Home » Changemaker
Category Archives: Changemaker
Changing the Narrative around Violence Against Women and Girls

For Criminology at UON’s 25th Birthday, in partnership with the Northampton Fire, Police and Crime Commissioner, the event “Changing the Narrative: Violence Against Women and Girls” convened on the 2nd April. Bringing together a professional panel, individuals with lived experience and practitioners from charity and other sectors, to create a dialogue and champion new ways of thinking. The first in a series, this event focused on language.
All of the discussions, notes and presentations were incredibly insightful, and I hope this thematic collation does it all justice.
“A convenient but not useful term.”
Firstly an overwhelming reflection on the term itself; ‘Violence Against Women and Girls’ – does it do justice to all of the behaviour under it’s umbrella? We considered this as reductionist, dehumanising, and often only prompts thinking and action to physical acts of violence, but perhaps neglects many other harms such as emotional abuse, coercion and financial abuse which may not be seen as, or felt as ‘severe enough’ to report. It may also predominantly suggest intimate partner or domestic abuse which may too exclude other harms towards women and girls such as (grand)parent/child abuse or that which happens outside of the home. All of which are too often undetected or minimised, potentially due to this use of language. Another poignant reflection is that we may not currently be able to consider ‘women and girls’ as one group, given that girls under 16 may not be able to seek help for domestic abuse, in the same way that women may be able to. We also must consider the impact of this term on those whose gender identity is not what they were assigned at birth, or those that identify outside of the gender binary. Where do they fit into this?
To change the narrative, we must first identify what we are talking about. Explicitly. Changing the narrative starts here.
“I do not think I have survived.”
We considered the importance of lived experience in our narratives and reflected on the way we use it, and what that means for individuals, and our response.
Firstly, the terms ‘victim’ and ‘survivor’ – which we may use without thought, use as fact, particularly as descriptors within our professions, but actually these are incredibly personal labels that only individuals with such experience can give to themselves. This may be reflective of where they are in their journey surrounding their experiences and have a huge impact on their experience of being supported. It was courageously expressed that we also must recognise that individuals may not identify with either of those terms, and that much more of that person still exists outside of that experience or label. We also took a moment to remember that some victims, will never be survivors.
Lived experience is making its way into our narratives more and more, but there is still much room for improvement. We champion that if we are to create a more supportive, inclusive, practical and effective narrative, we must reflect the language of individuals with lived experience and we must use it to create a narrative free from tick boxes, from the lens of organisational goals and societal pressure.
Lived experience must be valued for what it is, not in spite of what it is.
“In some cases, we allow content – which would otherwise go against our standards – if its newsworthy.”
A further theme was a reflection on language which appears to be causing an erosion of moral boundaries. For example, the term ‘misogyny’ – was considered to be used flippantly, as an excuse, and as a scapegoat for behaviour which is not just ‘misogynistic’ but unacceptable, abhorrent, inexcusable behaviour – meaning the extent of the harms caused by this behaviour are swept away under a ‘normalised’ state of prejudice.
This is one of many terms that along with things like ‘trauma bond’ and ‘narcissist’ which have become popular on social media without any rigour as to the correct use of the term – further normalises harmful behaviour, and prevents women and girls from seeking support for these very not normal experiences. In the same vein it was expressed that sexual violence is often seen as part of ‘the university experience.’
This use of language and its presence on social media endangers and miseducates, particularly young people, especially with new posting policies around the freedom of expression. Firstly, in that many restrictions can be bypassed by the use of different text, characters and emoji so that posts are not flagged for certain words or language. Additionally, guidelines from Meta were shared and highlighted as problematic as certain content which would, and should, normally be restricted – can be shared – as long as is deemed ‘newsworthy.’
Within the media as a whole, we pressed the importance of using language which accurately describes the actions and experience that has happened, showing the impact on the individual and showing the extent of the societal problem we face… not just what makes the best headline.
“We took action overnight for the pandemic.”
Language within our response to these crimes was reflected upon, in particular around the term ‘non-emergency’ which rape, as a crime, has become catalogued as. We considered the profound impact of this language for those experiencing/have experienced this crime and the effect it has on the resources made available to respond to it.
Simultaneously, in other arenas, violence toward women and girls is considered to be a crisis… an emergency. This not only does not align with the views of law enforcement but suggests that this is a new, emerging crisis, when in fact it is long standing societal problem, and has faced significant barriers in getting a sufficient response. As reflected by one attendee – “we took action overnight for the pandemic.”
“I’ve worked with women who didn’t report rape because they were aroused – they thought they must have wanted it.”
Education was another widely considered theme, with most talk tables initially considering the need for early education and coming to the conclusion that everyone needs more education; young and old – everything in between; male, female and everything in between and outside of the gender binary. No-one is exempt.
We need all people to have the education and language to pass on to their children, friends, colleagues, to make educated choices. If we as adults don’t have the education to pass on to children, how will they get it? The phrase ‘sex education’ was reflected upon, within the context of schools, and was suggested to require change due to how it triggers an uproar from parents, often believing their children will only be taught about intercourse and that they’re too young to know. It was expressed that age appropriate education, giving children the language to identify harms, know their own body, speak up and speak out is only beneficial and this must happen to help break the cycle of generational violence. We cannot protect young people if we teach them ignorance.
Education for all was pressed particularly around education of our bodies, and our bodily experiences. In particular of female bodies, which have for so long been seen as an extension of male bodies. No-one knows enough about female bodies. This perpetuates issues around consent, uneducated choices and creates misplaced and unnecessary guilt, shame and confusion for females when subjected to these harms.
“Just because you are not part of the problem, does not mean you are part of the solution.“
Finally, though we have no intention or illusion of resolution with just one talk, or even a series of them – we moved to consider some ways forward. A very clear message was that this requires action – and this action should not fall on women and girls to protect themselves, but for perpetrators for be stopped. We need allies, of all backgrounds, but in particular, we need male allies. We need male allies who have the education, and the words necessary to identify and call out the behaviour of their peers, their friends, their colleagues, of strangers on the bus. We asked – would being challenged by a ‘peer’ have more impact? Simply not being a perpetrator, is not enough.
Is Criminology Up to Speed with AI Yet?
On Tuesday, 20th June 2023, the Black Criminology Network (BCN) together with some Criminology colleagues were awarded the Culture, Heritage, and Environment Changemaker of the Year Award 2023. The University of Northampton Changemaker Awards is an event showcasing, recognising, and celebrating some of the key success and achievements of staff, students, graduates, and community initiatives.
For this award, the BCN, and the team held webinars with a diverse audience from across the UK and beyond to mark the Black History Month. The webinars focused on issues around the ‘criminalisation of young Black males, the adultification of Black girls, and the role of the British Empire in the marking of Queen Elizabeth’s Jubilee.’. BCN was commended for ‘creating a rare and much needed learning community that allows people to engage in conversations, share perspectives, and contextualise experiences.’ I congratulate the team!
The award of the BCN and Criminology colleagues reflects the effort and endeavour of Criminologists to better society. Although Criminology is considered a young discipline, the field and the criminal justice system has always demonstrated the capacity to make sense of criminogenic issues in society and theorise about the future of crime and its administration/management. Radical changes in crime administration and control have not only altered the pattern of some crime, but criminality and human behaviour under different situations and conditions. Little strides such as the installation and use of fingerprints, DNA banks, and CCTV cameras has significantly transformed the discussion about crime and crime control and administration.
Criminologist have never been shy of reviewing, critiquing, recommending changes, and adapting to the ever changing and dynamic nature of crime and society. One of such changes has been the now widely available artificial intelligence (AI) tools. In my last blog, I highlighted the morality of using AI by both academics and students in the education sector. This is no longer a topic of debate, as both academics and students now use AI in more ways than not, be it in reading, writing, and formatting, referencing, research, or data analysis. Advance use of various types of AI has been ongoing, and academics are only waking up to the reality of language models such as Bing AI, Chat GPT, Google Bard. For me, the debate should now be on tailoring artificial intelligence into the curriculum, examining current uses, and advancing knowledge and understanding of usage trends.
For CriminologistS, teaching, research, and scholarship on the current advances and application of AI in criminal justice administration should be prioritised. Key introductory criminological texts including some in press are yet to dedicate a chapter or more to emerging technologies, particularly, AI led policing and justice administration. Nonetheless, the use of AI powered tools, particularly algorithms to aid decision making by the police, parole, and in the courts is rather soaring, even if biased and not fool-proof. Research also seeks to achieve real-world application for AI supported ‘facial analysis for real-time profiling’ and usage such as for interviews at Airport entry points as an advanced polygraph. In 2022, AI led advances in the University of Chicago predicted with 90% accuracy, the occurrence of crime in eight cities in the US. Interestingly, the scholars involved noted a systemic bias in crime enforcement, an issue quite common in the UK.
The use of AI and algorithms in criminal justice is a complex and controversial issue. There are many potential benefits to using AI, such as the ability to better predict crime, identify potential offenders, and make more informed decisions about sentencing. However, there are also concerns about the potential for AI to be biased or unfair, and to perpetuate systemic racism in the criminal justice system. It is important to carefully consider the ethical implications of using AI in criminal justice. Any AI-powered system must be transparent and accountable, and it must be designed to avoid bias. It is also important to ensure that AI is used in a way that does not disproportionately harm marginalized communities. The use of AI in criminal justice is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about crime and justice. With careful planning and implementation, AI can be used to make the criminal justice system fairer and more effective.
AI has the potential to revolutionize the field of criminology, and criminologists need to be at the forefront of this revolution. Criminologists need to be prepared to use AI to better understand crime, to develop new crime prevention strategies, and to make more informed decisions about criminal justice. Efforts should be made to examine the current uses of AI in the field, address biases and limitations, and advance knowledge and understanding of usage trends. By integrating AI into the curriculum and fostering a critical understanding of its implications, Criminologists can better equip themselves and future generations with the necessary tools to navigate the complex landscape of crime and justice. This, in turn, will enable them to contribute to the development of ethical and effective AI-powered solutions for crime control and administration.
An alternative Christmas message

Sometime in October stores start putting out Christmas decorations, in November they slowly begin to play festive music and by December people organise office parties and exchange festive cards. For the best part of the last few decades these festive conventions seem to play a pivotal role in the lead up to Christmas. There are jumpers with messages, boxes of chocolates and sweets all designed to spread some festivity around. For those working, studying, or both, their December calendar is also a reminder of the first real break for some since summer.
The lead up to Christmas with the music, stories and wishes continues all the way to the New Year when people seem to share their goodwill around. Families have all sorts of traditions, putting up the Xmas tree on this day, ordering food from the grocers on that day, sending cards to friends and family by that day. An arrangement of dates and activities. On average every person starts in early December recounting their festive schedule. Lunch at mum’s, dinner at my brother’s, nan on Boxing Day with the doilies on the plates, New Years Eve at the Smiths where Mr Smith gets hilariously drunk and starts telling inappropriate jokes and New Year’s at the in-laws with their sour-faced neighbour.
People arrange festivities to please people around them; families reunite, friends are invited, meaningful gifts are bought for significant others and of course buy we gifts for children. Oh, the children love Christmas! The lights, the festive arrangements, the delightful activities, and the gifts! The newest trends, the must have toys, all shiny and new, wrapped up in beautiful papers with ribbons and bows. In the festive season, we must not forget the kind words we exchange, the messages send by local communities, politicians and even royalty. Words full of warmth, well-meaning, perspective and reflection. Almost magical the sights and sounds wrapped around us for over a month to make us feel festive.
It is all too beautiful, so you can be forgiven to hardly notice the lumbering shadow, at the door of an abandoned shop. Homelessness is not a lifestyle as despicably declared by a Conservative councillor/newspapers decades ago. It is the human casualty of those who have been priced out in the war of life. Even since the world went into a deep freeze due to the recession over a decade ago and the world is still in the clutches of that freeze. More people read about Christmas stories in books and in movies, because an even increasing number of people do not share the experience. Homelessness is the result of years of criminal indifference and social neglect that leads more people to live and experience poverty. A spectre is haunting Europe, the spectre of homelessness. There is no goodwill at the inn whilst the sins of the “father” are now returning in the continent! Centuries of colonial oppression across the world lead to a wave of refugees fleeing exploitation, persecution, and crippling poverty. Unlike the inn-keeper and his daughter, the roads are closed, and the passages are blocked. Clearly, they don’t fit with the atmosphere… nor do the homeless. Come to think of it, neither do the old people who live alone in their cold homes. None of these fit with the festive narrative.
As I walked down a street I passed a homeless guy is curled up in a shop door. A combination of cardboard, sleeping bag and newspapers all jumbled together. Next to him a dog on the cardboard and around them fairy lights. This man I do not know, his face I have not seen, his identity I ignore; but I imagine that when he was born, there was someone who congratulated his mother for having a healthy boy. Now he is alone, fortunate to have a canine companion, as so many do not have anyone. What stands out is that this person, who our festive plans had excluded, is there with his fairy lights, maybe the most festive of all people, without a burgundy coat, I hear some people like these days.
It is so difficult to say Merry Christmas this year. In a previous entry the world cup and its aftermath left a bitter taste in those who believe in making a better world. The economic gap between whose who have and those who do not, increases; the social inequalities deepen but I feel that we can be like that man with the fairy lights, fight back, rise up and end the party for those who like to wear burgundy, or those who like to speak for world events, at a price.
Merry Christmas, my dear criminologists, the world can change, when we become the agents of change.
Criminology First Week Activity (2021)

Before embarking on a new academic year, it is always worth reflecting on previous years. In 2020, the first year we ran this activity, it was a response to the challenges raised by the Covid-19 pandemic and was designed to serve two different aims. The first of these, was of course, academic, we wanted students to engage with a activity designed to explore real social problems through visual criminology, inspiring the criminological imagination for the year ahead. Second, we were operating in an environment that nobody was prepared for: online classes, limited physical contact, mask wearing, hand sanitising, socially distanced. All of these made it very difficult for staff and students to meet and to build professional relationships. The team needed to find a way for people to work together safely, within the constraints of the Covid legislation of the time and begin to build meaningful relationships with each other.
The start of the 2021/2022 academic year had its own pandemic challenges with many people still shielding, others awaiting covid vaccinations and the sheer uncertainty of going out and meeting people under threat of a deadly disease. After taking on board student feedback, we decided to run a similar activity during the first week of the new term. As before, students were placed into small groups, advised to take the default approach of online meetings (unless all members were happy to meet physically), provided with a very short prompt and limited guidance as to how best to tackle the project. The prompts were as follows:
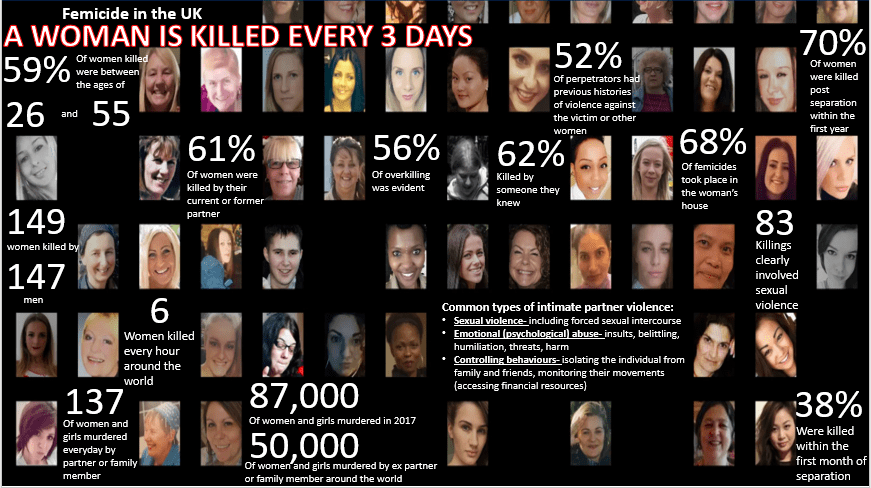
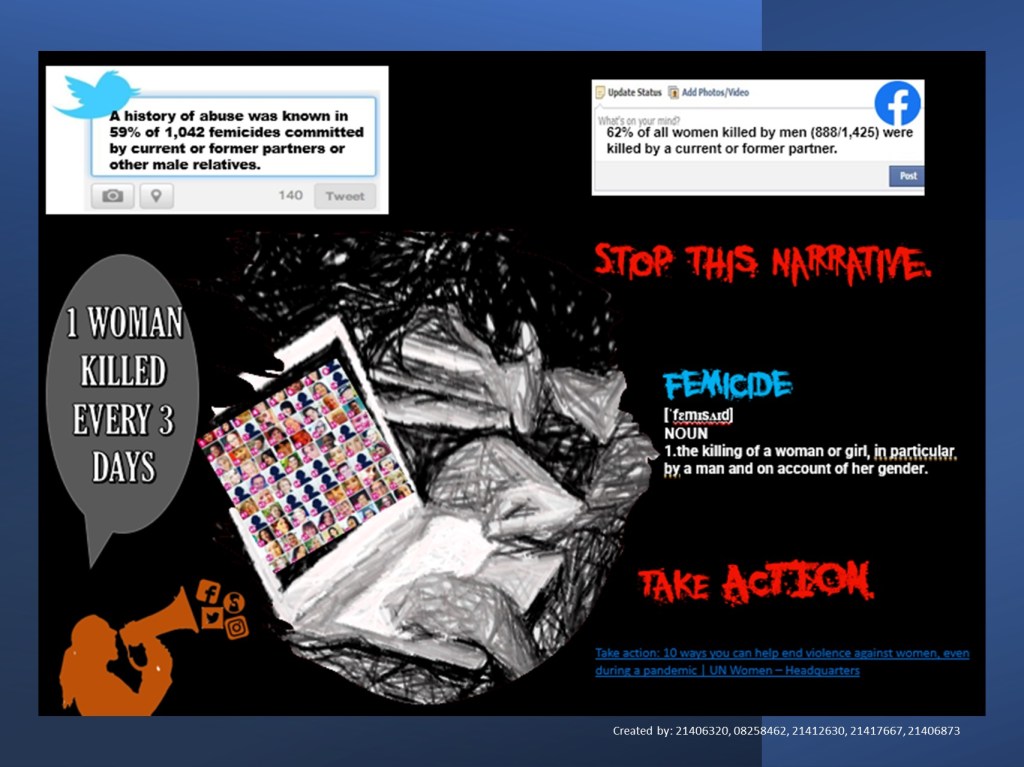
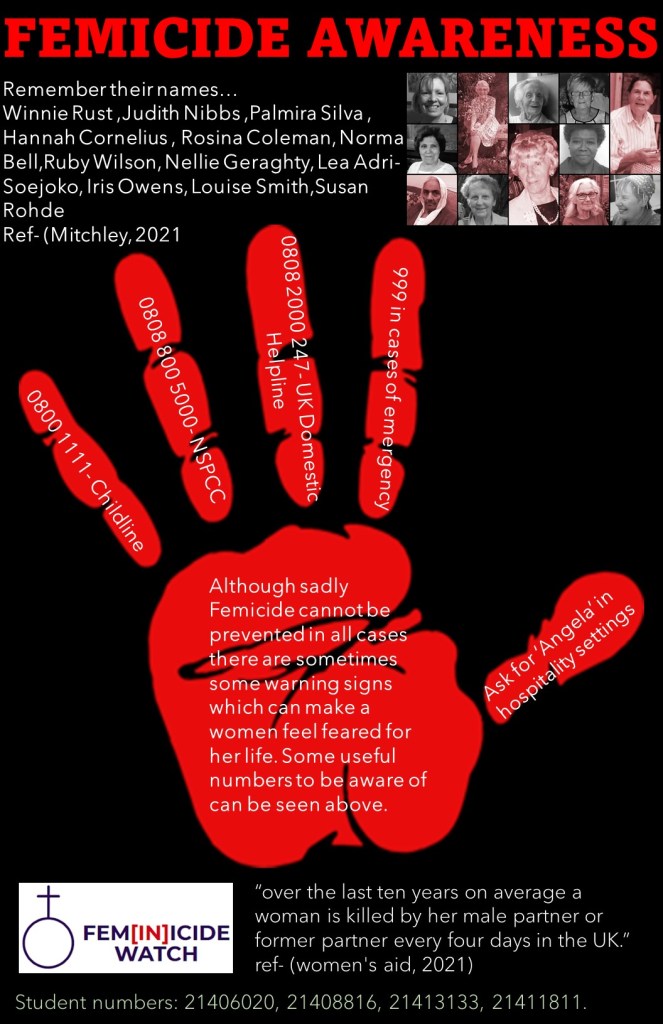
Year 1: Femicide
Year 2: Mandatory covid vaccinations
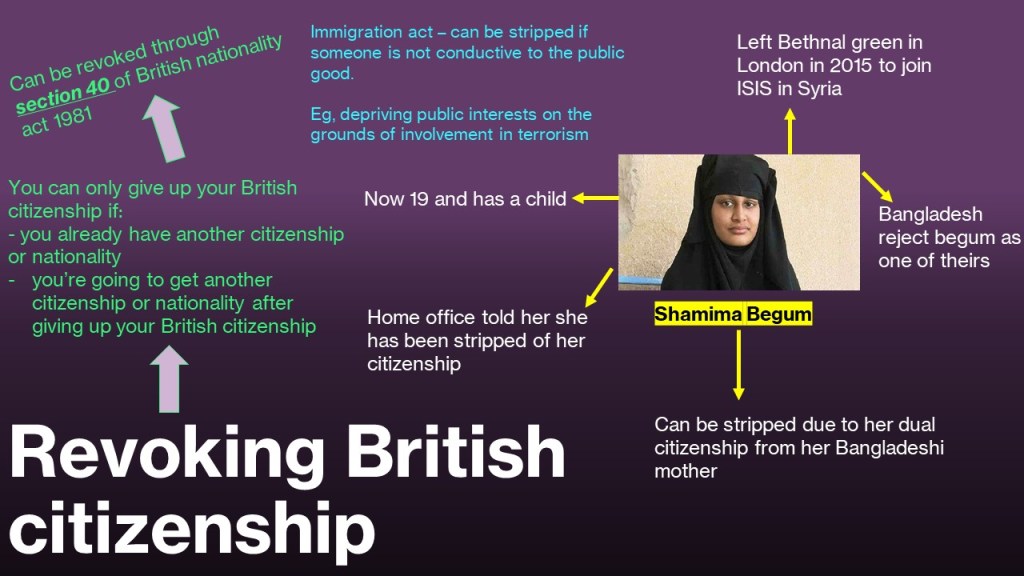
Year 3: Revoking British citizenship
Many of the students had never physically met, yet managed to come together in the midst of a pandemic, negotiate a strategy, carry out the work and produce well designed and thoughtful, criminological posters.
As can be seen from the collage below, everyone involved embraced the challenge and created some remarkable posters. Some of these have been shared previously across social media but this is the first time they have all appeared together in one place.
I am sure everyone will agree our students demonstrated knowledge, understanding, resilience and stamina. We will be running a similar activity for the first week of the academic year 2022-2022, with different prompts to provoke thought and encourage dialogue and team work. We’ll also take on board student and staff feedback from the previous two activities. Plato once wrote that ‘our need will be the real creator’, put more colloquially, necessity is the mother of all invention, and that is certainly true of our first week activity.
Who knows what exciting ideas and posters will be demonstrated this time, but one thing is for sure Criminology students have the opportunity to flex their activism, prepare to campaign for social justice, in the process becoming real #Changemakers.
Criminology First Week Activity (2020)

As we prepare to start the new academic year, it is worth reflecting on the beginning of the last one. In 2020 we began the academic year with a whole cohort activity designed to explore visual criminology and inspire the criminological imagination. Students were placed into small (socially distanced) groups, provided with a very short prompt and limited guidance as to how best to tackle the project. The prompts were as follows:
Year 1: Knife Crime
Year 2: Policing Protest (e.g. Black Lives Matter, Extinction Rebellion and so on)
Year 3: Creating Criminals: the CJS during the Covid-19 pandemic
Many of the students had never physically met, yet managed to come together in the midst of a pandemic, negotiate a strategy, carry out the work and produce well designed and thoughtful, criminological posters.
As can be seen from the collage below, everyone involved embraced the challenge and created some remarkable posters. Some of these have been shared previously across social media but this is the first time they have all appeared together in one place.
I am sure everyone will agree our students demonstrated knowledge, understanding, resilience and stamina. We will be running a similar activity for the first week of the academic year 2021-2022, with different prompts to provoke thought and encourage dialogue and team work. Who knows what exciting ideas and posters will be demonstrated this time, but one thing is for sure Criminology students have the opportunity to campaign for social justice becoming real #Changemakers.
As a Member Pioneer supporting the Police
Stephanie graduated in 2015 having read BA (Hons) Criminology (with Education Studies
Since January 2018, I have worked part time as a Co-op Member Pioneer, for the area of Yardley Wood in Birmingham. In my role, I do charity work, support the local causes, aid the community and local people, run a litter pickers’ forum, build and establish local networks, do work with the council and the police. Throughout my time doing this role, I have loved every challenge thrown at me, and have increasingly done more work supporting the police.
When I first met with some of the PCSOs [Police Community Support Officers] last year, I began doing more work supporting them, and helping the community with crime-related issues. I had been informed by one of the PCSOs that the Billseley Police (whom cover Yardley Wood) are the smallest police team in the country, made up of 7 staff (the Sergeant, 4 PCSOs and 2 police officers, soon to become 3 as one of the PCSOs is training to be a full officer).
In June 2018 and 2019, during the Co-op Fortnight, I hosted a ‘Meet your Member Pioneer’ event in store, where the local community could anonymously write down something to make the local community better. I received a huge number of crime related issues, such as people knowing where drug dealers and addicts were, issues of people speeding and parking dangerously outside schools, issues of knife crime, anti-social behaviour, and people wanting there to be more police on the streets for safety and protection.
On both occasions, after getting all the crime-related notes out, I emailed the police department everything that had been written down, helping the police get more information from the public on different issues that were all dealt with. Being a community pioneer in non-police uniform, it made it easier for the public to privately disclose and offload their crime-related concerns, knowing that it would be taken seriously, and forwarded on. In an effort to further support the police with extending the reach to the local community, I advertise their events on my social media sites, saving them time and resources, and encourage people to attend, or message me any concerns they would like me to take forward.
After being introduced to staff, from Livingstone House (an organisation that helps recovering addicts), SIFA Fireside (that deals with homelessness and social exclusion), the Moseley Exchange (a business enterprise group that runs various community projects), I’m helping build community networks that the police can rely on to help people from different demographics, as well as aid them in their understanding of how to help addicts, beggars, the homeless, and many others. This has enabled the police to have access to a range of resources and information and contacts whom they can rely on and get advice from.
More recently, after getting in touch with David Jamieson, the Police and Crime Commissioner, I am helping the police set up a knife bank near the station. I’ve also gotten in touch with and organisation called Activating Creative Talent that does knife crime awareness training in schools, and am working with one of the PCSOs on delivering knife awareness education in schools and in the community. It’ll be a big, ongoing community project that is soon to take off!
In the role, I love all that I do supporting the police. I never imagined that as a community pioneer, I would aid and support the police in the capacity that I have.
Thinking “outside the box”

Having recently done a session on criminal records with @paulaabowles to a group of voluntary, 3rd sector and other practitioners I started thinking of the wider implications of taking knowledge out of the traditional classroom and introducing it to an audience, that is not necessarily academic. When we prepare for class the usual concern is the levelness of the material used and the way we pitch the information. In anything we do as part of consultancy or outside of the standard educational framework we have a different challenge. That of presenting information that corresponds to expertise in a language and tone that is neither exclusive nor condescending to the participants.
In the designing stages we considered the information we had to include, and the session started by introducing criminology. Audience participation was encouraged, and group discussion became a tool to promote the flow of information. Once that process started and people became more able to exchange information then we started moving from information to knowledge exchange. This is a more profound interaction that allows the audience to engage with information that they may not be familiar with and it is designed to achieve one of the prime quests of any social science, to challenge established views.
The process itself indicates the level of skill involved in academic reasoning and the complexity associated with presenting people with new knowledge in an understandable form. It is that apparent simplicity that allows participants to scaffold their understanding, taking different elements from the same content. It is easy to say to any audience for example that “every person has an opinion on crime” however to be able to accept this statement indicates a level of proficiency on receiving views of the other and then accommodating it to your own understanding. This is the basis of the philosophy of knowledge, and it happens to all engaged in academia whatever level, albeit consciously or unconsciously.
As per usual the session overran, testament that people do have opinions on crime and how society should respond to them. The intriguing part of this session was the ability of participants to negotiate different roles and identities, whilst offering an explanation or interpretation of a situation. When this was pointed out they were surprised by the level of knowledge they possessed and its complexity. The role of the academic is not simply to advance knowledge, which is clearly expected, but also to take subjects and contextualise them. In recent weeks, colleagues from our University, were able to discuss issues relating to health, psychology, work, human rights and consumer rights to national and local media, informing the public on the issues concerned.
This is what got me thinking about our role in society more generally. We are not merely providing education for adults who wish to acquire knowledge and become part of the professional classes, but we are also engaging in a continuous dialogue with our local community, sharing knowledge beyond the classroom and expanding education beyond the campus. These are reasons which make a University, as an institution, an invaluable link to society that governments need to nurture and support. The success of the University is not in the students within but also on the reach it has to the people around.
At the end of the session we talked about a number of campaigns to help ex-offenders to get forward with work and education by “banning the box”. This was a fitting end to a session where we all thought “outside the box”.