Home » Crime and Punishment (Page 8)
Category Archives: Crime and Punishment
How I became an evil man

My love of poetry came in my sleep like a dream, a fever I could not escape and in little hours of the day I would read some poetry from different people who voice the volume of their emotions with words. In one of those poems by Elleni Vakalo How he became a bad man, she introduced me to a new understanding of criminological thinking. The idea of consequences, that lead a seemingly good person to become bad, without the usual motivational factors, other than fear. This was the main catalyst that became the source of this man’s turn to the bad.
This almost surrealistic description of criminal motivation has since fascinated me. It is incredibly focused, devoid of social motivations and personal blame. In fact, it demonstrates a social cognition that once activated is powerful enough to lead a seemingly decent person to behave in uncharacteristic moves of violence. This interesting perspective was forged during the war and the post war turmoil experienced. Like Camus, the act of evil is presented as a matter of fact and the product of thoughts that are originally innocent and even non-threatening.
The realisation in this way of thinking, is not the normalisation of violence, but the simplicity that violence in innate to everyone. The person who commits it, is not born for it, does not carry an elaborate personal story or trauma and has no personal compulsion to do it. In some ways, this violence is more terrifying, as criminality can be the product of any person without any significant predispositions, an everyday occurrence that can happen any time.
The couple that will meet, fall in love, cohabit, and get married, starting a family, follow all the normal everyday stages that millions of people follow or feel socially obliged to follow. In no part of this process do they discuss how he will control her, demean her, call her names, slap her, hit her or kick her. There is no plan or discussion of how terrified she will become, socially isolated and humiliated. At no point in the planning, will she be thinking of ways to exit their home, access helplines or spend a day in court. It happens, as a product of small thoughts and expressed emotions, that convert into micro aggressions, that become overt hostility, that leads to violence. No significant changes, just a series of events that lead to a prolonged suffering.
In some way, this matter of fact violence explains the confusion the victims feel, trapped in a relationship that they cannot recognise as abusive, because all other parts fall under the normality of everyday life. Of course, in these situations, emotion plays a key role and in a way that rearranges logic and reason. We are driven by emotion and if we are to leave criminological theory for a minute a series of decisions, we will make daily take a journey from logic to emotions and back.
This emotional change, the manifestation of thoughts is not always criminal nor destructive. The parents who are willing to fight an entire medical profession so that their newborn has a fighting chance are armed with emotion. Many stories come to mind of those who owe their lives to their determination of their parents who fought logic and against the odds, fought to keep them alive. Friends and partners of people who have been written off by the criminal justice system that assessed them as high risk for society and stuck with them, holding on to emotion as logic departs.
In Criminology, we talk about facts and figures, we consider theories and situations, but above all as a social science we recognise that we deal with people; people without emotions do not exist. So how do you/how do I become a bad man? Simple…the same way you are/I am a good man.
This is the poem by Eleni Vakalo, with my painful translation:
How He Became A Bad Man
I will tell you how it happened
In that order
A good little man met on his way
a battered man
the man was so close from him laying
he felt sad for him
He was so sad
That he became frightened
Before approaching him to bend down to
help him, he thought better
“What do you want, what are you looking for”
Someone else will be found by so many around here,
to assist this poor soul
And actually
I have never seen him
And because he was scared
So he thought
Would he not be guilty, after all no one is hit without being guilty?
And they did him good since he wanted to play with the nobles
So he started as well
To hit him
Beginning of the fairy tale
Good morning
Nothing is black and white: the intransigence of fools

One thing we criminologists know is that it is impossible to prevent crime. Many a great criminologist has tried to theorise why crime occurs (my shelves are full of their books) and whilst almost all have made valuable contributions to our understanding of crime, it is an unfortunate fact that crime continues. But then crime itself is difficult to define and has its basis in time, power, opportunity and social discourses. What is criminal today will not be criminal tomorrow and what is important today will lose its importance tomorrow, in favour of some new or maybe, old, manifestation of that elusive concept we call crime. Perhaps we should we grateful, for in the industry of crime lies mass employment. From criminologists to those that attempt to stem the tide of crime, those that deal with its aftermath and those that report on it or write about it (real or fictional), there is money to be made. If we stopped crime, we would all be out of a job.
Most, if not all of us have at some stage in our lives committed some sort of crime. Most crimes will fortunately be almost inconsequential, maybe a flouting of a law such as driving a car over the speed limit. Other crimes will be more serious and whilst some criminals will be brought to book most are not. The inconsequential crime of driving over the speed limit, albeit perhaps due to a lapse of concentration, can have dire consequences. There is clear evidence that the survival rates of pedestrians struck by cars has a direct correlation with speed. So the inconsequential becomes the consequential, the ephemerality of crime, the reality.
When we think of crime, we often have little concept of its reality. We apply labels and our own rules to that we know and find acceptable. Speeding is not criminal, well not generally, unless it’s a boy racer. Drink driving is a no-no, but we might take it to the alcohol limit when having a drink. Drugs (the criminalised type) are ok, well some are and some aren’t, it all depends on your viewpoint. Drugs (the prescription type) are ok, even if they impair our ability to drive. Alcohol, well that’s absolutely ok, even if the abuse of it leads to more deaths than drugs and the consequences of that misuse has a really significant impact on the NHS. Tax evasion, illegal if you get caught, ok if you don’t. A bit like fraud really, ok if you can get away with it but then maybe not, if the victim is a little old lady or me. Assault, well it depends on the seriousness and the situation and probably the victim. Robbery, not good to go into an off licence with a gun and threaten the shopkeeper, bullying if you take lunch money off the lad outside the school gates.
Criminals don’t walk around with a label that says ‘criminal’ and even if they did, there would have to be a method of bestowing the label in an instance. Nonsense of course, only a fool would suggest such a thing. What about the people that committed a crime but have changed their ways I hear my colleagues ask? What about those that haven’t, or have and then relapse, I reply.
Nothing is black and white; the concept of crime is elusive, as are criminals (both by concept and nature). And yet we happily castigate those that attempt to uphold the law on our behalf and in doing so view crime and criminals as clear concepts. Each has a clear label, each is clearly identifiable, so how can they get it so wrong so many times. Whilst criticising those that attempt, and let’s be quite honest, fail most of the time to stem this tide of crime, perhaps we might also think about the impossibility of the job in hand. That’s not to say that a lot of the criticisms are not justified, nor that things should not change, but if we only examine all that is wrong, we lose sight of reality and only an intransigent fool would continue an argument that sees the problems and solutions as simply black and white.
A racist and no solution

I am a white, middle class some might say (well my students anyway), ageing, male. I wasn’t always middle class, I’m from working class stock. I’m a university lecturer now but wasn’t always. I spent 30 years in the police service in a small, ethnically diverse, county in England. I didn’t consider myself a racist when I was in the police service and I don’t consider myself a racist now. Nobody has called me a racist to my face, so why the title? It’s how I’m constantly labelled. Every time someone says the police are racist or the police are institutionally racist, they are stating that about me. Just because I have left the police organisation doesn’t change who I am, my beliefs or my values. So, if the police are racist, then by default, I must be.
I’m not suggesting that some police officers are not racist, of course some are. Nor am I denying that there has been and probably still is some form of institutional racism within the police service, perhaps as a whole or perhaps at a more localised or departmental level. But bad apples and poorly thought-out, naïve or even reckless policies, strategies and procedures are not enough to explain what is going on in policing and policing of ethnic minority groups in particular. I’m talking about policing in this country, not across the pond where policing is very different in so many ways that it is hard to even suggest a realistic comparison. That of course is the first problem, what happens in the United States of America is immediately translated into what happens here.
As a lecturer, I constantly hear from students and read students’ work about the racist and brutal police, often interchanging commentary from the United States with commentary here in the United Kingdom, whilst also failing to recognise that there is different policing in Scotland and Northern Ireland. Institutional racism, as defined by Macpherson, is now part of the lexicon, but it no longer has the meaning Macpherson gave it, it is now just another way of saying the police are and every police officer is racist. Some students on finding out that I was a police officer show an instant dislike and distrust of me and sometimes it can take the whole three years to gain their trust, if at all. Students have been known to request a different dissertation supervisor, despite the fact that their research subject is in policing. This is not a complaint, just a statement of facts, painful as it is.
As I try to make sense of it all, I have so many unanswered questions. What is exactly going on? What is causing this conflict between the police and ethnic minority groups? Why is there a conflict, why is there distrust? More importantly, how can it be fixed? Some of the answers may lay in what the police are asked to do, or at least think they are asked to do. Reiner suggests that policing is about regulating social conflict, but which conflict and whose conflict is it? Other authors have suggested that the police are simply a means to allow the rich and privileged to maintain power. There may be some merit in the argument, but most policing seems to take place in areas of deprivation where the disadvantaged are committing crimes against the disadvantaged. The rich and powerful of course commit crimes but they are nowhere near as tangible or easy to deal with. One the problems might be that the rich and powerful are not particularly visible to policing but the disadvantaged are.
Maybe some of the answers lay in notions of stereotyping, sometimes even unconsciously. Experience or narratives of experiences cause a wariness, even a different stance to one people might normally assume. Being thumped on the nose by a drunk, does tend to make a person wary of the next drunk they encounter. So, could stereotyping be a problem on both sides of the divide? My dissertation student that didn’t want me as a supervisor was later to reveal experiences of racist abuse aimed at the police officers she went out on patrol with. Policing is dominated by white males and despite recruitment drives to address the ethnicity gap, this really hasn’t been that successful. If it was meant to help solve a problem, it hasn’t.
I get the sense though that the problem is much deeper routed than policing. Policing and the problems of policing is just a sub plot in a much wider issue of a divided society and one that is in constant conflict with itself. If the police are guilty of racism, then it is society that has caused this. Our society’s values, our society’s beliefs. An unequal society where the poorest suffer the most and the rich get richer regardless. A society where we are all equal but only because someone somewhere said so at some time, it is not reality. I think of Merton’s ‘American Dream’, I don’t buy into the whole concept, but there is something about not having opportunities, equally when I think of Lea and Young and the concept of relative deprivation, whilst not explaining all crime, it has some merit in that notion that the disenfranchised have no voice.
As I write this I am conscious that I have commentated on a very emotive subject particularly at this time. As I watch the events unfold in America, I fear the worst, action followed by reaction. Both becoming increasingly violent and I see the possibility of it happening in this country. I fear that the term ‘police racism’ will become another convenient label. Convenient in the sense that the problems are seen solely as that of policing. If we examine it through a different lens though, we might just find that policing is simply part of the whole rotten tree, society. Fix society and you fix policing. If the label racist fits, it fits the society we live in.

“A small case of injustice”

Pride as a movement in the UK but also across the world signals a history of struggles for LGBTQ+ community and their recognition of their civil rights. A long journey fraught with difficulties from decriminalisation to legalisation and the eventual acceptance of equal civil rights. The movement is generational, and in its long history revealed the way social reactions mark our relationship to morality, prejudice, criminalisation and the recognition of individual rights. In the midst of this struggle, which is ongoing, some people lost their lives, others fell compelled to end theirs whilst others suffer social humiliation, given one of the many colourful pejoratives the English language reserved for whose accused or suspected for being homosexuals.
This blog will focus on one of the elements that demonstrates the relationship between the group of people identified homosexual and the law. In sociological terms, marginalised groups, has a meaning and signals how social exclusion operates against some groups of people, in these case homosexuals but it does apply to any group. These groups face a “sharper end” of the law, that presumably is equal to all. This is the fallacy of the law; that there are no inherent unfairness or injustice in laws. The contention for marginalised groups is that there are presumptions in the law on purported normality that disallows them to engage fully with the wider community in some cases forced to live a life that leads all the way to segregation.
Take for example “entrapment”. Originally the practice was used by law enforcement officers to identify counterfeit money, later to investigate the sales of untaxed tobacco or the use of unlicensed taxis. The investigation in law allows for the protection of the public, non uniform officers to pose as customers in order to reveal criminalities that occur in the dark corners of society. The focus predominantly was to protect consumers and the treasury from unpaid tax. So, from that how did the law enforcement officers use it to arrest homosexuals? It is interesting to note we can separate the letter of the law as opposed to the spirit of the law. This distinction is an important one criminologically whilst for the law enforcement agencies evidently there is no such distinction.
The most recent celebrity case led to the arrest of George Michael in Los Angeles, US; the operation led to the outing of the artist and his conviction. As a practice across many years, entrapment played a significant part in the way numerous homosexuals found themselves arrested given a criminal record, loss of employment and in some cases ending up in prison. It is important to note that prior to the Sexual Offences Act of 1967, the biggest sexual crime in England and Wales was that of homosexuality (recorded as indecency or buggery). It took decades for that statistic to change, although historically remains still the highest category.
The practice of entrapment employed by the police demonstrates the uphill struggle the LGBTQ+ community faced. Not only they had to deal with social repulsion of the wider community that detested, both their practices and their existence, but also with public officials who used entrapment to criminalise them. This was happening whilst the professionals were divided about the origins of homosexual “anomaly” and how to deal with it, the practice of entrapment added new convictions and supplied more humiliation to those arrested. For the record, the criminological community was split along theoretical lines on this; the classicists such as Bentham argued for the decriminalisation of sodomy whilst the positivists namely Lombroso considered homosexuals to be in the class of moral criminals (one of the worst because they are undeterred) .
The issue however is neither theoretical, nor conceptual; for those who were aware of their sexuality it was real and pressing. During the post WWII civil rights movement, people started taking note of individual differences and how these should be protected by privacy laws allowing those who do not meet the prescribed “normal” lifestyles to be allowed to live. It emerged that people who were successful in their professional lives, like Alan Turing, John Forbes Nash Jr, John Gielgud etc etc, found themselves facing criminal procedures, following string operations from the police. This injustice became more and more evident raising the profile of the change in the law but also in the social attitudes.
In 2001 Lord Nicholls of Birkenhead addressed the issue of entrapment head on. In his judgement in Regina v Looseley:
“It is simply not acceptable that the state through its agents should lure its citizens into committing acts forbidden by the law and then seek to prosecute them for doing so. That would be entrapment. That would be a misuse of state power, and an abuse of the process of the courts. The unattractive consequences, frightening and sinister in extreme cases, which state conduct of this nature could have are obvious. The role of the courts is to stand between the state and its citizens and make sure this does not happen.”
This was the most damming condemnation of the practice of entrapment and a vindication for all those who faced prosecution as the unintended consequence of the practise. For the record, in 2017 under the Policing and Crime Act, included the “Alan Turing law” that pardoned men who were cautioned or convicted for historical homosexual acts. The amnesty received mixed reviews and some of those who could apply for denied doing so because that would require admission of wrongdoing. The struggle continues…
Regina v Looseley, 2001 https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/ld200102/ldjudgmt/jd011025/loose-1.htm
Criminology 2020 AD

2020 will be a memorable year for a number of reasons. The big news of course was people across the world going into lockdown and staying home in order to stop the transmission of a coronavirus Covid-19. Suddenly we started counting; people infected, people in hospitals, people dead. The social agenda changed and our priorities altered overnight. During this time, we are trying to come to terms with a new social reality, going for walks, knitting, baking, learning something, reading or simply surviving, hoping to see the end of something so unprecedented.
People are still observing physical distancing, and everything feels so different from the days we were discussing future developments and holiday plans. During the last days before lockdown we (myself and @paulaabowles) were invited to the local radio by April Dawn to talk about, what else, but criminology. In that interview we revealed that the course started 20 years ago and for that reason we shall be having a big party inviting prospective, current and old students together to mark this little milestone. Suffice to say, that did not happen but the thought of celebrating and identifying the path of the programme is very much alive. I have written before about the need to celebrate and the contributions our graduates make to the local, regional and national market. Many of whom have become incredibly successful professionals in the Criminal Justice System.
On this entry I shall stand on something different; the contribution of criminology to professional conduct, social sciences and academia. Back in the 1990s Stan Cohen, wrote the seminal Against Criminology, a vibrant collection of essays, that identified the complexity of issues that once upon a time were identified as radical. Consider an academic in the 1960s imagining a model that addresses the issue of gender equality and exclusion; in some ways things may not have changed as much as expected, but feminism has entered the ontology of social science.
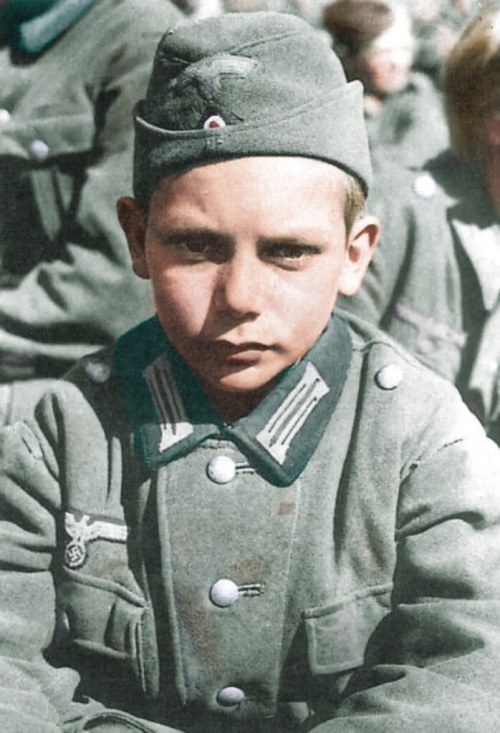
Criminology as a discipline did not speak against the atrocities of the Nazi genocide, like many other disciplines; this is a shame which consecutive generations of colleagues since tried to address and explain. It was in the 1960s that criminology entered adulthood and embraced one of its more fundamental principles. As a theoretical discipline, which people outside academia, thought was about reading criminal minds or counting crime trends only. The discipline, (if it is a discipline) evolved in a way to bring a critical dimension to law and order. This was something more than the original understanding of crime and criminal behaviour and it is deemed significant, because for the first time we recognised that crime does not happen in a social vacuum. The objectives evolved, to introduce scepticism in the order of how systems work and to challenge established views.
Since then, and through a series of events nationally and internationally, criminology is forging a way of critical reflection of social realities and professional practices. We do not have to simply expect a society with less crime, but a society with more fairness and equality for all. The responsibilities of those in position of power and authority is not to use and abuse it in order to gain against public interest. Consider the current pandemic, and the mass losses of human life. If this was preventable, even in the slightest, is there negligence? If people were left unable to defend themselves is that criminal? Surely these are questions criminology asks and this is why regardless of the time and the circumstances there will always be time for criminology to raise these, and many more questions.