence, but the simplicity that violence in innate to everyone. The person who commits it, is not born for it, does not carry an elaborate personal story or trauma and has no personal compulsion to do it. In some ways, this violence is more terrifying, as criminality can be the product of any person without any significant predispositions, an everyday occurrence that can happen any time.
The couple that will meet, fall in love, cohabit, and get married, starting a family, follow all the normal everyday stages that millions of people follow or feel socially obliged to follow. In no part of this process do they discuss how he will control her, demean her, call her names, slap her, hit her or kick her. There is no plan or discussion of how terrified she will become, socially isolated and humiliated. At no point in the planning, will she be thinking of ways to exit their home, access helplines or spend a day in court. It happens, as a product of small thoughts and expressed emotions, that convert into micro aggressions, that become overt hostility, that leads to violence. No significant changes, just a series of events that lead to a prolonged suffering.
In some way, this matter of fact violence explains the confusion the victims feel, trapped in a relationship that they cannot recognise as abusive, because all other parts fall under the normality of everyday life. Of course, in these situations, emotion plays a key role and in a way that rearranges logic and reason. We are driven by emotion and if we are to leave criminological theory for a minute a series of decisions, we will make daily take a journey from logic to emotions and back.
This emotional change, the manifestation of thoughts is not always criminal nor destructive. The parents who are willing to fight an entire medical profession so that their newborn has a fighting chance are armed with emotion. Many stories come to mind of those who owe their lives to their determination of their parents who fought logic and against the odds, fought to keep them alive. Friends and partners of people who have been written off by the criminal justice system that assessed them as high risk for society and stuck with them, holding on to emotion as logic departs.
In Criminology, we talk about facts and figures, we consider theories and situations, but above all as a social science we recognise that we deal with people; people without emotions do not exist. So how do you/how do I become a bad man? Simple…the same way you are/I am a good man.
This is the poem by Eleni Vakalo, with my painful translation:
How He Became A Bad Man
I will tell you how it happened
In that order
A good little man met on his way
a battered man
the man was so close from him laying
he felt sad for him
He was so sad
That he became frightened
Before approaching him to bend down to
help him, he thought better
“What do you want, what are you looking for”
Someone else will be found by so many around here,
to assist this poor soul
And actually
I have never seen him
And because he was scared
So he thought
Would he not be guilty, after all no one is hit without being guilty?
And they did him good since he wanted to play with the nobles
So he started as well
To hit him
Beginning of the fairy tale
Good morning
Nothing is black and white: the intransigence of fools

One thing we criminologists know is that it is impossible to prevent crime. Many a great criminologist has tried to theorise why crime occurs (my shelves are full of their books) and whilst almost all have made valuable contributions to our understanding of crime, it is an unfortunate fact that crime continues. But then crime itself is difficult to define and has its basis in time, power, opportunity and social discourses. What is criminal today will not be criminal tomorrow and what is important today will lose its importance tomorrow, in favour of some new or maybe, old, manifestation of that elusive concept we call crime. Perhaps we should we grateful, for in the industry of crime lies mass employment. From criminologists to those that attempt to stem the tide of crime, those that deal with its aftermath and those that report on it or write about it (real or fictional), there is money to be made. If we stopped crime, we would all be out of a job.
Most, if not all of us have at some stage in our lives committed some sort of crime. Most crimes will fortunately be almost inconsequential, maybe a flouting of a law such as driving a car over the speed limit. Other crimes will be more serious and whilst some criminals will be brought to book most are not. The inconsequential crime of driving over the speed limit, albeit perhaps due to a lapse of concentration, can have dire consequences. There is clear evidence that the survival rates of pedestrians struck by cars has a direct correlation with speed. So the inconsequential becomes the consequential, the ephemerality of crime, the reality.
When we think of crime, we often have little concept of its reality. We apply labels and our own rules to that we know and find acceptable. Speeding is not criminal, well not generally, unless it’s a boy racer. Drink driving is a no-no, but we might take it to the alcohol limit when having a drink. Drugs (the criminalised type) are ok, well some are and some aren’t, it all depends on your viewpoint. Drugs (the prescription type) are ok, even if they impair our ability to drive. Alcohol, well that’s absolutely ok, even if the abuse of it leads to more deaths than drugs and the consequences of that misuse has a really significant impact on the NHS. Tax evasion, illegal if you get caught, ok if you don’t. A bit like fraud really, ok if you can get away with it but then maybe not, if the victim is a little old lady or me. Assault, well it depends on the seriousness and the situation and probably the victim. Robbery, not good to go into an off licence with a gun and threaten the shopkeeper, bullying if you take lunch money off the lad outside the school gates.
Criminals don’t walk around with a label that says ‘criminal’ and even if they did, there would have to be a method of bestowing the label in an instance. Nonsense of course, only a fool would suggest such a thing. What about the people that committed a crime but have changed their ways I hear my colleagues ask? What about those that haven’t, or have and then relapse, I reply.
Nothing is black and white; the concept of crime is elusive, as are criminals (both by concept and nature). And yet we happily castigate those that attempt to uphold the law on our behalf and in doing so view crime and criminals as clear concepts. Each has a clear label, each is clearly identifiable, so how can they get it so wrong so many times. Whilst criticising those that attempt, and let’s be quite honest, fail most of the time to stem this tide of crime, perhaps we might also think about the impossibility of the job in hand. That’s not to say that a lot of the criticisms are not justified, nor that things should not change, but if we only examine all that is wrong, we lose sight of reality and only an intransigent fool would continue an argument that sees the problems and solutions as simply black and white.
What’s in the future for criminology?

This year marks 20 years that we have been offering criminology at the University of Northampton and understandably it has made us reflect and consider the direction of the discipline. In general, criminology has always been a broad theoretical discipline that allows people to engage in various ways to talk about crime. Since the early days when Garofalo coined the term criminology (still open to debate!) there have been 106 years of different interpretations of the term.
Originally criminology focused on philosophical ideas around personal responsibility and free will. Western societies at the time were rapidly evolving into something new that unsettled its citizens. Urbanisation meant that people felt out of place in a society where industrialisation had made the pace of life fast and the demands even greater. These societies engaged in a relentless global competition that in the 20th century led into two wars. The biggest regret for criminology at the time, was/is that most criminologists did not identify the inherent criminality in war and the destruction they imbued, including genocide.
In the ashes of war in the 20th century, criminology became more aware that criminality goes beyond individual responsibility. Social movements identified that not all citizens are equal with half the population seeking suffrage and social rights. It was at the time the influence of sociology that challenged the legitimacy of justice and the importance of human rights. In pure criminological terms, a woman who throws a brick at a window for the sake of rights is a crime, but one that is arguably provoked by a society that legitimises inequality and exclusion. Under that gaze what can be regarded as the highest crime?
Criminologists do not always agree on the parameters of their discipline and there is not always consensus about the nature of the discipline itself. There are those who see criminology as a social science, looking at the bigger picture of crime and those who see it as a humanity, a looser collective of areas that explore crime in different guises. Neither of these perspectives are more important than the other, but they demonstrate the interesting position criminology rests in. The lack of rigidity allows for new areas of exploration to become part of it, like victimology did in the 1960s onwards, to the more scientific forensic and cyber types of criminology that emerged in the new millennium.
In the last 20 years at Northampton we have managed to take onboard these big, small, individual and collective responses to crime into the curriculum. Our reflections on the nature of criminology as balancing different perspectives providing a multi-disciplinary approach to answering (or attempting to, at least) what crime is and what criminology is all about. One thing for certain, criminology can reflect and expand on issues in a multiplicity of ways. For example, at the beginning of 21st terrorism emerged as a global crime following 9/11. This event prompted some of the current criminological debates.
So, what is the future of criminology? Current discourses are moving the discipline in new ways. The environment and the need for its protection has emerge as a new criminological direction. The movement of people and the criminalisation of refugees and other migrants is another. Trans rights is another civil rights issue to consider. There are also more and more calls for moving the debates more globally, away from a purely Westernised perspective. Deconstructing what is crime, by accommodating transnational ideas and including more colleagues from non-westernised criminological traditions, seem likely to be burning issues that we shall be discussing in the next decade. Whatever the future hold there is never a dull moment with criminology.
20 years of Criminology

It was at the start of a new millennium that people worried about what the so-called millennium will do to our lives. The fear was that the bug will usher a new dark age where technology will be lost. Whilst the impending Armageddon never happened, the University College Northampton, as the University of Northampton was called then, was preparing to welcome the first cohort of Criminology students.
The first cohort of students joined us in September 2000 and since then 20 years of cohorts have joined since. During these years we have seen the rise of University fees, the expansion of the internet and google search and of course the emergence of social media. The original award was focused on sociolegal aspects, predominantly the sociology of deviance, whilst in the years since the changes demonstrate the departmental and the disciplinary changes that have happened.
Early on, as criminology was beginning to find its voice institutionally, the team developed two rules that have since defined the focus of the discipline. The first is that the subject will be taught in a multi-disciplinary approach, widely inclusive of all the main disciplines involved in the study of crime; so alongside sociology, you will find psychology, law, history, philosophy to name but a few. The impetus was to present these disciplines on an equal footing and providing opportunity to those joining the course, to discover their own voice in criminology. The second rule was to give the students the opportunity to explore contentious topics and draw their own perspective. Since the first year of running it, these rules have become the bedrock of UoN Criminology.
The course since the early years has grown and gone through all those developmental stages, childhood, adolescence and now eventually we have reached adulthood. During these stages, we managed to forge a distinctiveness of what criminology looks like; introducing for example a research placement to allow the students to explore the theory in practice. In later years we created courses that reflect Criminology in the 21st Century always relating to the big questions and forever arming learners with the skills to ask the impossible questions.
Through all these years students join with an interest in studying crime and by the time they leave us, to move onto the next chapter of their lives, they have become hard core criminologists. This is always something that we consider one of the course’s greatest contribution to the local community.
In an ordinary day, like any other day in the local court one may see an usher, next to a probation officer, next to a police officer, next to a drugs rehabilitation officer, all of them our graduates making up the local criminal justice system. A demonstration of the reach and the importance of the university as an institution and the services it provides to the local community. More recently we developed a module that we teach in prison comprised by university and prison students. This is a clear sign of the maturity and the journey we have done so far…
As the 21st century entered, twin towers fell, bus and tube trains exploded, consequent wars were made, riots in the capital, the banking crisis, the austerity, bridge attacks, Brexit, extinction rebellion, buildings burning, planes coming down, forest fires and #metoo, and we just barely cover 20 years. These and many more events keep criminological discourse relevant, increase the profile of the subject and most importantly further the conversation we are having in our society as to where we are heading.
As I raise my glass to salute the first 20 years of Criminology at the University of Northampton, I am confident that the next 20 years will be even more exciting. For those who have been with us so far a massive thank you, for those to come we are looking forward to discussing some of the many issues with you. We are passionate about criminology and we want you to infect you with our passion.
As they say in prison, the first 20 years are difficult the rest you just glide through…
Empathy Amid the “Fake Tales of San Francisco”*

This time last week, @manosdaskalou and I were in San Francisco at the American Society of Criminology’s conference. This four-day meeting takes place once a year and encompasses a huge range of talkers and subjects, demonstrating the diversity of the discipline. Each day there are multiple sessions scheduled, making it incredibly difficult to choose which ones you want to attend.
Fortunately, this year both of our two papers were presented on the first day of the conference, which took some of the pressure off. We were then able to concentrate on other presenters’ work. Throughout discussions around teaching in prison, gun violence and many other matters of criminological importance, there was a sense of camaraderie, a shared passion to understand and in turn, change the world for the better. All of these discussions took place in a grand hotel, with cafes, bars and restaurants, to enable the conversation to continue long after the scheduled sessions had finished.
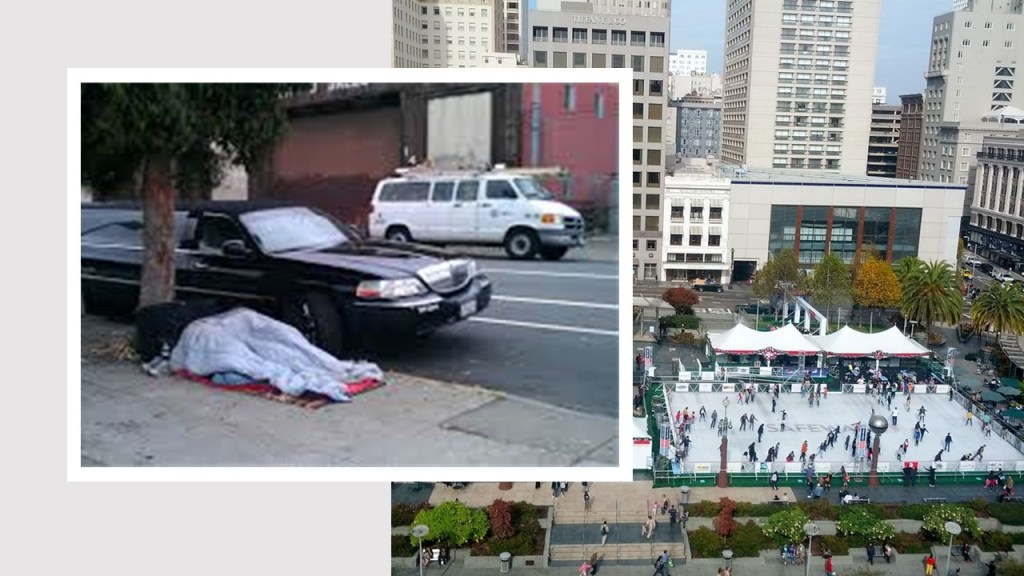
Outside of the hotel, there is plenty to see. San Francisco is an interesting city, famous for its Golden Gate Bridge, the cable cars which run up and down extraordinarily steep roads and of course, criminologically speaking, Alcatraz prison. In addition, it is renowned for its expensive designer shops, restaurants, bars and hotels. But as @haleysread has noted before, this is a city where you do not have to look far to find real deprivation.
I was last in San Francisco in 2014. At that point cannabis had been declassified from a misdemeanour to an infraction, making the use of the drug similar to a traffic offence. In 2016, cannabis was completely decriminalised for recreational use. For many criminologists, such decriminalisation is a positive step, marking a change from viewing drug use as a criminal justice problem, to one of public health. Certainly, it’s a position that I would generally subscribe to, not least as part of a process necessary to prison abolition. However, what do we really know about the effects of cannabis? I am sure my colleague @michellejolleynorthamptonacuk could offer some insight into the latest research around cannabis use.
When a substance is illegal, it is exceedingly challenging to research either its harms or its benefits. What we know, in the main, is based upon problematic drug use, those individuals who come to the attention of either the CJS or the NHS. Those with the means to sustain a drug habit need not buy their supplies openly on the street, where the risk of being caught is far higher. Thus our research population are selected by bad luck, either they are caught or they suffer ill-effects either with their physical or mental health.
The smell of cannabis in San Francisco is a constant, but there is also another aroma, which wasn’t present five years ago. That smell is urine. Furthermore, it has been well documented, that not only are the streets and highways of San Francisco becoming public urinals, there are also many reports that public defecation is an increasing issue for the city. Now I don’t want to be so bold as to say that the decriminalisation of cannabis is the cause of this public effluence, however, San Francisco does raise some questions.
- Does cannabis cause or exacerbate mental health problems?
- Does cannabis lead to a loss of inhibition, so much so that the social conventions around urination and defecation are abandoned?
- Does cannabis lead to an increase in homelessness?
- Does cannabis increase the likelihood of social problems?
- Does the decriminalisation of cannabis, lead to less tolerance of social problems?
I don’t have any of the answers, but it is extremely difficult to ignore these problems. The juxtaposition of expensive shops such as Rolex and Tiffany just round the corner from large groups of confused, homeless people, make it impossible to avoid seeing the social problems confronted by this city. Of course, poor mental health and homelessness are not unique to San Francisco or even the USA, we have similar issues in our own town, regardless of the legal status of cannabis. Certainly the issue of access to bathroom facilities is pressing; should access to public toilets be a right or a privilege? This, also appears to be a public health, rather than CJS problem, although those observing or policing such behaviour, may argue differently.
Ultimately, as @haleysread found, San Francisco remains a City of Contrast, where the very rich and the very poor rub shoulders. Unless, society begins to think a little more about people and a little less about business, it seems inevitable that individuals will continue to live, eat, urinate and defection and ultimately, die upon the streets. It is not enough to discuss empathy in a conference, no matter how important that might be, if we don’t also empathise with people whose lives are in tatters.
*Turner, Alex, (2006), Fake Tales of San Francisco, [CD]. Recorded by Arctic Monkeys in Whatever People Say I Am, That’s What I’m Not, The Chapel: Domino Records