Home » politics (Page 3)
Category Archives: politics
ASUU vs The Federal Government
It will be 8 months in October since University Lecturers in Nigeria have embarked on a nationwide strike without adequate intervention from the government. It is quite shocking that a government will sit in power and cease to reasonably address a serious dispute such as this at such a crucial time in the country.
As we have seen over the years, strike actions in Nigerian Universities constitute an age-long problem and its recurring nature unmasks, quite simply, how the political class has refused to prioritise the knowledge-based economy.
In February 2022, the Academic Staff Union of Universities (ASUU) leadership
(which is the national union body that represents Nigerian University Lecturers during disputes) issued a 4-week warning strike to the Nigerian government due to issues of funding of the public Universities. Currently, the striking University Lecturers are accusing the government of failing to revitalise the dilapidated state of Nigerian Universities, they claim that the government has refused to implement an accountability system called UTAS and that representatives of the government have continued to backtrack on their agreement to adequately fund the Universities.
The government on the other hand is claiming that they have tried their best in negotiating with the striking lecturers – but that the lecturers are simply being unnecessarily difficult. Since 2017, several committees have been established to scrutinize the demands and negotiate with ASUU, but the inability of these committees to resolve these issues has led to this 8-month-long closure of Nigerian Universities. While this strike has generated multiple reactions from different quarters, the question to be asked is – who is to be blamed? Should the striking lecturers be blamed for demanding a viable environment for the students or should we be blaming the government for the failure of efforts to resolve this national embarrassment?
Of course, we can all understand that one of the reasons why the political class is often slow to react to these strike actions is because their children and families do not attend these schools. You either find them in private Universities in Nigeria or Universities abroad – just the same way they end up traveling abroad for medical check-ups. In fact, the problems being faced in the educational sector are quite similar to those found within the Nigerian health sector – where many doctors are already emigrating from the country to countries that appreciate the importance of medical practitioners and practice. So, what we find invariably is a situation where the children of the rich continue to enjoy uninterrupted education, while the children of the underprivileged end up spending 7 years on a full-time 4-year program, due to the failure of efforts to preserve the educational standards of Nigerian institutions.
In times like these, I remember the popular saying that when two elephants fight, it’s the grass that suffers. The elephants in this context are both the federal government and the striking lecturers, while those suffering the consequences of the power contest are the students. The striking lecturers have not been paid their salaries for more than 5 months, and they are refusing to back down. On the other hand, the government seems to be suggesting that when they are “tired”, they will call off the strike. I am not sure that strike actions of the UK UCU will last this long before some sort of agreement would have been arranged. Again, my heart goes out to the Nigerian students during these hard times – because it is just unimaginable what they will be going through during these moments of idleness. And we must never forget that if care is not taken, the idle hand will eventually become the devil’s workshop!
Having said this, Nigerian Universities must learn from this event and adopt approaches through which they can generate their income. I am not inferring that they do not, but they just need to do more. This could be through ensuring large-scale investment programs, testing local/peculiar practices at the international level, tapping into research grant schemes, remodeling the system of tuition fees, and demonstrating a stronger presence within the African markets. As a general principle, any institution that wishes to reap the dividends of the knowledge-based economy must ensure that self-generated revenues should be higher than the government’s grants – and not the other way. So, Universities in Nigeria must strive to be autonomous in their engagements and their organisational structure – while maintaining an apolitical stance at all times.
While I agree that all of these can be difficult to achieve (considering the socio-political dynamics of Nigeria), Universities must remember that the continuous dependence on the government for funds will only continue to subject them to such embarrassments rather than being seen as respected intellectuals in the society. Again, Nigerian Universities need a total disruption; there is a need for a total overhaul of the system and a complete reform of the organisational structure and policies.
Chaos in Colombo: things fall apart

Following the mutiny that we witnessed in Downing street after members of the Johnson’s cabinet successfully forced him to resign over accusations of incompetency and the culture of inappropriate conducts in his cabinet, the people of Sri Lanka have also succeeded in chasing out their President, G. Rajapaksa, out of office over his contributions to the collapse of the country’s economy. This blog is a brief commentary on some of the latest events in Sri Lanka.
Since assuming office in 2019, the government of Rajapaksa has always been indicted of excessive borrowing, mismanagement of the country’s economy, and applying for international loans that are often difficult to pay back. With the country’s debt currently standing at $51bn, some of these loans, is claimed to have been spent on unnecessary infrastructural developments as well as other ‘Chinese-backed projects’, (see also; the Financial Times, 2022). Jayamaha (2022; 236) indicated that ‘Sri Lanka had $7.6 billion in foreign currency reserves at the end of 2019. However, by March 2020, it had exhausted its reserves to just $1.93 billion.’ One of Rajapaksa’s campaign promises was to cut taxes, which he did upon assuming office. His critics faulted this move, claiming it was unnecessary at that particular time. His ban on fertilizers, in a bid for the country to go organic (even though later reversed), had its own effect on local farmers. Rice production for example, fell by 20% following the ban – a move that eventually forced the government to opt for rice importation which was in itself expensive (see also; Nordhaus & Shah 2022). Critics warned that his investments and projects have no substantial and direct impact on the lives of the common people, and that what is the essence of building roads when the common people cannot afford to buy a car to ride on those roads? The fact that people have to queue for petrol for 5 days and only having to work for 1 day or where families cannot afford to feed their children simply shows how the government of Rajapaksa seem to have mismanaged the economy of the country. Of course, the problem of insecurity and the pandemic cannot be left out as crucial factors that have also impacted tourism levels and the economy of the country.
Foreign reserves have depleted, the importation of food is becoming difficult to actualise, living expenses have risen to high levels, the country is struggling with its international loan repayments, the value of Rupees has depreciated, there is inflation in the land, including shortages of food supplies and scarcity of fuel. Those who are familiar with the Sri Lanka’s system will not be particularly surprised at the nationwide protests that have been taking place in different parts of the country since May, because the Rajapaksa’s regime was only sitting on a keg of gun powder, ready to explode.
In an unprecedented fashion on July 9, several footages and images began to emerge online showing how protesters had successfully overpowered the police and had broken into the residence of the President. Their goal was to occupy the presidential palace and chase the president out of his residence. In fact, there are video footages online allegedly showing the motorcade of the president fleeing from his residence as the wave of protest rocked the capital.
Upon gaining entry into the innermost chambers of the president’s dwelling, protesters started touring and taking selfies in euphoria, some of them had quickly jumped into the presidential shower, others helped themselves to some relaxation on the president’s bed after days of protests, some were engaged in a mock presidential meeting in the president’s cabinet office, some preferred to swim in the president’s private pool while others helped themselves to some booze.
Indeed, these extraordinary scenes should not be taken for granted for they again reaffirm WB Yeats classic idea of anarchy (in ‘the second coming’ poem), being the only option to be exercised when the centre can no longer hold.
Of course, some may ask that now that they have invaded the presidential villa, what next? In my view, the people of Sri Lanka seem to be on the right direction as President Rajapaska has eventually bowed to pressure and agreed to resign. The next phase now is for the country to carefully elect a new leader who will revive the sinking ship, amend the economic policies, foster an effective democratic political culture which (hopefully) should bring about a sustainable economic plan and growth reforms.
Importantly, this is a big lesson not just for the political class of Sri Lanka, but for other wasteful leaders who continue to destroy their economies with reckless and disastrous policies. It is a lesson of the falcon and the falconer – for when the falcon can no longer hear the falconer, scenes like these may continue to be reproduced in other locations of the world.
Indeed, things fell apart in Colombo, but it is hoped that the centre will hold again as the country prepare to elect its new leaders.
Here is wishing the people of Colombo, and the entire Sri Lankans all the best in their struggle.
References
Financial Times (2022) [Twitter] 20 July. Available at: https://mobile.twitter.com/FinancialTimes/status/1549554792766361603
Jayamaha, J. (2022) “The demise of Democracy in Sri Lanka: A study of the political and economic crisis in Sri Lanka (Based on the incident of the Rambukkana shooting)”, Sprin Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, 1(05), pp. 236–240. doi: 10.55559/sjahss.v1i05.22.
Nordhaus, T & Shah S, (2022) In Sri Lanka, Organic Farming Went Catastrophically Wrong, March 5, FP. Available at: https://foreignpolicy.com/2022/03/05/sri-lanka-organic-farming-crisis/
What’s happened to the Pandora papers?
Sometime last week, I was amid a group of friends when the argument about the Pandora papers suddenly came up. In brief, the key questions raised were how come no one is talking about the Pandora papers again? What has happened to the investigations, and how come the story has now been relegated to the back seat within the media space? Although, we didn’t have enough time to debate the issues, I promised that I would be sharing my thoughts on this blog. So, I hope they are reading.
We can all agree that for many years, the issues of financial delinquencies and malfeasants have remained one of the major problems facing many societies. We have seen situations where Kleptocratic rulers and their associates loot and siphon state resources, and then stack them up in secret havens. Some of these Kleptocrats prefer to collect luxury Italian wines and French arts with their ill-gotten wealth, while others prefer to purchase luxury properties and 5-star apartments in Dubai, London and elsewhere. We find military generals participating in financial black operations, and we hear about law makers manipulating the gaps in the same laws they have created. In fact, in some spheres, we find ‘business tycoons’ exploiting violence-torn regions to smuggle gold, while in other spheres, some appointed public officers refuse to declare their assets because of fear of the future. Two years ago, we read about the two socialist presidents of the southern Spanish region and how they were found guilty of misuse of public funds. Totaling about €680m, you can imagine the good that could have been achieved in that region. We should also not forget the case of Ferdinand Marcos and his wife, both of whom (we are told) amassed over $10 billion during their reign in the Philippines. As we can see below that from the offshore leak of 2013 to the Panama papers of 2016 and then the 2017 Paradise papers, data leaks have continued to skyrocket. This simply demonstrates the level to which politicians and other official state representatives are taking to invest in this booming industry.
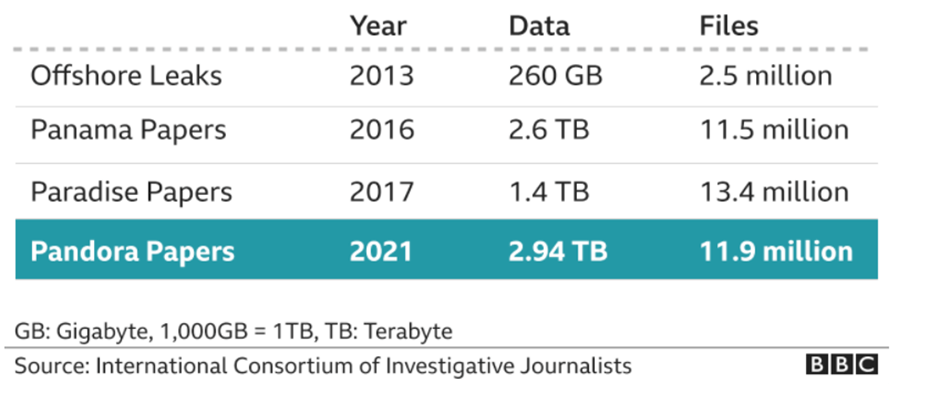
These stories are nothing new, we have always read about them – but then they fade away quicker than we expect. It is important to note that while some countries are swift in conducting investigation when issues like these arise, very little is known about others. So, in this blog, I will simply be highlighting some of the reasons why I think news relating to these issues have a short life span.
To start with, the system of financial corruption is often controlled and executed by those holding on to power very firmly. The firepower of their legal defence team is usually unmatchable, and the way they utilise their wealth and connections often make it incredibly difficult to tackle. For example, when leaks like these appear, some journalists are usually mindful of making certain remarks about the situation for the avoidance of being sued for libel and defamation of character. Secondly, financial crimes are always complex to investigate, and prosecution often takes forever. The problem of plurality in jurisdiction is also important in this analysis as it sometimes slows down the processes of investigation and prosecution. In some countries, there is something called ‘the immunity clause’, where certain state representatives are protected from being arraigned while in office. This issue has continued to raise concerns about the position of truth, power, and political will of governments to fight corruption. Another issue to consider is the issue of confidentiality clause, or what many call corporate secrecy in offshore firms. These policies make it very difficult to know who owns what or who is purchasing what. So, for as long as these clauses remain, news relating to these issues may continue to fade out faster than we imagine. Perhaps Young (2012) was right in her analysis of illicit practices in banking & other offshore financial centres when she insisted that ‘offshore financial centers such as the Cayman Islands, often labelled secrecy jurisdictions, frustrate attempts to recover criminal wealth because they provide strong confidentiality in international finance to legitimate clients as well as to the crooks and criminals who wish to hide information – thereby attracting a large and varied client base with their own and varied reasons for wanting an offshore account’, (Young 2012, 136). This idea has also been raised by our leader, Nikos Passas who believe that effective transparency is an essential component of unscrambling the illicit partnerships in these structures.
While all these dirty behaviours have continued to damage our social systems, they yet again remind us how the network of greed remains at the core centre of human injustice. I found the animalist commandant of the pigs in the novel Animal Farm, by George Orwell to be quite relevant in this circumstance. The decree spells: all animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others. This idea rightly describes the hypocrisy that we find in modern democracies; where citizens are made to believe that everyone is equal before the law but when in fact the law, (and in many instances more privileges) are often tilted in favour of the elites.
I agree with the prescription given by President Obama who once said that strengthening democracy entails building strong institutions over strong men. This is true because the absence of strong institutions will only continue to pave way for powerful groups to explore the limits of democracy. This also means that there must be strong political will to sanction these powerful groups engaging in this ‘thievocracy’. I know that political will is often used too loosely these days, but what I am inferring here is genuine determination to prosecute powerful criminals with transparency. This also suggests the need for better stability and stronger coordination of law across jurisdictions. Transparency should not only be limited to governments in societies, but also in those havens. It is also important to note that tackling financial crimes of the powerful should not be the duty of the state alone, but of all. Simply, it should be a collective effort of all, and it must require a joint action. By joint action I mean that civil societies and other private sectors must come together to advocate for stronger sanctions. We must seek collective participation in social movements because such actions can bring about social change – particularly when the democratic processes are proving unable to tackle such issues. Research institutes and academics must do their best by engaging in research to understand the depth of these problems as well as proffering possible solutions. Illicit financial delinquencies, we know, thrive when societies trivialize the extent and depth of its problem. Therefore, the media must continue to do their best in identifying these problems, just as we have consistently seen with the works of the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists and a few others. So, in a nutshell and to answer my friends, part of the reasons why issues like this often fade away quicker than expected has to do with some of the issues that I have pointed out. It is hoped however that those engaged in this incessant accretion of wealth will be confronted rather than conferred with national honors by their friends.
References
BBC (2021) Pandora Papers: A simple guide to the Pandora Papers leak. Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-58780561 (Accessed: 26 May 2022)
Young, M.A., 2012. Banking secrecy and offshore financial centres: money laundering and offshore banking, Routledge
Policy, procedures, processes, and failure
Examine any organisation and you will find a myriad of policy and procedures that are designed to inform its processes and guide employees. On paper, these formalised ideals and directions make absolute sense but frequently they bear no relationship to reality and rather than empowering, they constrain and often demoralise. These idealistic notions of how an organisation should function facilitate the dehumanising effects of managerial diktat and engender an internalisation of failure amongst employees.
By way of an example, in the 1990s police forces began to consider notions of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) in respect of crime investigation. These SOPs seemed on the face of it to be a good idea. The police service, driven by government notions of New Public Management, were being measured on crime reduction and crime detection. Performance indicators were propped up by idealistic notions coming out of government supported by HMIC and the now defunct Audit Commission that catching more criminals would engender a virtuous circle resulting in crime reduction. Nothing of course, was further from the truth. But the introduction of SOPs was meant to attempt to address police failings. These, certainly in one force, were at the outset seen as a guide, a minimum standard required in an investigation. They weren’t intended to constrain.
A small department was set up in this force to measure adherence to these SOPs and to report back where there were inherent failures. For example, on attending a house burglary, the attendant officers were required to take a statement from the householder, and they were required to carry out house to house enquiries in the vicinity. At the very least, they needed to knock on doors either side of the house that had been burgled and a couple of houses across the road. Frequently the statement wasn’t taken, or the house-to-house enquiries hadn’t been completed. It became clear that the officers were failing to carry out simple procedures. Measuring adherence to SOPs and providing feedback to promote improvement soon resulted in measuring adherence in order to enforce compliance.
In hindsight, there should have been a realisation that the SOPs, far from being helpful were in fact having a detrimental effect. Where officers could have carried out further investigations based on their professional judgement, they adhered to the minimum required in the SOPs or simply failed to comply with them fully. This was partially resultant of a notion amongst officers that discretion was being curtailed, but more notably it was driven by other processes and organisational priorities. These other processes were to do with attendance at other incidents. Graded as a priority by the control room, officers were being pulled off the burglary investigation and therefore couldn’t comply with the burglary investigation SOPs. Police forces were also being measured on how quickly they responded to and arrived at various calls for service. There was clearly a direct conflict between management ideals and reality with the officers being set up to fail in one aspect or another. There were simply not enough staff to do all the work and to manage the overwhelming demands at certain times.
One way of dealing with the failures was to link these to the performance and development review (PDR) process. The development aspect was a somewhat redundant term as the PDR was all about performance. Of course, each time the PDR came around the officers had failed to achieve their objectives. This provided lots of evidence of people not doing their job properly. In the wider gamut of crime figures officers at various levels began to realise that the only way to avoid accusations of poor performance was to manipulate the crime figures. In the meantime, those driving the behaviours, washed their hands of them whenever someone was found out, often hiding behind the SOPs and policy. The misuse of the PDR process and the consistent scrutiny of performance metrics resulted in the internalising of failure by staff. Whole systems and processes had been set up to measure failure, after all how could success be measured if it could never be achieved. Of course, it could never be achieved because the ambition and driving force behind this, government’s notions of crime control, were based on ideals and rhetoric not science. But the overriding fact was that it could never be achieved because there were never enough resources to achieve it.
The failure of course wasn’t in the officers that didn’t adhere to the SOPs or those that manipulated crime figures to try to avoid overbearing scrutiny, it was the failure of managers to provide adequate resources. It was a failure of managers to try to understand what reality looked like and it was a failure of managers to deal with the dehumanising effects of policy, procedure and processes.
Having left the police, I thought higher education would somehow be different. I don’t think I need to say anymore.
They think it’s all over…….

Probably the most famous quote in the history of English football was that made by Kenneth Wolstenholme at the end of the 1966 World Cup final where he stated as Geoff Hurst broke clear of the West German defence to score the 4th goal that “Some people are on the pitch…. they think it’s all over…….it is now”. I have been reminded of this quote as we reach April 1st, 2022 when all Coronavirus restrictions in England essentially come to an end. We are moving from a period of pandemic restrictions to one of “living with Covid”. Whilst the prevailing narrative has focussed on “it’s over” the national data sets would suggest it is most definitely not. We are currently experiencing another wave of infections driven by the Omicron BA-2 variant. Cases of Covid infection have been rising steadily over the past couple of weeks and we are now seeing hospital admissions and deaths rise too. This has led to an interesting tension between current politically driven and public health driven advice.
The overriding question then is why remove all restrictions now if infection rates are so high. The answer sits with science and the success of the vaccination programme, and the protection it affords, which to date has seen 86% of the eligible population have two jabs and 68% boosted with a third. Furthermore, we are now at the start of the Spring booster programme for the over 75s and the most vulnerable. The introduction of the vaccine has seen a dramatic fall in serious illness associated with infection and the UK government now believe that this is a virus we can live with and we should get on with our lives in a sensible and cautious way without the need for mandated restrictions. The advances gained in both the vaccination programme, anti-viral therapies and treatments have been enormous and underpin completely the current and future situation. So, the narrative shifts to one that emphasises learning to live with the virus and to that end the Government has provided us with guidance. The UK Government’s “Living with Covid Plan” COVID-19 Response – Living with COVID-19.docx (publishing.service.gov.uk) has four key principles at its heart:
- Removing domestic restrictions while encouraging safer behaviours through public health advice, in common with longstanding ways of managing most other respiratory illnesses;
- Protecting people most vulnerable to COVID-19: vaccination guided by Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) advice, and deploying targeted testing;
- Maintaining resilience: ongoing surveillance, contingency planning and the ability to reintroduce key capabilities such as mass vaccination and testing in an emergency; and
- Securing innovations and opportunities from the COVID-19 response, including investment in life sciences.
So, in addition to the restrictions already removed from 1 April, the Government will:
- Remove the current guidance on voluntary COVID-status certification in domestic settings and no longer recommend that certain venues use the NHS COVID Pass.
- Update guidance setting out the ongoing steps that people with COVID-19 should take to minimise contact with other people. This will align with the changes to testing.
- No longer provide free universal symptomatic and asymptomatic testing for the general public in England.
- Consolidate guidance to the public and businesses, in line with public health advice.
- Remove the health and safety requirement for every employer to explicitly consider COVID-19 in their risk assessments.
- Replace the existing set of ‘Working Safely’ guidance with new public health guidance
My major concern with these changes is the massive scaling back of infection testing. In doing so we run the risk of creating a data vacuum. Being able to test and undertake scientific surveillance of the virus’s future development would help us identify any future threats from new variants; particularly those classified as being “of concern”. What we should have learned from the past two years is that the ability to understand the virus and rapidly scale up our response is critical.
What is also now abundantly clear from the current data is that this is far from over and it is going to take some time for us to adapt as a society. The ongoing consequences for the most vulnerable sections of our society are still incredibly challenging. It will not be a surprise to any health professional that the pandemic was keenest felt in communities already negatively impacted by health inequalities. This has been the case ever since the publication of the “Black Report” (DHSS 1980), which showed in detail the extent to which ill-health and death are unequally distributed among the population of the UK. Indeed, there is evidence that these inequalities have been widening rather than diminishing since the establishment of the National Health Service in 1948. It is generally accepted that those with underlying health issues and therefore most at risk will be disproportionately located in socially deprived communities. Consequently, there is a genuine concern that the most vulnerable to the virus could be left behind in isolation as the rest of society moves on. However, we are now at a new critical moment which most will celebrate. Regardless of whether you believe the rolling back of restrictions is right or not, this moment in time allows us an opportunity to reflect on the past two years and indeed look forward to what has changed and what could happen in terms of both Coronavirus and any other future pandemic.
Looking back, I have no doubt that the last two years have changed life considerably in several positive and negative ways. Of course, we tend to migrate to the negative first and the overall cost of life, levels of infection and the long-term consequences have been immense. The longer-term implications of Covid (Long Covid) is still something we need to take seriously and fully understand. What is not in doubt is the toll this has had on individuals, families, communities and the future burden it places on our NHS. The psychological impact of social isolation and restrictions has been enormous and especially so for our children, young people, the vulnerable and the elderly. The social and educational development of school children is of particular concern. The wider economic implications of the pandemic will take some time to recover. Yet, whilst the negative implications cause us grave concern many features of our lives have improved. Many have identified that this pandemic has helped them re-asses what is important in life, how important key workers are in ensuring society continues to operate smoothly and the critical role health and social services must play in times of health crisis. Changing perspectives on work, work life balance and alternative ways of conducting business have been embraced and many argue that the world of work will never be the same again.
On that final note it’s important that as a society we have learned from what I have previously described as the greatest public health crisis in my lifetime. Pandemic planning was shown to be woefully inadequate and we must get this better because there is no doubt there will be another pandemic of this magnitude at some point in the future. Proper support for health and social services are critical and the state of the NHS at the start of all this was telling. Yes, it rose to the challenge as it always does but health and social care systems were badly let down in the early stages of this pandemic with disastrous consequences. Proper investment in science and research is paramount, for let’s be honest it was science that came to our rescue and did so in record time. There will inevitably be a large public enquiry into all aspects of the pandemic, its management and outcomes. We can only hope that lessons have been learned and we are better prepared for both the ongoing management of this pandemic and inevitably the next one.
Dr Stephen O’Brien
FHES
Originally posted here
DIE in Solidarity with Diversity-Inclusion-Equality
As an associate lecturer on a casual contract, I was glad to stand in solidarity with my friends and colleagues also striking as part of UCU Industrial Action. Concurrently, I was also glad to stand in solidarity with students (as a recent former undergrad and masters student … I get it), students who simply want a better education, including having a curriculum that represents them (not a privileged minority). I wrote this poem for the students and staff taking part in strike action, and it comes inspired from the lip service universities give to doing equality while undermining those that actually do it (meanwhile universities refuse to put in the investment required). This piece also comes inspired by ‘This is Not a Humanising Poem’ by Suhaiymah Manzoor-Khan, a British author-educator from Bradford in Yorkshire.
Some issues force you to protest
the way oppression knocks on your front door
and you can’t block out the noise
“protest peacefully, non-violently”
I have heard people say
show ‘the undecided’, passive respectability
be quiet, leave parts of yourself at home
show them you’re just as capable of being liked
enough for promotion into the canteen,
protest with kindness and humour
make allusions to smiling resisters in literature
they’d rather passive images of Rosa Parks all honestly
but not her politics against racism, patriarchy, and misogyny

but I wanna tell them about British histories of dissent
the good and the bad – 1919 Race Riots
the 1926 general strikes, and the not so quiet
interwar years of Caribbean resistance to military conscription
I wanna talk about how Pride was originally a protest
I wanna talk about the Grunwick Strike and Jayaben Desai
and the Yorkshire miners that came to London in solidarity
with South Asian migrant women in what was 1980s austerity
I want to rant about Thatcherism as the base
for the neoliberal university culture we work in today
I want to talk about the Poll Tax Riots of 1990
and the current whitewashing of the climate emergency
they want protesters to be frugal in activism,
don’t decolonise the curriculum
they say decolonise
they mean monetise, let’s diversify …
but not that sort of diversity
nothing too political, critical, intellectual
transform lives, inspire change?
But no,
they will make problems out of people who complain
it’s your fault, for not being able to concentrate
in workplaces that separate the work you do
from the effects of Black Lives Matter and #MeToo
they make you the problem
they make you want to leave
unwilling to acknowledge that universities
discriminate against staff and students systemically
POCs, working-class, international, disabled, LGBT
but let’s show the eligibility of staff networks
while senior leaders disproportionately hire TERFs

staff and students chequered with severe floggings
body maps of indenture and slavery
like hieroglyphics made of flesh
but good degrees, are not the only thing that hold meaning
workers rights, students’ rights to education
so this will not be a ‘people are human’ poem
we are beyond respectability now
however, you know universities will DIE on that hill
instead,
treat us well when we’re tired
productive, upset, frustrated
when we’re in back-to-back global crises
COVID-19, Black Lives Matter, femicide,
failing in class, time wasting, without the right visas,
the right accents; Black, white, homeless, in poverty,
women, trans, when we’re not A-Grade students, when we don’t
have the right last name; when we’re suicidal
when people are anxious, depressed, autistic
tick-box statistics within unprotected characteristics
all permeates through workers’ and student rights
When you see staff on strike now,
we’re protesting things related to jobs yes,
but also, the after-effects
as institutions always protect themselves
so sometimes I think about
when senior management vote on policies…
if there’s a difference between the nice ones ticking boxes
and the other ones that scatter white supremacy?
I wonder if it’s about diversity, inclusion, and equality [DIE],
how come they discriminate in the name of transforming lives
how come Black students are questioned (under caution) in disciplinaries
like this is the London Met maintaining law and order …
upholding canteen cultures of policing
Black and Brown bodies. Decolonisation is more
than the curriculum; Tuck and Yang
tell us decolonisation is not a metaphor,
so why is it used in meetings as lip service –

why aren’t staff hired in
in critical race studies, whiteness studies, decolonial studies
why is liberation politics and anti-racism not at the heart of this
why are mediocre white men failing upwards,
they tell me we have misunderstood
but promotion based on merit doesn’t exist
bell hooks called this
imperialist heteropatriarchal white supremacy
you know Free Palestine, Black Lives Matter, and the rest
we must protest how we want to protest
we must never be silenced; is this being me radical, am I radical
Cos I’m tired of being called a “millennial lefty snowflake”, when I’m just trying not to DIE?!
Further Reading
Ahmed, Sara (2012) On Being Included: Racism and Diversity in Institutional Life. London: Duke.
Ahmed, Sara (2021) Complaint. London: Duke.
Bhanot, Kavita (2015) Decolonise, Not Diversify. Media Diversified [online].
Double Down News (2021) This Is England: Ash Sakar’s Alternative Race Report. YouTube.
Chen, Sophia (2020) The Equity-Diversity-Inclusion Industrial Complex Gets a Makeover. Wired [online].
Puwar, Nirmal (2004) Space Invaders: Race, Gender and Bodies Out of Place. Oxford: Berg.
Read, Bridget (2021) Doing the Work at Work What are companies desperate for diversity consultants actually buying? The Cut [online].
Ventour, Tré (2021) Telling it Like it is: Decolonisation is Not Diversity. Diverse Educators [online].
A microcosm of deviancy

A little over a week ago our university introduced the compulsory wearing of face masks indoors. This included wearing of masks in classrooms as well as common areas and offices. Some may argue that the new rules were introduced a little too late in the day, whilst I’m sure others will point to the fact that government guidance is that the wearing of face masks is advisory and therefore the introduction of the new rules was unwarranted. Let’s be honest the government and their political party haven’t set much of an example regarding the basic safety ideas, let alone rules, as evidenced by the recent Conservative party conference. The new rules at the university, however, are not enforced, instead there is a reliance that students and staff will comply. This of course creates several dilemmas for students and staff where there is a failure to comply and it makes for some interesting observations about general human behaviour and deviance. To that extent, university life might be viewed as a microcosm of life in the general population and this lends itself quite nicely to the analogy of behaviours whilst driving on a road.
Driving behaviours vary, from those drivers that consistently and diligently stick to the speed limit despite what others may be doing, to those that have complete disregard for limits or indeed others including those that police the roads. Let us be quite clear at this stage, speed limits are nearly always there for a reason. There is ample research that speed kills and that reductions in speed limits injuries and saves life. Whilst those drivers that drive over the speed limit will not always be involved in a collision and that a collision will not always result in serious injury or death, there is a much greater potential for this. The risks of course are spread across the population in the locality, the impact is not just felt by the speeding driver but other drivers and pedestrians as well. To some extent we can make the comparison to the risks associated with catching Covid and the wearing of masks and social distancing, failure to comply increases risks to all. As a quick reminder, the wearing of masks is to protect others more so than it is to protect the individual mask wearer.
Observations of behaviours regarding staff and students wearing masks at the university are interesting. There are those that comply, regardless of what others are doing, some of these will have been wearing masks indoors before the new rules came in. Not dissimilar to the careful driver, sticking to the speed limit but also prepared to drive slower where they perceive there is a greater risk. Then there is the well-intentioned mask wearer, the one that knows the rules and will stick to them but through absent mindedness or through some of life’s many distractions, they fail to wear their masks at various points of the day. As with the well-meaning driver, they are easily reminded and often apologetic, even if it is only to themselves. Of course, there is the ‘follow the flock’ wearer, the person that could quite easily be persuaded to not wear their mask by the rest of the flock as they fail to wear theirs. The driver that joins the rest and drives at 40mph in a 30mph limit because the rest of the traffic is doing so. Next is the deviant that has disregard for the rules as long as no one in authority is looking. The person that keeps their mask handy, probably under their chin and then when challenged in some way, perhaps by a disapproving look from a member of staff or by a direct challenge, puts their mask on but only for the duration they are under observation. Not dissimilar to the speedster that slows down when they see a police vehicle or a static speed camera only to speed up again when the danger of being caught and sanctioned has passed. Finally, there is the person that has complete disregard for any rules, they will blatantly fail to wear a mask and wave away with complete disdain any attempt by student ambassadors positioned at the door to offer them a mask. They like the speeding driver that fails to obey any of the rules of the road have complete disregard for the rules or indeed any rules.
Whilst we may lament the fact that some people forget, are distracted but are generally well meaning, we probably wouldn’t want to impose any sanction for their deviance. But what of those that have complete disregard for the rules? It is worth returning here to the general ethos of wearing masks; to protect others. The disregard for the rules is inter alia a disregard for the safety of others. Whilst we might observe that the deviancy is apparent amongst several students (a problem that might be generalised to society), it is somewhat disconcerting that there are a significant number of staff who clearly do not think the rules apply to them. They seem to neither care about their colleagues nor the students and it would seem consider themselves above the rules. Another comparable trait in general society where those in positions of power seem to have a disregard for rules and others. Finally, we might consider how we could police these new rules as clearly our university society of students and staff are unable to do so. I can hear the cries now, haven’t you got anything better to do, this is a sledgehammer to crack a nut and all the usual rhetoric endured by the police across the land. If you make a rule, you must be prepared to enforce it otherwise there’s no point in having it. Imposing an unenforceable rule is simply playing politics and attempting to appease those that question the conditions in which students and staff work. Imagine speed limits on the road but no enforcement cameras, no police and no sanctions for breaches. It will be interesting to see how long the general population at the university follow the new rules, recent observations are that the flock of sheep mentality is starting to come to the fore. As a parting thought, isn’t it amazing how easy it is to study crime and deviance.

The pathology of performance management: obscuration, manipulation and power
My colleague @manosdaskalou’s recent blog Do we have to care prompted me to think about how data is used to inform government, its agencies and other organisations. This in turn led me back to the ideas of New Public Management (NPM), later to morph into what some authors called Administrative Management. For some of you that have read about NPM and its various iterations and for those of you that have lived through it, you will know that the success or failure of organisations was seen through a lens of objectives, targets and performance indicators or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). In the early 1980s and for a decade or so thereafter, Vision statements, Mission statements, objectives, targets, KPI’s and league tables, both formal and informal became the new lingua franca for public sector bodies, alongside terms such as ‘thinking outside the box’ or ‘blue sky thinking’. Added to this was the media frenzy when data was released showing how organisations were somehow failing.
Policing was a little late joining the party, predominately as many an author has suggested, for political reasons which had something to do with neutering the unions; considered a threat to right wing capitalist ideologies. But policing could not avoid the evidence provided by the data. In the late 1980s and beyond, crime was inexorably on the rise and significant increases in police funding didn’t seem to stem the tide. Any self-respecting criminologist will tell you that the link between crime and policing is tenuous at best. But when politicians decide that there is a link and the police state there definitely is, demonstrated by the misleading and at best naïve mantra, give us more resources and we will control crime, then it is little wonder that the police were made to fall in line with every other public sector body, adopting NPM as the nirvana.
Since crime is so vaguely linked to policing, it was little wonder that the police managed to fail to meet targets on almost every level. At one stage there were over 400 KPIs from Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary, let alone the rest imposed by government and the now defunct Audit Commission. This resulted in what was described as an audit explosion, a whole industry around collecting, manipulating and publishing data. Chief Constables were held to account for the poor performance and in some cases chief officers started to adopt styles of management akin to COMPSTAT, a tactic born in the New York police department, alongside the much vaunted ‘zero tolerance policing’ style. At first both were seen as progressive. Later, it became clear that COMPSTAT was just another way of bullying in the workplace and zero tolerance policing was totally out of kilter with the ethos of policing in England and Wales, but it certainly left an indelible mark.
As chief officers pushed the responsibility for meeting targets downwards through so called Performance and Development Reviews (PDRs), managers at all levels became somewhat creative with the crime figures and manipulating the rules around how crime is both recorded and detected. This working practice was pushed further down the line so that officers on the front line failed to record crime and became more interested in how to increase their own detection rates by choosing to pick what became known in academic circles as’ low hanging fruit’. Easy detections, usually associated with minor crime such as possession of cannabis, and inevitably to the detriment of young people and minority ethnic groups. How else do you produce what is required when you have so little impact on the real problem? Nobody, perhaps save for some enlightened academics, could see what the problem was. If you aren’t too sure let me spell it out, the police were never going to produce pleasing statistics because there was too much about the crime phenomenon that was outside of their control. The only way to do so was to cheat. To borrow a phrase from a recent Inquiry into policing, this was quite simply ‘institutional corruption’.
In the late 1990s the bubble began to burst to some extent. A series of inquiries and inspections showed that the police were manipulating data; queue another media frenzy. The National Crime Recording Standard came to fruition and with it another audit explosion. The auditing stopped and the manipulation increased, old habits die hard, so the auditing started again. In the meantime, the media and politicians and all those that mattered (at least that’s what they think) used crime data and criminal justice statistics as if they were somehow a spotlight on what was really happening. So, accurate when you want to show that the criminal justice system is failing but grossly inaccurate when you can show the data is being manipulated. For the media, they got their cake and were scoffing on it.
But it isn’t just about the data being accurate, it is also about it being politically acceptable at both the macro and micro level. The data at the macro level is very often somehow divorced from the micro. For example, in order for the police to record and carry out enquiries to detect a crime there needs to be sufficient resources to enable officers to attend a reported crime incident in a timely manner. In one police force, previous work around how many officers were required to respond to incidents in any given 24-hour period was carefully researched, triangulating various sources of data. This resulted in a formula that provided the optimum number of officers required, taking into account officers training, days off, sickness, briefings, paperwork and enquiries. It considered volumes and seriousness of incidents at various periods of time and the number of officers required for each incident. It also considered redundant time, that is time that officers are engaged in activities that are not directly related to attending incidents. For example, time to load up and get the patrol car ready for patrol, time to go to the toilet, time to get a drink, time to answer emails and a myriad of other necessary human activities. The end result was that the formula indicated that nearly double the number of officers were required than were available. It really couldn’t have come as any surprise to senior management as the force struggled to attend incidents in a timely fashion on a daily basis. The dilemma though was there was no funding for those additional officers, so the solution, change the formula and obscure and manipulate the data.
With data, it seems, comes power. It doesn’t matter how good the data is, all that matters is that it can be used pejoratively. Politicians can hold organisations to account through the use of data. Managers in organisations can hold their employees to account through the use of data. And those of us that are being held to account, are either told we are failing or made to feel like we are. I think a colleague of mine would call this ‘institutional violence’. How accurate the data is, or what it tells you, or more to the point doesn’t, is irrelevant, it is the power that is derived from the data that matters. The underlying issues and problems that have a significant contribution to the so called ‘poor performance’ are obscured by manipulation of data and facts. How else would managers hold you to account without that data? And whilst you may point to so many other factors that contribute to the data, it is after all just seen as an excuse. Such is the power of the data that if you are not performing badly, you still feel like you are.
The above account is predominantly about policing because that is my background. I was fortunate that I became far more informed about NPM and the unintended consequences of the performance culture and over reliance on data due to my academic endeavours in the latter part of my policing career. Academia it seemed to me, had seen through this nonsense and academics were writing about it. But it seems, somewhat disappointingly, that the very same managerialist ideals and practices pervade academia. You really would have thought they’d know better.
Not so Priti politics: setting a clear example
Of course Priti Patel the home secretary is correct when she declared that England fans have a right to boo England football players taking the knee before the England versus Croatia match on Sunday. Correct that is, in considering the spirit of the European Convention on Human Rights and Article 10, Freedom of Expression. This being encapsulated in our own Human Rights Act 1998. But whilst, the home secretary considers such booing, lets call it a form of protest, acceptable, she then adds that the ‘taking of the knee’ is simply ‘gesture politics’ and finds this form of protest unacceptable. The players and others through television advertising have made it clear that the statement is not political, it is simply a reminder of the need to tackle inequality and racism.
So, I’m left considering this, according to Priti Patel, it is acceptable to protest against those that oppose inequality and in particular racism, but it is not acceptable to protest against that in equality and racism. The first is a right, the second is some form of gesture politics. Ms Patel doesn’t end it there though but bemoans the Black Lives Matter protests and the ‘devastating impact they had on policing’. Somehow, I think she’s missed the point. If it is simply about the resources required to police the BLM protests, well the right of expression you say people have (you can boo if you want to) was simply being exercised and the police have a duty to facilitate those protests, devastating or not. If the devastation was about some other impact such as morale, then I think a bit of introspection wouldn’t go amiss. There is far too much evidence to show that the criminal justice system and the application of policing in particular is unequal, unfair and in need of change.
The home secretary is ultimately in charge of policing in this country. A politician, yes, but also supposedly a leader, who should be leading by example. What sort of example have her views set police forces across the country? Carry on folks, this is just gesture politics. No empathy, no understanding and a devil may care attitude, suggests that tackling inequality is not on the home secretary’s, let alone this government’s, agenda. This is not politics of the right, this smacks of politics of the far right. This is something we should all be worried about.
Fifty Pounds Per Child Per Year

Usually I consume my news through the BBC app, although occasionally I enjoy getting the run down of political affairs from the horses mouth, so to speak. Often I watch the Prime Ministers Questions, getting riled up at the majority of topics raised. However, yesterday (9/06/21), I found myself getting particularly outraged and passionate at a certain issue that has also been highly reported in the news.
Earlier last week, the Prime Minister outlined his Covid recovery package for schools, he pledged £1.4bn to enable students to catch up on the work, education and socialisation that has been missed. The controversy appears when comparing this figure to £13.5bn, originally suggested by Education Policy Institute (Education Policy Institute, 2021). To put it into perspective, £1.4bn equates to about £50 per child, per year- apparently you certainly can put a price on children’s education. Even with Johnson’s additional £1bn funding that will stretch across the next three years, the ‘recovery’ package is frankly laughable, it was a move that saw the education recovery commissioner, Kevan Collins, resign in protest.
Putting funding and economics aside, I think that this was a prime example of how the importance of education is once again, being forgotten. The potential power of the education system is not being utilised by any means. Politicians are still not realising that education reform doesn’t have to mean tougher discipline and it doesn’t have to mean more Ofsted checks and it certainly doesn’t have to mean more stressful, ‘rigorous testing’ of students, something which former education secretary Michael Gove pushed for in 2013 (Adams, 2013).
“Simply making exams harder does not guarantee higher standards nor mean that students will be prepared for a job.”
~ Brian Lightman (Adams, 2013)
Forcing misbehaved children out of school through punitive disciplinary actions, suspensions and exclusions simply puts them on the road to loosing faith in the education system and increases their likely hood of antisocial behaviour, which can lead to criminal careers later in life. The importance of creating an educational environment that students actually want to be a part of cannot be understated.
Furthermore, the importance of altering the current curriculum is completely overlooked. School has the potential to give children and teenagers the ability to have more autonomy over so many aspects of their later life; adequate lessons about political ideology, history and the voting system, done in an accessible way, has the potential to raise more politically aware, inclined individuals that feel equipped to engage and participate in the democratic process on a local and national scale.
Appropriate finance and law classes could eventually go on to raise a higher number of adults who feel able to handle their money situations in a better, healthier way; they could also begin to understand their rights and the court processes better. Finally, focusing on the decolonisation of the curriculum could allow ethnic minorities and other marginalised demographics to learn about their ancestors, history and culture in a more mainstream, impartial way. The impacts of restructuring the standard and the content of the schooling curriculum could have an abundance of benefits, not only to individuals but to society itself.
However, with no clear moves for the education secretary to explore theses benefits further and implement any changes, along with the promised £50 per pupil, per year, it is evident that the potential power of the education system has once again been understated and that, education is, indeed, not a priority for the current government.
Adams, R., 2013. GCSEs to become more demanding and rigorous, says Michael Gove. [online] The Guardian. Available at: <https://www.theguardian.com/education/2013/jun/11/gcse-demanding-rigorous-michael-gove>
Education Policy Institute. 2021. EPI responds to the government’s new education recovery package – Education Policy Institute. [online] Available at: <https://epi.org.uk/comments/epi-responds-to-the-governments-new-education-recovery-package/>
A link for the Prime Minister’s Questions episode: https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=zQkiEAZ2oh0&feature=youtu.be
A link for the Prime Minister’s Question with BSL: https://youtu.be/ZgcnQqbChZs















